Neuro Flashcards
(156 cards)
Anterior white commissures (what crosses here?)
Pain and temperature tracts (Commonly compressed in a syringomyelia — loss of pain and temp in upper extremities due to syrinx at C8-T1)
What do the lateral hypothalamic tracts contain?
Sympathetics to the face (lesion= Horner’s syndrome)
Signs of a LMN lesion?
Muscle weakness, atrophy, fasciculations, decrs tone & hyporeflexia
Signs of an UMN lesion?
Increased tone, hyperreflexia (spasticity),clonus, Babinski sign, posturing
Autosomal recessive, triplet repeats in the Frataxin gene Progressive damage to the nervous system Spinal nervous tissue degenerates over time causing ataxia, speech problems, muscle weakness, vision, hearing impairment Also assoc with development of diabetes and heart disease
Friedrich’s Ataxia
Secondary structures of proteins (alpha helices and beta sheets) are held in tact by what type of bond?
Hydrogen bonds
Melanocytes are derived from what?
Neural crest cells
a monocular scotoma is caused by a lesion ______
at the retina, optic disk or optic nerve (possible causes include Macular degeneration or optic neuritis)
Right anopia is caused by a lesion at the _____
right optic nerve (retinal artery or central vein occlusion)
Bitemporal hemianopia is caused by a lesion at the ______
Optic chiasm (pituitary tumor, craniopharyngioma or aneurysm of anterior communicating artery)
Right nasal hemianopia is caused by a lesion at the ________
right peri-chiasm (caused by a calcification or aneurysm of the internal carotid artery pressing on uncrossed lateral retinal fibers)
Left homonymous hemianopia (with a Marcu Gunn pupil) is caused by a lesion __________
Right optic tract or optic radiation (occlusion of anterior choroidal artery or MCA branch)
Left homonymous superior quadrantanopia is caused by __________
a lesion in the right temporal lobe (Meyer’s loop) – caused by a lesion / stroke in temporal lobe
Left homonymous inferior quadrantanopia is caused by __________
right parietal lobe lesion or stroke
left homonymous hemianopia w/ macular sparing caused by _________
right primary visual cortex (occipital lobe) – caused by a PCA occlusion, macula is spared b/c of collateral blood flow
What are the afferent & efferent nerves for the corneal reflex?
CN V (sensation of eye) , CN VII (reflex blink)
pt with hearing loss, tinnitus, asymmetric smile and loss of corneal reflex on same side—> a mass is most likely located ___________
at the cerebellopontine angle (the location of CN VIII…… CN V and VII are also nearby & could be affected)
Demyelination decreases the _________ constant
space (aka ‘length’) constant —> the distance along the axon the AP can propogate
Which muscle close the jaw?
masseter, medial pterygoid & temporalis muscles (supplied by the 3rd division of the Trigeminal n.–V3)
Which muscle opens the jaw?
Lateral pterygoid muscle (CN V3)
Which nerve roots produce ‘saddle anesthesia’ if pinched?
S3,4,5
low back pain radiating to legs, saddle anesthesia, loss of anocutaneous reflex, bowel & bladder dysfunction, loss of ankle jerk reflex and weak plantarflexion of the foot
Cauda equina syndrome (damage to the lumbar plexus nerve roots)
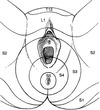
Man with short term memory loss, nystagmus, ophthalamoplegia & ataxia who’s breath smells like alcohol….. which of the structures is most likely damaged in this man’s brain?

B- the mammillary bodies –> he is experiencing Wernicke Encephalopathy and could progress to Korsakoff psychosis
CSF flows from the lateral ventricles to the 3rd ventricle via __________________ and then to the 4th ventricle via the _______________ and then out of the 4th and into the subarachnoid space through the __________ & __________
interventricular foramina of Monroe , cerebral aquaduct , lateral foramina of Luschka (2) or the medial foramin of Magendie













