Multidimensional integration Flashcards
Describe the transformation between cartesian coordinates (x,y,z) and spherical coordinates
x = rsinθcosϕ
y = rsinθsinϕ
z = rcosθ
Describe the transformation between cartesian coordinates (x,y,z) and cylindrical coordinates
x = pcosϕ
y = psinϕ
z = z
Note that cylindrical coordinates are just polar coordinates in 3D with z for the third variable
Give the equation of a line integral for the vector field G(r)
Note that the value of the line integral along a path C is independent of the parametrisation of the path

Give the equation of a loop integral for vector field G(r)
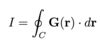
Give the equation of an area integral for any scalar field f(r)
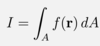
Give the transformation between cartesian coordinates and polar coordinates
x = rcosφ
y = rsinφ
Give the line element in polar coordinates

Give the area element in polar coordinates

Give the volume element for the function f(r) in cartesian coordinates
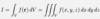
Give the line element in cylindrical coordinates
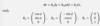
Give the volume element in cylindrical coordinates

Give the line element in spherical coordinates

Give the volume element in spherical coordinates

Give the general equation for the surface integral for any scalar field
f(r) = f(x,y,z)

Give the general equation for the total flux of a vector field G(r)
Note that total flux is given by the surface area, as only perpendicular components of G contribute to flux

Define dS
S is parametrised by r = r(s,t)
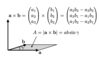
Note that x denotes the cross product
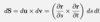
Give the relationship between dV and dS
dV = dSdr
State Gauss’s theorem
Fhe flux of a vector field G(r) through a closed surface S = ∂V is equal to the integral of the divergence of G over the enclosed volume V

State Stokes’s theorem
The loop integral of a vector field G(r) around the boundary C = ∂S of an open surface S is equal to the flux of the curl of the vector field
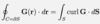
Define flux
Flux describes an effect that appears to move through a surface or substance
Define dS when z = g(x,y)
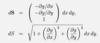
Define the vector product or cross product for two vectors a and b