Neuroanatomy Flashcards
What is meant by the terms: superior, inferior, posterior, anterior, dorsal, ventral, rostral and caudal? Can you label them on this diagram?

Superior - above
Inferior - below
Posterior - back / behind
Anterior - in front / ahead
Dorsal - relating to the back of a structure
Ventral - relating to the front of a structure
Rostral - situated towards the oral / nasal region
Caudal - situated towards the hind region

What are the 3 different planes used in medicine?


hypothalamus, cerebellum, frontal and temporal lobes, medulla
Fill in the table about the cranial fossae:


lateral, third and fourth ventricles, central canal, interventricular foramen, aqueduct
Fill in the labels about the ventricular system:

lateral, third, fourth, aqueduct
Fill in the table about which ventricles supply which parts of the brain:


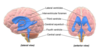
Label this diagram of the brain:


Gyrus, sulcus, fissure
Name and define the 3 main surface features of the brain:
Gyri - ridges on the cerebral cortex
Sulci - groove in the cortex, shallow grooves between the gyri
Fissures - larger grooves that divide the brain into lobes

Name and label the 4 lobes on this diagram (of the cerebrum):


olfactory (CN I), optic (CN II), oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), trigeminal (CN V), abducent (or abducens; CN VI), facial (CN VII), vestibulocochlear (CN VIII), glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X), accessory (CN XI), and hypoglossal (CN XII)
Label the CNs onto this diagram:

CN 1 - Olfactory, CN II - Optic, CN III - Oculomotor, CN IV - Trochlear, CN V - Trigeminal (3 branches), CN VI - Abducens, CN VII - facial, CN VIII - Vestibulocochlear, CN IX - Glossopharyngeal, CN X - Vagus, CN XI - Accessory, CN XII - Hypoglossal
CN I, II - cerebrum | CN III, IV - midbrain | CN V, VI, VII, VIII - pons | CN IX, X, XI, XII - brainstem

Broca’s, Wernicke’s, Primary Motor, Primary auditory, Primary somatosensory, visual
Fill in the labels on this diagram:


What is the Circle of Willis?
Which 5 arteries come together at the Circle of Willis?
Arterial blood supply to the brain - located at the base of the brain, encircling the stalk of the pituitary gland
It is circulatory anastomosis (i.e., a connection between two blood vessels
- Internal carotid artery (left and right)
- Anterior cerebral artery (left and right)
- Anterior communicating artery
- Posterior cerebral artery (left and right)
- Posterior communicating artery (left and right)
Fill in the labels on this diagram of the Circle of Willis:


choose between: middle, anterior and posterior cerebral arteries
Fill in this table about the cortical (outer layer of the cerebrum) arterial blood supply:


What is somatotopy?
What is the somatotopy of the motor cortex and somatosensory cortex strips?

The point-for-point correspondence of an area of the body to a specific point on the CNS

Define the structures of the CNS:
Nucleus
Lamina
White matter tract
Nucleus - a collection of neuronal cell bodies
Lamina - a layer of neurons
White matter tract - collection of axons
Define the sturctures of the PNS:
Ganglion
Nerve
Ganglion - collection of neuronal cell bodies
Nerve - a collection of a axons
Using the terms nucleus, lamina, white matter tract, ganglion or nerve, label these images:

Image on the left - nucleus
Imagine on the right (purple) - nerve
Using the terms nucleus, lamina, white matter tract, ganglion or nerve, label these images:

Image on the left (pink) - lamina
Image on the right -
Using the terms nucleus, lamina, white matter tract, ganglion or nerve, label these images:

Image on the left - ganglion
Image on the right - 1. white matter tract, 2. nucleus
Using the terms nucleus, lamina, white matter tract, ganglion or nerve, label these images:

Nerve
Using the following diagrams, label the structures from 1 to 17:


CN I - Olfactory Nerve:
- Component(s) - Afferent (A) or Efferent (E)
- Exit from skull
- Function
- Special Afferent - SA
- Cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone
- Smell - receptors located in the roof and upper parts of the nasal cavity
CN II - Optic Nerve:
- Component(s) - A or E
- Exit from skull
- Function
- Special Afferent - SA
- Optic Canal
- Vision - receptors are photoreceptors in the retina
CN III - Occulomotor nerve:
- Component(s) - A or E
- Exit from skull
- Function
- General somatic and general visceral efferent - GSE + GVE
- Superior orbital fissure
- Eye movements - GSE innervates the levator palpebrae superioris, superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, and inferior oblique muscles (most of the extraocular muscles); GVE innervates the sphincter pupillae for pupillary constriction, ciliary muscles for accommodation of the lens for near vision (parasympathetic innervation)




