Neuroimaging Flashcards
MRI TI, AKA?
Anatomical sequence because gray matter is gray and white matter is white.
This is as it appears in gross pathology.
Landmark on CT and MRI for central sulcus?
Omega sign. Anterior is frontal lobe, posterior is parietal lobe.
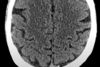
What level is this?
Identify structures.

Ventricles
Head of caudate, internal capsule, lentiform nucleus, thalamus, insular cortex, anterior temporal lobe.

Identify sylvian fissure (AKA). What artery runs along here?
What does the sylvian fissure separate?

Lateral sulcus
Middle cerebral artery
Frontal/Parietal lobe from temporal lobe

Identify Midbrain, basal cistern, medial temporal lobe “uncus”, temporal horn of lateral ventricle (what is specific for a normal appearance)?
Why is it important to local the medial temporal lobe?
What does it mean for the temportal horn of lateral ventricle to be dilated?

Uncus can herniate onto the midbrain
Temporal horn of lateral ventricle should normally be slit like.
Early sign of hydrocephalus if temporal horn of lateral ventricle is dilated.

What level is this?
Identify brachium pontins, direction of connection between brachium pontis and cerebellum, 4th ventricle, and cerebello-pontine angle.

Mid pontine level
Brachium pontins Will hug the 4th ventricle

Identify Medulla, 4th ventricle, and cerebellum


Identify foramen magnum and spinal cord


Steps for interpret Neuroimaging (5)
Identification - use landmarks
Symmetry
Density/Intensity
Pattern of Enhancement
Lesion location
What appears dense on CT?
Sensitivity to detect blood?
Mineralized structures such as calcified bone or chronic calcified lesions.
>90% sensitivity to detect blood
Identify hyperdense structures

Calvarium, lens, pineal gland, choroid plexus

Diagnosis?

Neurocysticercosis
Calcified scolex in cysticercosis
Scolex - the anterior end of a tapeworm, bearing suckers and hooks for attachment.
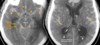
Diagnosis

Acute basal ganglia hemorrhage with intraventricular extension

Provide simple description
Diagnosis

Chalk outlining the sulci
Diffuse subarachnoid hemorrhage which is extraxial + intraventricular extension
For suspected extraxial epidural hematoma what can be done when reading the image?
Adjust to bone window to observe for calvarial sutures and fractures

Identify hyperdensities

Hyperdense MCA sign in the sylvian fissure
Between the cerebral peduncles in the interpeduncular cisterns -> Dense vessel sign (top of basilar artery)

Hypodense typically represent (4)?
Chronic lesions
Fluids
Cystic component
Edema
Define encephalomalacia
Define atrophy
Softening or loss of brain tissue after cerebral infarction, cerebral ischemia, infection, craniocerebral trauma, or other injury
Loss of NEURONS and the connections between them. Atrophy can be generalized, which means that all of the brain has shrunk; or it can be focal, affecting only a limited area of the brain and resulting in a decrease of the functions that area of the brain controls.
CT characteristics suggestive of chronic stroke vs traumatic brain injury?
Isodense to CSF
Follows vascular territory vs not

Is this intraxial or extraxial?

Fronto-temporal arachnoid cyst

Timeline for an acute stroke to present with hypodensity (edema) on CT?

6-8 hours
Describe

Vasogenic edema surround a metastatic lesion

MRI Brain without contrast
What are the basic sequences (4) + Optional
- T1WI
- T2WI + Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR)*
- DWI + Apparent Diffusion Coefficient**
- Gradient Echo Sequence (GRE)
- T1 with Gadolinium contrast
WI- Weighted Image
* Most filling and useful sequences
** Designed to diagnose energy failure and ischemia
What are some specialized MR sequences?
MR Angiogram and Venogram
Fat suppresion
Perfusion
Spectroscopy
Tractography





























