Neurologic monitoring PPT-josh Flashcards
Know where the common/internal.external Carotids arise:
where does the common arise from
- Arotic arch (2nd take off)
- innominant artery
Know where the common/internal.external Carotids arise:
what take off is first when traveling the common carotid, the external or internal?
- external
Know where the common/internal.external Carotids arise:
what is the last take off when traveling the common carotid, teh external or internal?
- internal (you could have got this via process of elimination of the last 2 cards, but good job anyways)
what suppies the cerebral blood supply
Circle of willis
Lable this
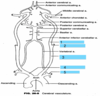
- Internal Carotid
- External carotid
- Common Carotid
- Brachiocephalic
- Subclavian

Ok so I was a little confused!!! Basically about all the take offs and where the actual comon carotids arise from!!!
So i went searching and this is what i came up with! I will ask the question then give the answers!!!!
Explain the Aortic arch and takoffs from start and finish with the internal carotids!!!
- Ascending arch
- innominant artery
- brachiocephalic (or right subclavian) and Right common carotid
- Rght common carotid divides into right external carotid
- then right common carotid divides into the right internal carotid
- Next take off on arch is the left common carotid
- The left common carotid divides into the left external carotid
- then the left common carotid divides into the left internal carotid
- the last take off of arch is the Left subclavian
I hope that helps!! her diagram sucks ass!!!
here is a pic

What are 4 NON-invasive monitors for cerebral blood flow
- Intavascular tracer compounds
- Jugular bulb Venous O2 Sat
- Transcranial doppler US
- Cerebral Oximetry
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: IV tracer compounds
this allows direct measurement of what?
CBF
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: IV tracer compounds
Determines kinetics of wash-in and/or wash-out of an inert tracer compound (usually radioactive isotope of what)
Xenon
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: IV tracer compounds
so in a laymen’s or josh terms what the fuck is this?
- You shoot some IV shit usually xenon into the IV and measure somehow how it goes in and out
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: IV tracer compounds
________ detectors over specific brain areas measure radioactivity
Gamma
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: IV tracer compounds
what are some of the draw backs of this method?
- Exposure to radioactivity
- Cumbersome
- Focal ischemic area may be missed
- Just give a “snapshot” of CBF
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: Jugular bulb Venous O2 Saturation
Measure the _______ extraction of the brain
Oxygen
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: Jugular bulb Venous O2 Saturation
Requires retrograde placement of a fiberoptic probe in the ____ ______ using flouro
Jugular bulb
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: Jugular bulb Venous O2 Saturation
do the right and left jugular bulbs drain the same or different regions?
Different
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: Jugular bulb Venous O2 Saturation
it is only considered a measurement of ______ cerebral oxygenation
Global
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: Jugular bulb Venous O2 Saturation
In josh terms what the hell is this test
- measures the heads cerebral O2 use, by sticking a prob in the jugular bulbs w/ flouro
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: transcranial doppler US
it is an inference of CBF by measuring blood flow ______ in large arteries to the brain
Velocity
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: transcranial doppler US
Often times it uses continuous measurment of flow through the ____ ____ Artery
Middle cerebral artery
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: transcranial doppler US
besides juust flow it can also alert tot he presence of what?
- particulate emboli
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: transcranial doppler US
the particulate emboli will appear as a high density transient signals and a _____ in the background sounds
Chirp
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: transcranial doppler US
this measurement assumed to work b/c it is thought that blood flow velocity is directly r/t ____ _____ only if the diameter of the vessel is measured and Doppler probe is constant
Blood Flow
Non-invasive CBF monitoring: transcranial doppler US
should this be used as the sole monitor of CBF
Nope



