Neuroanatomy Flashcards
LO
- Anatomy catch up lecture, and preparation for lectures to come
- Cranial Nerves:
- Name the 12 cranial nerves and describe the location within the brain/brainstem - where their nuclei are located and where the nerve emerges
- Discuss the main function of each cranial nerve
- Limbic Lobe:
- Describe the main parts of the limbic lobe/system
- Discuss the Trisynaptic circuit of the hippocampus, and functional connections
What does each spinal nerve have attached to them and where does this lead to?
Each spinal nerve has Roots that join together to form mixed* spinal nerves which then branch to reach their target structures in the body.
Each segment of the spinal cord gives rise to a pair of spinal nerves that consist of what 3 things…?
- Axons of motor neurons that innervate a group of muscles
- Axons of sensory neurons that innervate a defined area of skin
- Axons of sympathetic neurons to structures in the body wall that control body temp (blood vessels, sweat glands etc.)
Label this spinal nerves and tell me what each one brings or goes to

- Dorsal root brings in afferent fibres (sensory)
- Ventral root brings in efferent fibres (motor)
- Dorsal ramus goes to back
- Ventral ramus goes everywhere else and contains sympathetic ganglia

Tell me the spinal nerve names and order from head to pelvis

What does the brain stem serve as?
Serves as a conduit for ascending & descending tracts connecting the spinal cord to higher centres (cerebrum, cerebellum)
What does the brain stem contain?
- Contains important reflex centres associated with control of respiration, heart rate & blood pressure, and consciousness
- Contains cranial nerve nuclei; Cranial nerves III – XII emerge from it.
Are there peripheral nerves in the head and neck?
These are the cranial nerves which emerge from the brainstem (except I & II). They follow a different pattern to spinal nerves. They can be purely sensory, purely motor, or mixed. They also don’t have the architecture of the spinal nerve.
Label these 3 main structures in the brain


How are cranial nerves distinct from spinal nerves and what do they supply ?
- Cranial nerve- nerve supply to the head, neck and face
- Distinct from Spinal nerves:
- Cranial nerves contain branchial efferent fibres
- Cranial nerves contain special sensory (afferent) fibres
- Some Cranial nerves are completely sensory, completely motor, or mixed
Tell me what the 5 arches are that are present during development that are the precursors to structures in the head and neck
What are the words that describe them/ their name?
Embryonic structural layout that gives rise to structures in head and neck (branchial)

Cranial nerves

Name the cranial nerves from front to back…

How many cranial nerves are there?
All nerves are paired (so 24 singles but 12 pairs of cranial nerves)
With the sensory systems located within the head, what are the 5 special senses?
audition
balance/equilibrium
vision
olfaction
gustation*
Tell me the purely sensory cranial nerves
Their main function
Location of neurons

What nerves do the purely sensory cranial nerves contain
These cranial nerves contain special sensory (afferent) fibres/nerves
What nerve provide audition and balance?
The 8th nerve
Tell me about the polarity of the olfactory neurons
they are bipolar
Are the sensory cranial nerver in the CNS?
No
What type of nerves are purely motor cranial nerves?
Generally somatic efferent nerves: prokect to striated muscles
What nuclei do the brain stems contains in the purely motor cranial nerve section?
Brainstems contain somatic motor nuclei homologous to the ventral horn of the spinal cord
What are the purely motor cranial nerves
Their main function and location of the neurons

Tell me the purely motor cranial nerves that project to striated muscle
Their main function and location of the neurons

Tell me the mixed motor and sensory cranial nerves
Their main function and location of neurons
- these are the larger cranial nerves as are carrying afferent and efferent fibres
- 5,7, and 9 nerves are located slightly higher in the brain stem
- Gustation split between 7, 9 and 10 cranial nerves

Tell me the autonomic fibres within cranial nerves? think parasympathetic

Tell me the divisions of the peripheral nervous system

Summary of the functional groups of cranial nerves

Identify the regions on this brain diagram and what are they each involved in?


What is the limbic system considered to be and what is it related to?
Considered to be the ‘Emotional’ or ‘Feeling’ brain. (The ‘reacting’ Brain). Under control of the ‘thinking’ brain.
Relates to brain structures that deal with emotion, memory, and basic drives. Species preservation, self-preservation.
What structures does the limbic system interconnect and what structure does it sit on top of?
Interconnected structures in telencephalon & diencephalon. Sits on top of the brainstem.
What are the major component parts of the limbic system and are they thought to be the input or output parts?
Major component parts:
- Hypothalamus (output)
- Amygdala (input)
- Hippocampus (input)
Label the major component parts of the limbic system
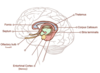

Is the hypothalamus part of the telencephalon or the diencephalon?
diencephalon
What does the hypothalamus regulate?
- Regulates systems homeostasis (autonomic control!)
e. g Hunger, thirst, body temperature, hormones - Regulates sexual motivation & other emotional behaviours
Tell me the endocrine function of the hypothalamus
Endocrine function: Communicates with pituitary gland for hormone production/release
Tell me about the output and input and the hypothalamus and limbic system
- primary output node of the limbic system, with connections to the frontal lobes and brainstem.
- Receives input from hippocampus and amygdala.
Label these structures of the brain


What nucleus is located in the hypothalamus and what is this involved in?
Suprachiasmatic nucleus – circadian rhythms
What load is the amygdala located in?
What is it comprised of?
Located within the temporal lobe
comprised of a group of nuclei
What is the amygdala the center for?
- Emotional centre of the brain; Fear centre of the brain
- Controls aggression (‘fight’) and (‘fear’)
- Responsible for arousal, fear, excitement, anxiety, violence
What does the amygdala have reciprocal connections with?
Has reciprocal connections with many brain regions (hippocampus, brain stem, diencephalon, olfactory cortex, etc).
What converges into the amygdala ?
Various (sensory) stimuli and autonomic input converge in amygdala
What does amygdala generate?
‘learned’ emotional responses
Label this diagram of the brain


What is the hippocampus located within?
The temporal lobe
What is the hippocampus involved in?
- Spatial memory
- Memory processing (storage – short & long; consolidation, encoding, retrieving)
Does the hippocampus have anatomical changes when it comes to an neurodegenerative disease like alzhemiers?
yes

Tell me the structures that form the hippocampus
- Hippocampus (CA1 – CA4)
- Other part makes the hippocampus formation
- Dentate gyrus
- Parahippocampal gyrus (Subiculum & entorhinal cortex)

Label the structures involved in the hippocampal formation


Tell me the input and output of the parahippocampal gyrus
Parahippocampal gyrus:
- Entorhinal cortex (input)
- Subiculum (main output)
What ciruit is present in the limbic system?
Trisynaptic circuit
Tell me about the Trisynaptic circuit in the limbic system
what is it made up of?
- Trisynaptic Circuit: 3 interconnected afferent pathways, taking information into the hippocampus for processing – memory retrieval
- Consists of 3 cell groups: (all distinct neuron types even though called cells)
- Granule cells in DG
- Pyramidal cells in CA3
- Pyramidal cells in CA1
All 3 are excitatory neurons
What 3 synapses are present in the trisynaptic circuit?

(synapse 1) Entorhinal Cortex → DG via the perforant path
(synapse 2) DG → CA3 via mossy fibres
(synapse 3) CA3 → CA1 via Schaffer collaterals (as seen in purple on the diagram)


