MSK Upper Limb Flashcards
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- extensor digiti minimi
- lateral epicondyle; extensor hood of little finger (along with extensor digitorum)
- radial nerve
- extends little finger (also contributes to extension at wrist)

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
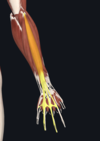
- extensor digitorum
- lateral epicondyle; tendon splits into four and inserts on extensor hood of each finger
- radial nerve
- extends medial four fingers at MCP and interphalangeal joints
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- deltoid
- lateral third of clavicle; acromion and spine of scapula; deltoid tuberosity of humerus
- axillary nerve
- anterior fibres- flexion and medial rotation; posterior fibres- extension and lateral rotation; middle fibres- major abductor of the arm (beyond 15degrees)
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

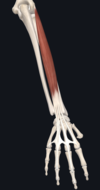
- flexor carpi ulnaris
- medial epicondyle; pisiform carpal bone
- ulnar nerve
- flexion and adduction of wrist

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- Pectoralis minor
- 3rd-5th ribs; coracoid process of scapula
- medial and lateral pectoral nerves (C5-T1)
- stabilises the scapula (involved a bit in shoulder abduction and depression)
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

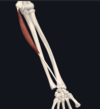
- palmaris longus (absent in around 15% population)
- medial epicondyle; flexor retinaculum at wrist
- median nerve
- flexion of wrist
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
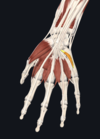
- opponens digiti minimi
- hook of hamate, flexor retinaculum; metacarpal V
- ulnar nerve
- opposes little finger (rotates metacarpal of little finger towards the palm)

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
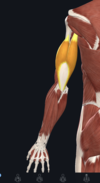
- triceps brachii
- long head- infraglenoid tubercle; lateral head- humerus; medial head- humerus; all heads converge onto olecranon of ulna
- radial nerve
- extension of elbow

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
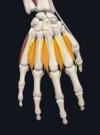
- dorsal interossei
- each orginates from lateral and medial surfaces of metacarpals; attach to extensor hood and proximal phalanx of each finger
- ulnar nerve
- abduct fingers at MCP joint
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- extensor pollicis longus
- posterior surface of ulna; distal phalanx of thumb
- radial nerve
- extends all joints of thumb (CMC, MCP, interphalangeal)
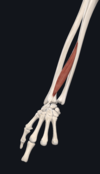
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- latissimus dorsi
- spinous processes of T7-12,L1-5; posterior half of iliac crest; 9-12th rib; intertubercular sulcus of humerus
- thoracodorsal nerve (C6-C8)
- extends, adducts, and medially rotates the upper limb
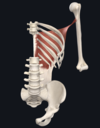
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- flexor carpi radialis
- medial epicondyle; base of metacarpals II and III
- median nerve
- flexion and abduction of wrist
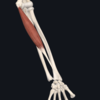
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- subscapularis (rotator cuff muscle)
- subscapular fossa on costal surface of scapula; lesser tubercle of humerus
- upper and lowr subscapular nerves
- medially rotates arm
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- infraspinatus (rotator cuff muscle)
- infraspinous fossa of scapula; greater tubercle of humerus
- suprascapular nerve
- laterally rotates arm
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- flexor pollicis brevis
- trapezium and flexor retinaculum; base of proximal phalanx of thumb
- median nerve (with deep head innervated by branch of ulnar nerve)
- flexes the MCP joint of thumb
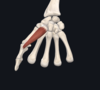
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- flexor digiti minimi
- hook of hamate, flexor retinaculum; proximal phalanc of little finger
- ulnar nerve
- flexes at MCP joint of little finger
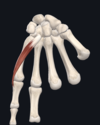
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- teres major
- posterior surface of inferior angle of scapula; intertubercular groove of humerus
- lower subscapular nerve
- adducts and extends shoulder; medially rotates arm

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- palmar interossei
- each orginates from medial or lateral surface of a metacarpal; attach to extensor hood and proximal phalanx of same finger
- ulnar nerve
- adducts fingers at MCP joint
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- brachialis
- medial and lateral surfaces of humeral shaft; ulnar tuberosity
- musclocutaneous nerve (and some radial nerve)
- flexes elbow

