Nephritis I and II Flashcards
(37 cards)
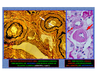
What are the histological findings of diffuse lupus proliferative glomerulo-nephritis (DPLGN)?
wire-loop lesions - with IgG deposits
karyorrhexis

What are the electron micrograph findings of DPLGN?
subendothelial deposits
paracrystalline structures

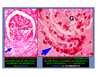
general characteristics of post-streptococal glomerulonephritis
presents as a nephritic state
history of infection
high anti-strepto (ASO) and anti-DNase B titers
petechial hemorrhages on the kidney surface (severe disease)
hypercellular glomeruli and hump-like deposits
deposits made up of C3 and IgG
What are the histological findings of post-strep GN?
hypercellular glomeruilus with PMNs in the capillary and urinary space

What are the electron micrograph findings of post-strep GN?
heavy influx of PMNs sticking to the basement membrane throughout
subepithelial humps

general characteristics of IgA nephropathy (Berger’s Disease)
history of episodes of gross hematuria (URI, GI problems)
history of episodes of Henoch-Scholein purpura
mesangial cell proliferation with deposits
deposits of IgA and C3 in the mesangium
What are the histologic findings of IgA nephropathy?
mesangial cell proliferation and deposits of IgA
purpuric rash on feet and buttocks

What are the electron micrograph findings of IgA nephropathy?
paramesangial deposit

general characteristics of Type I membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN)
neprotic with mild hematuria
history of URI, ventriculoatrial shunts, hepatitis-B, or subacute endocarditis
C3 alternate and classical pathways involved (low levesl of complement in blood)
subendothelial deposits of IgG and C3
hypercellular glomeruli with accentuated lobules and mesangial interposition
What are the histological findings of MPGN-I?
lobulations
mesangial interposition or GBM duplication
*seen through a silver stain
fringe pattern fluorescence of IgG or C3 and formation of lobules

What are the electron micrograph findings of MPGN-I?
proliferation of mesangial and endothelial cells and lobulation of the glomerulus
mesangial interposition of GBM duplication

general characteristics of goodpasture’s syndrome
anti-basement membrane antibody (cross-reactive with lung and kidney)
target is the type IV collagen
pulmonary hemorrhage and RPGN
crescentic glomerulonephritis (linear GBM immunofluorescence with IgG and C3)
What are the histological findings of GPS?
hemorrhagic surface of the kidney
proliferation of intrinsic cells with crescent
antibody binds GBM where the antigen lies

What are the electron micrograph findings of GPS?
disruption of the GBM with repair
inbetween, proteins, cells, and debris can get through the membrane

Where is the GP antigen located?
in the NC1 domain of type IV collagen of the GBM
general characteristics of Wegener’s Granulomatosis (WG)
triad of nasopharyngeal granuloma, microscopic vasculitis, and necrotizing glomerulitis
C-anti neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (C-ANCA) anti-PR3 reactivity

What are the histologic findings of Wegener’s Granulomatosis?
necrotizing cystic pulmonary lesions
multi-nucleated giant cells in the glomerulus
segmental necrosis of the glomerulus

What are the protein targets of C-ANCA? Where are they found? What disease are they associated with?
antibodies directed against PR3, serine protease, 29 kDa
found in azurophilic granules
common to Wegener’s Granulomatosis
What are the protein targets of P-ANCA? Where are they found? What disease are they associated with?
antibodies that target MPO, elastase, lactoferrin
MPO and elastase are found in azurophilic granules
lactoferrin is found in specific granules
associated with crescentic glomerulonephritis
What is the difference between C-ANCA and P-ANCA in terms of disease presentation and cellular location?
C-ANCA is cytoplasmic and is found in both microscopic vasculitis as well as Wegener’s granulomatosis
P-ANCA is perinuclear and is found in only microscopic vasculitis

What is the common histological finding in pauci-immune complex glomerulonephritis?
proliferation of intrinsic cells with cresecent
this crescent finding is not specific to this disease or Goospasture’s
types of tubulo-interstitial diseases
ischemia and toxins (acute tubular necrosis, ATN)
infections (pyelonephritis)
metabolic/physical factors (stones)
immunologic factors (transplant rejection)
vascular diseases (hypertension)
miscellaneous (polycystic disease)
primary vs. secondary hypertension
primary - cause unknown, can be benign or malignant
secondary - renal, endocrine, vascular, neurogenic cuases
benign hypertension
more than 160/90 mmHg
over 60 years, worsened by diabetes