MSK Lower Limb Flashcards
1
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- pectineus
- pectineal line on anterior surface of pelvis; posterior side of femur (just inferior to lesser trochanter)
- femoral nerve
- adduction and flexion of hip

2
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- extensor digitorum brevis
- calcaneus, interoessous talocalcaneal ligament and inferior extensor retinaculum; proximal phalanx of great toe and medial toes 2-4 (not little toe)
- deep fibular nerve
- aids extensor digitorum longus in extension of medial four toes at MTP and interphalangeal joints
3
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- gluteus minimus
- ilium; anterior side of greater trochanter
- superior gluteal nerve
- abducts and medially rotates lower limb (also prevents pelvic drop of other limb during movement)

4
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- adductor brevis
- pubis and inferior pubic rami; posterior surface of femur
- obturator nerve
- adducts thigh

5
Q
name thee hip abductors
A
- gluteus medius
- glutues minimus
- piriformis
6
Q
identify the structures in the image

A
- lateral collateral ligament: posterior talofibular part
- anterior tibiofibular ligament
- lateral collateral ligament: calcaneofibular part
- lateral collateral ligament: anterior talofibular part
7
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- flexor hallucis longus
- posterior surface of fibula; plantar surface of phalanx of great toe
- tibial nerve
- flexes great toe

8
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- quadratus femoris
- ischial tuberosity; intertrochanteric crest
- nerve to quadratus femoris
- lateral rotation

9
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- tensor fascia lata
- ASIS; iliotibial tract (which then attaches to lateral condyle of tibia
- superior gluteal nerve
- flexion, abduction, and medial rotation of leg

10
Q
which letters correspond to the lesser and greater trochanters of the femur?

A
b= lesser trochanter
d= greater trochanter
11
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- extensor hallucis longus
- medial surface of fibular shaft; base of distal phalanx of great toe
- deep fibular nerve
- extension of great toe and dorsiflexion of foot

12
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- iliopsoas
- psoas major- lumbar vertebrae; iliacus- iliac fossa of pelvis; both insert together onto lesser trochanter of femur
- psoas major- L1-L3; iliacus- femoral nerve
- flexes thigh at hip joint

13
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- quadratus plantae
- calcaneus; attaches to tendons of flexor digitorum longus
- lateral plantar nerve
- assists flexor digitorum longus in flexing the lateral four digits

14
Q
- name five external rotators of the hip
A
- piriformis
- obturator internus
- obturator externus
- superior and inferior gemellii
- quadratus femoris
15
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- extensor hallucis brevis
- calcaneous; base of proximal phalanx of great toe
- deep fibular nerve
- aids extensor hallucis longus in extension of great toe at MTP joint
16
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- gracilis
- pubis; medial surface of tibia (between sartiorisu [anteriorly] and semitendinosus [posteriorly])
- obturator nerve
- adduction of thigh at hip; flexion of knee

17
Q
Give:
- name of muscles
- layer of foot they are in
- movements

A
- dorsal (green) interossei and plantar (yellow) interossei
- fourth layer
- dorsal- abduct digits; plantar- adduct digits
18
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- soleus
- soleal line of tibia/proximal femur area; joins calcaneal tendon (inserting onto calcaneus)
- tibial nerve
- plantarflexion of ankle

19
Q
where do the lymph nodes accompanying the great saphenous vein drain into?
A
superficial inguinal nodes
20
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- obturator externus
- membrane of obturator foramen; posterior aspect of greater trochanter of femur
- obturator nerve
- adduction and lateral rotation of thigh

21
Q
which vein is the arrow pointing to?

A
small saphenous vein
22
Q
- which nerve divides to form the deep and superficial fibular nerves?
- which nerve supplies the lateral compartment of the lower leg?
A
- common fibular nerve
- superficial fibular nerve
23
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- quadriceps femoris
- consists of: vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, vastus medialis, rectus femoris; all unite to form quadriceps tendon which attached to the patella
- femoral nerve
- main extensor of the knee (also stabilises the patella)

24
Q
Give:
- name of muscle
- attachment(s)
- innervation
- movement(s)

A
- gluteus medius
- gluteal surface of ilium; lateral surface of greater trochanter
- superior gluteal nerve
- abducts and medially rotates leg (also prevents pelvic drop of opposite limb during movement)

25
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. piriformis
2. anterior surface of sacrum; greater trochanter of the femur (goes through greater sciatic foramen)
3. nerve to piriformis
4. lateral rotation and abduction

26
1. what are the root values of the sciatic nerve
2. what foramen in the pelvis does it pass through
1. L4-S3
2. greater sciatic foramen
27
1. which superficial vein of lower limvascends anterior to medial malleolus of tibia?
2. which superificial vein ascends posterior to lateral malleolus of tibia?
3. which superficial vein drains into femoral vein?
4. which superficial vein drains into popliteal vein?
1. great saphenous vein
2. small saphenous vein
3. great saphenous vein
4. small saphenous vein
28
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. sartorius (longest muscle in the body)
2. ASIS; superior, medial surface of tibia
3. femoral nerve
4. flexes, abducts and laterally rotates hip; flexor of knee