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- trapezius
- occipital protuberance; spinous processes of C7-T12; posterior aspect of lateral third of clavicle; acromion; spine of scapula
- accessory nerve (CN XI)
- upper fibres: elevate and rotate scapula during abduction; middle fibres: retract scapula; lower fibres: pull scapula inferiorly
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
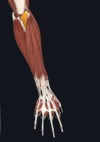
- aconeus (can be difficult to distinguish from triceps brachii)
- lateral epicondyle; posterior and lateral part of olecranon
- radial nerve
- extends and stabilises elbow joint; abducts ulna during pronation

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- levator scapulae
- transverse processes of C1-C4; superior angle of scapula/medial border of scapula superior to the spine of the scapula
- dorsal scapular nerve
- elevates the scapula
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
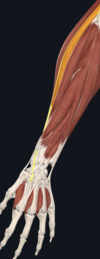
- extensor carpi radialis longus
- supracondylar ridge of humerus; metacarpal bones II and III
- radial nerve
- extends and abducts wrist

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- pectoralis major
- clavicle, sternum, greater tuberosity of humerus
- medial and lateral pectoral nerves
- adducts and medially rotates shoulder; depresses the shoulder
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
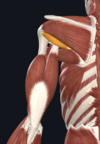
- teres minor (rotator cuff muscle)
- posterior surface of scapula; greater tubercle of humerus
- axillary nerve
- laterally rotates arm
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
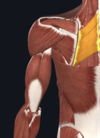
- Rhomboids (major and minor)
- major- spinous proccesses of T2-T5, medial border of scapula; minor- spinous processes of C7-T1, medial border of the scapula
- dorsal scapular nerve
- adducts/retracts and rotates scapula
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- brachioradialis
- humerus; distal end of radius
- radial nerve
- flexes elbow

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
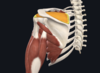
- supraspinatus (this is a rotator cuff muscle)
- supraspinous fossa of scapula; greater tubercle of humerus
- suprascapular nerve
- abducts arm 0-15 degrees, then helps deltoid to abduct arm from 15-90degrees
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
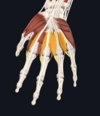
- lumbricals
- each lumbrical originates from a tendon of flexor digitorum profundus; insert on extensor hoods of each finger
- lateral two (index and middle finger)- median nerve; medial two (ring and little fingers)- ulnar nerve
- flexion at MCP and extension at interphalangeal joints of fingers

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
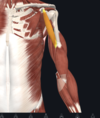
- coracobrachialis
- coracoid process of scapula; medial side of humeral shaft
- musclocutanous nerve
- flexion (abduction) of shoulder; weak contribution of adduction
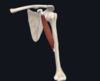
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- abductor pollicis longus
- interosseous membrane and posterior surfaces of radius and ulna; lateral base of metacarpal I (thumb metacarpal)
- radial nerve
- abducts thumb
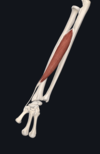
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- serratus anterior muscle
- 1st-9th ribs; medial border of scapula
- long thoracic nerve (C5-C7)
- protracts and upwardly rotates shoulder
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachement(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
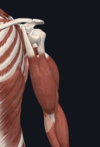
- biceps brachii
- long head orginates from supraglenoid tubercle of scapula; short head originates from coracoid process of scapula; both head insert of radfial tuberosisty
- musclocutanous nerve
- flexes elbow and shoulder; supination of forearm

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- abductor digiti minimi
- pisiform and tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris; proximal phalanx of little finger
- ulnar nerve
- abducts the little finger

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- flexor digitorum superficialis
- one head originates from medial epicondyle of humerus; other head from radius; four tendons attach onto middle phalanges of the four fingers
- median nerve
- flexes MCP joints and PIJ at 4 fingers; flexes wrist

