Neuroanatomy Flashcards
Neuraxis
Imaginary line drawn throught the spinal cord to the front of the brain.

Rostral - Caudal
Anterior - Posterior
Rostral: toward the nose
Anterior: toward the front
Caudal: toward the tail
Posterior: toward the rear

Ventral - dorsal
Inferior - superior
Ventral: toward the front
Inferior: below
Dorsal: toward the back
Superior: above

Medial - Lateral
Medial: toward the midline
Lateral: away from the midline
NB: midline is the medial line of the body which divides the body into halves that are mirrror images of each other

Nervous system

Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
Voluntary control/senses
Autonomic Nervous System
Subsconscious body control: visceral function, heart rate, respiration rate, digestion, salivation, pupil dilation, sexual arousal
- Efferent nerves
- Parasympathetic nervous system
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Afferent nerves
Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)
Rest and digest
- Eyes: accommodation for near vision (miosis)
- Saliva: copious liquid
- Heart: rate and blood pressure down
Sympathetic nervous system
4 Fs:
- Fight
- Flight
- Fright
-
Fuck
- Eyes: pupillary dilation
- Saliva: little, viscous
- Heart: rate, force and blood pressure up
- CNS: drive and alertness up
Hindbrain (metencephalon and myelencephalon)
Brain stem (midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata) and cerebellum

Cerebellum
Involved in motor control especially voluntary movement, body position and motor learning.
Contains 50% of total neurons in brain
Grey and white matter
Known as ‘little brain’
Pons
Bridge between cerebrum and cerebellum + medulla oblongata
Siutated on top of the brainstem
Brainstem
Midbrain + pons + medulla oblongata
Connects spinal cord with forebrain and cerebellum

Formatio reticularis (reticular formation)
Regulates activity/sleep

Medulla oblongata
Relays motor and sensory signals between the spinal cord and higher brain regions.
Reflex control centre (ANS) e.g. heart rate

Midbrain
Tectum (dorsal) + tegmentum (ventral) + periaqueductal gray (PAG)

Tectum
- Inferior colliculi
- Auditory function
- Superior colliculi
- Visual function
Inferior colliculi
Auditory functino
Superior colliculi
Visual functio
Tegmentum
Substantia nigra + red nucleus
–> Voluntary movement control
Periaqueductal gray (PAG)
Tissue around the cerebral aqueduct that connects the 3rd and 4th ventricles

Forebrain (telencephalon and diencephalon)
- Diencephalon
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
- Telecephalon
- Cortex
- Basal ganglia
- Limbic system
Diencephalon
Thalamus and hypothalamus
Telencephalon
Cortex + basal ganglia + limbic system
Thalamus
Gateway of the cortex: all sensory pathways (except olfaction) relay in the thalamus before terminating in the cerrebral cortex

Gyrus (pl: gyri)
Convolution or bump protruding rounded surfaces

Sulcus (pl: sulci)
Valley between gyri and enfolded regions that appears as surface lines (gaps between gyri)

Longitudinal fissure
Divides the two hemispheres (also known as interhimispheric fissures)

Lobes and sulci


Frontal lobes
The ‘executive’ brain: planning and guiding behaviour, (moral) judgement
Broca’s speach area
Primary motor cortex

Temporal lobes
- Language processing –> Wernicke’s area
- Longterm memory/knowledge –> Parahippocampal gyrus
- Primary auditory cortex

Parietal lobes
Association cortex: integrates sensory information from multiple modalities
- Spatial processing –> superior parietal gyrus
- Primary somatosensory cortex –> postcentral gyrys
- Cortical association area (visual+auditory) –> inferior parietal gyrus

Occipital lobes
Vision
Primary visual cortex –> located in and around the calcarine fissure

Basal ganglia
Prepares starting and stopping of voluntary motions –> Parkinson’s
- Direct pathway: starts movement
- Indirect pathway: stops movement

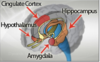
Limbic system
Hypothalamus
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Cingulate cortex
Anterior thalamus
Mammilary bodies
–> emotional regulation, learning and memory, emotional memories, recognition of emotions in other people
Hypothalamus
- Regulates hormones (sexual behaviour, diurnal rhythms, fight or flight etc)
- Controls food and fluid intake

Hippocampus
- Establishing memories
- New contextual learning
- Memory retrieval
- Understanding spatial relations

Amygdala
Coordinates behavioural, autonomic and endocrine responses to environment stimuli, especially those with emotional content
No amygdala, no fear!

Corpus callosum
- Major fibre connection between the hemispheres (from lating, literally meaning tough body)
- Allows communication between cerebral hemispheres

Brain barrier systems
- Skull
- Meninges
- Dura mater
- Arachnoid mater
- Pia mater
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Blood-brain barrier (BBB)
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Function:
- Buoyancy: allows the brian to maintain its density without being impaired by its own weight
- Protection: protects the brain tissue from injury when jolted or hit
- Chemical stability: allows for homeostatic regulation
Hydrocephalus
- From latin: water (hydro) in the head (cephalus)
- CSF build-up puts pressure on the brain
- Usually in infancy (congenital hydrocephalus) –> delayed cognitive development
- Maybe acquired after head injury or brain cancer

Blood-brain barrier
Tightly packed blood vessels creating a berrier that only allows certain molecules to pass through


