Central Nervous System Flashcards
What 2 branches can the Nervous System (NS) be divided into?
CNS - Central Nervous System
PNS - Peripheral Nervous System
What is the CNS composed of?
Spinal cord and brain
What is the PNS composed of?
Composed of nerves (cranial and spinal)
Ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord
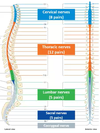
What are the spinal nerves?
Part of the PNS
Nerves that emerge out of the spinal cord and join onto other nerves
What is the brain composed of? Fill in the labels of this diagram:

Forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
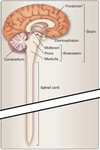
Fill in the divisions of the brain:
>>
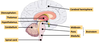
What type of section is this of the brain?
Fill in the missing labels of this diagram:

Mid-saggital section
The darker green below the hypathalamus is the pituitary gland, and the hypathalamus and pituitary gland communicate with each other for regulation of the body
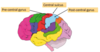
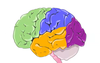
What are the 4 lobes of the brain?
Frontal - higher order, coginitive, executive (planning, attention, memory), and motor functions,
Parietal - Sensation, sensory aspects of speech, spatial orientation and self-perception
Temporal - processing auditory information
Occipital - processing visual information
Label the 4 different lobes on this diagram:
>>

What are the different areas circled called?
What are the functions of these areas?

Baby pink = central sulcus (divides the frontal and parietal lobes)
Yellow = pre-central gyrus (anterior) and post-central gyrus (posterior) - house the primary cortices of the motor and sensory respectively
Brown = lateral fissure (separated the temporal, parietal and front lobes)
Baby blue = parieto-occipital sulcus (divides the parietal and occipital lobes)

What is the lobe called highlighted in green and what is its function?

Limbic Lobe - composed of the amygdala, hippocampus, mamillary body, and congulate gyrus
Limbic system involved in learning, memory, motivation (esp. reward systems)
What is the lobe that lies deep within the lateral fissure and what is its function?

Insular cortex
Functions include - receives viceral sensations from the organs, autonomic control, introception (understanding what is going on inside you), some auditory processing, visual vestibular integration (breakdown causes dizziness / motion sickness)
What are the 3 layers of the meninges?
What are the 2 layers of the dura, and what do they form?
What is the space called between the arachnoid and pia?

Dure - divides into the periosteal and meningeal layer, both together form the dural sinuses
Arachnoid - thin, transparent, fibrous membrane that forms spiderlike projections (does not go into the folds)
Pia - thin membrane, that follows the folds
Sub-arachnoid space

What is CSF, where is it formed, where does it travel and what does it do (i.e. why is it important?
Cerebrospinal fluid - made within the ventricles, flows out of the ventricles, pools into the subarachnoid space, reabsorbed into the bloodstream at these sinuses
Cushions the brain within the skull, shock absorber for the CNS, also circulates nutrients, removes waste products from the brain
The red arrows indicate the flow of CFS.
Where specifically is CSF produced?
Where does it occupy and how does it get there?
Through what is the CSF reabsorbed?
How much CSF is produced daily?
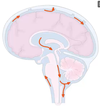
Produced in modified epithelial cells called the choroid plexuses of lateral, 3rd and 4th ventricles
Occupies ventricular system (closed system but greatly expanded within the brain) and sub-arachnoid space (when it emerges from the ventricles at 3 foramen)
Reabsorbed via arachnoid villi (granulations on the SSS) into the superior sagittal sinus (SSS)
~125 ml volume and 500 ml produced each day

What is the Ventricular System?
Where are the 4 ventricles and what else are they connected to?
Brain ventricles - four cavities located within the brain that contain CSF
Two lateral ventricles - one on each side of the cerebral cortex. The lateral ventricles are continuous with the third ventricle, which is lower in the brain. The third ventricle is continuous with the fourth ventricle, which runs along the brainstem
Ventricles are interconnected with each other, and the central canal of the spinal cord and the subarachnoid space

)What are the differences (especially in consistency) between the CSF and blood plasma?
What is CFS used for clinically?
Lower pH, less glucose, protein and potassium than plasma
As an indicator something may be wrong / a diagnostic tool - it should not contain many proteins, or any blood

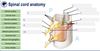
What is the spinal cord made up of?
Segments
How many nerves come out of each segment?
How are the segments named?
One from each side of the spinal cord (a pair of spinal nerves)
Corresponds to their position in the back / where it is on the spinal cord
What is the difference between the substances that make up the structures at 2 and 4?

Grey matter and white matter
What are the 2 projections (8 and 6) that go into and out of the grey matter?
What signals are conveyed through them?

Dorsal Root (posterior) - sensory / afferent
and Ventral Root (anterior) - motor / efferent
What are the smaller versions of the projections (5 and 7)?
The Dorsal and Ventral Rootlets
The grey matter in the spinal cord can be divided into which 2 parts (1 and 3)?
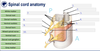
The Dorsal and Ventral Horns (posterior and anterior respectively)
What is that part of the nerve (10) and what signal travels though there?
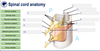
Mixed spinal nerve - at this point the afferent nerves have not yet broken away, and the efferent have already joined the nerve