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
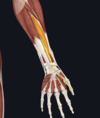
- flexor pollicis longus
- radius; base of distal phalanx of thumb
- median nerve
- flexes interphalangeal joint and MCP joint of thumb
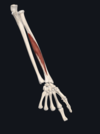
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- extensor carpi ulnaris
- lateral epicondyle; base of metacarpal V
- radial nerve
- extension and adduction of wrist
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- abductor pollicis brevis
- scaphoid and trapezium and flexor retinaculum; proximal phalanx of thumb
- median nerve
- abducts thumb

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
- flexor digitorum profundus
- ulna; the four tendons attach to distal phalanges of the four fingers
- medial half (acting on ring and little fingers)- ulnar nerve; lateral (acting on middle and index fingers)- median nerve
- flexed DIP joints (only muscles that can do this); flexes MCP and wrist

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- opponens pollicis
- trapezium; flexor retinaculum; first metacarpal
- median nerve
- opposes thumb (think of making an ‘OK’ sign) by medially rotating and flexing metacarpal on trapezium

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- palmaris brevis
- palmar apopneurosis, flexor retinalculum; dermis of skin of medial margin of hand
- ulnar nerve
- wrinkles skin of hypothenar emience and deepens curvature of hand- improving grip

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- adductor pollicis
- one head- metacarpal III; other head- capitate and adjacent areas of metacarpals II and III; both insert onto proximal phalanx of thumb
- ulnar nerve
- adductor of thumb
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- extensor carpi radialis brevis
- lateral epicondyle; tendon attches to metacarpal bone II and III
- radial nerve
- extends and abducts wrist

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- pronator teres
- medial epicondyke; coronoid process of ulna; mid-shaft of radius
- median nerve
- pronation of forearm

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- pronator quadratus
- anterior surface of ulnar; anterior surface of radius
- median nerve
- pronates forearm
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)
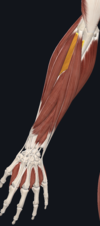
- supinator
- one head- lateral epicondyle; other head- posterior surface of ulna; both insert together onto posterior surface of radius
- radial nerve
- supinates forearm

Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

- extensor pollicis brevis (lateral border of anatomical snuffbox)
- posteriors surface of radius; base of proximal phalanx of thumb
- radial nerve
- extension of MCP and carpometacarpal joints of thumb
- what ventral rami make up the brachial plexus
- describe Erb’s palsy
- what nerves come from the posterior cord of the plexus
- what nerves come from the medial cord
- what nerves come from the lateral cord
- C5-T1
- injury to upper trunk of brachial plexus; medial rotation of arm with wrist flexion
- axillary and radial nerves from posterior only
- ulnar nerve from medial only
- musculocutaneous from lateral only
median nerve comes from both lateral and medial cord
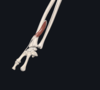
name the vessels in the image

top arrow= radial artery
bottom arrow= ulnar artery
- name the ligaments in the image
- what part of the shoulder joint capsule is weakest
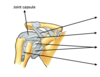
top arrow= coraco-acromial ligament
second arrow= coracohumeral ligament
third arrow= glenohumeral ligaments
bottom arrow= transverse humeral ligament
- inferior part is weakest as not protected by other muscles or ligaments
what is the clinical sign of radial nerve injury?
wrist drop
describe the path of the median nerve through the forearm
enters medial to brachial artery
goes under FDS and passes down forearm between FDS and FDP
enters the hand through the carpal tunnel
describe the contents of the carpal tunnel
- the 4 tendons of FDS
- the 4 tendons of FDP
- flexor pollicis longus tendon
- median nerve
- what artery is the main contributor to the superifical palmer arch
- what artery is the main contributor to the deep palmar arch
- ulnar
- radial
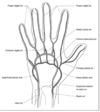
name the carpal bones going from bottom row radial side to ulnar side and then top row ulnar side to radial side (like a circle)
- scaphoid
- lunate
- triquetrum
- pisiform
- hamate
- capitate
- trapezoid
- trapezium
remember it by: So Long Top Part, Here Comes The Thumb

give the boundaries of the anatomical snuff box
what artery passes through this
- medial border- tendon of extensor pollicis longus
- lateral border- tendons of extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus
- floor- scaphoid and trapezium bones
radial artery passes through



