Hormones Flashcards
1
Q
Endocrine system
A
- Collection of glands of an organism that secrete hormones

2
Q
Amine and peptide hormones
A
- Act on Metabotropic receptors (G-coupled proteins)
- Relatively quick (seconds to minutes): act on the surface of target cells via second messengers
- Examples include:
-
Oxytocin - produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary
- “pro-social”
- Implicated in social bonding, trust
- Released during childbirth, breastfeeding
- Ghrelin – produced by the stomach
-
Leptin – produced by fat cells
- These are “appetite hormones” – act to stimulate or suppress hunger
-
Oxytocin - produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary
3
Q
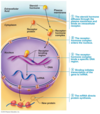
Steroid hormones
A
- Lipid-soluble → cross the plasma membrane
- Receptors are typically localized in the cytosol and nucleus of a cell
- Bind to transcription factors → capable of binding to DNA and altering gene synthesis → Alterations in the number of receptors, amount of neurotransmitter, peptides, proteins or hormones synthesized and stored within a cell.
- Slow action (hours to days) - may also act by nongenomic means
- Glucocorticoids (e.g. cortisol) – produced by the adrenal gland, affect immune/metabolic activity
- Sex hormones (androgens/estrogens) – produced by ovaries/testes
4
Q
Hypothalamus
A
- Located at the base of the brain, near the pituitary gland
- Acts to maintain homeostasis (maintenance of body’s internal environment): temperature, blood pressure, blood glucose ⇒ Synthesizes and secretes hormones

5
Q
Secretory hypothalamus
A
- The hypothalamus has control of the pituitary gland which then releases hormones into the bloodstream:
- the hypothalamus releases its own hormones called either releasing (RH) or inhibiting (IH) hormones
- RH and IH will travel a short distance to the pituitary gland and regulate it to release its own hormones into the bloodstream
- Pituitary cells can secrete: growth hormones, sex hormones, adrenocorticotropic-stimulating hormone (ACTH - implicated in production of cortisol)
6
Q
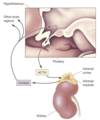
Stress response
A
- Hypothalamus decides whether a stimulus is stressful or not
- Secretes CRH which travels to the pituitary
- The pituitary releases ACTH
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) travels to the adrenal cortex
- Cortisol release - important in stress response
⇒ Pathway is called the Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal (HPA) pathway (also known as HPA axis)
7
Q
Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal (HPA) axis
A
- Responds to stress
- Short-term ⇒ Sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight, prepare for action)
- Increases metabolism
- Supresses Immune system
- Increases perception & attention
- Norepinephrine release
- Long-term
- Immune changes
- Loss of muscle and bone mass
- Hippocampus neuronal death
8
Q
Sex hormones
A
- Pituitary and Hypothalamus Control of Sex Hormones
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone triggers Pituitary release of the Gonadotropins :
- luteinizing hormone (LH)
- follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Males- LH signals testes to produce testosterone;
- FSH aids sperm maturation
- Females- FSH initiates follicular growth;
- LH triggers ovulation when follicle has matured
- Those hormones determine the sexual differentiation of the foetus.