29
name the ligaments of the hip joint labelled 1, 2, and 3

1. iliofemoral ligament
2. pubofemoral ligament
3. ischiofemoral ligament
30
give the:
1. medial boundary of femoral triangle
2. lateral boundary
3. base
4. muscles making up floor
1. adductor longus
2. sartorius
3. inguinal ligament
4. pectineus, iliopsoas, adductor longus
31
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. tibialis posterior
2. posterior surfaces of tibia and fibula; tendon enters foot posterior to medial malleolus and attaches to plantar surfaces of medial tarsal bone
3. tibial nerve
4. inverts and plantarflexes foot; maintains medial arch of foot

32
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. extensor digitorum longus
2. lateral condyle of tibial and medial surface of fibula; fibres converge into tendon which then splits into four and each inserts on a toe
3. deep fibular nerve
4. extension of lateral four toes; dorsiflexion of foot

33
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. abductor hallucis
2. calcaneus; medial base of proximal phalanx of great tow
3. medial plantar nerve
4. abducts and flexes great toe

34
what structures are in the femoral sheath?
and what order are they in (lateral to medial)?
femoral artery (most lateral), femoral vein (intermediate), deep inguinal lymph noes (most medial)
the femoral nerve is also present in the femoral triangle but not within the sheath
35
Give:
1. name of muscles
2. what layer of the foot they are in
3. what their general actions are
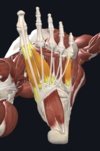
1. flexor hallucis brevis (far left), adductor hallucis (middle), flexor digiti minimi brevis (far right)
2. third layer
3. adductors and short flexors of the toes
36
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)
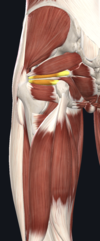
1. superior and inferior gemelli
2. superior- ischial spine; inferior- ischial tuberosity; both attach to greater trochanter of femur
3. superior- nerve to obturator internus; inferior- nerve to quadratus femoris
4. lateral rotation and abduction

37
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. gluteus maximus
2. gluteal/posterior surface of ilium, sacrum and coccyx; iliotibial tract; gluteal tuberosity of femur
3. inferior gluteal nerve
4. main extensor of thigh; assists lateral rotation

38
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. adductor longus
2. pubis; femur (is fan shaped)
3. obturator nerve
4. flexor and adductor of thigh

39
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. tibialis anterior
2. lateral surface of tibia; medial cuneiform and base of metatarsal I
3. deep fibular nerve
4. dosrsiflexion and inversion of foot

40
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. fibularis brevis
2. inferolateral surface of fibular shaft; tubercle on metatarsal V
3. superficial fibular nerve
4. eversion of foot

41
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. semimembranosus
2. ischial tuberosity; medial tibial condyle
3. tibial part of sciatic nerve
4. flexion and medial rotation of knee; extention and medial rotation of hip joint

42
name the muscles involved in plantarflexion
1. gastrocnemius
2. soleus
3. tibialis posterior
4. flexor hallucis longus
5. flexor digitorum longus
43
name the structures passing through the door to the foot
1. flexor **H**allucis longus
2. **T**ibialis posterior
3. flexor **D**igitorum longus
4. posterior tibial **A**rtery
5. tibial **N**erve
remember order by: **T**om, **D**ick, **AN**d **H**arry
44
Give:
1, 2, 3
and
a-i

1= ilium
2=ischium
3=pubis
a= ASIS
b= illiac crest
c= illiac fossa
d= pubic tubercle
e= pubic crest
f= obturator foramen
g= acetabular cavity
h= ischial spine
i- ischial tuberosity
45
name the structures each arrow point at

top arrow= greater sciatic foramen
second arrow= sacrotuberous ligament
third arrow= sacrospinoud ligament
fourth arrow= lesser sciatic foramen
46
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. obturator internus
2. pubis and ischium at obturator foramen; greater trochanter of femur (travels through lesser sciatic foramen)
3. nerve to obturator internus
4. lateral rotation and abduction

47
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. fibularis tertius
2. medial surface of fibula; metatarsal V (similar path to extensor digitorum longus)
3. deep fibular nerve
4. eversion and dorsiflexion of foot

48
where do lymph nodes accompanying the small saphenous vein drain into?
popliteal lymph nodes
49
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. popliteus
2. lateral condyle of femur; inserts just above origin of soleus on tibia
3. tibial nerve
4. lateral rotation of femur on tibia; 'unlocks' knee joint so flexion can begin

50
name the knee bursae

1. prepatellar
2. deep infrapatellar
3. subcutaneous infrapatellar
51
name the knee ligaments

1. lateral collateral ligament
2. medial collateral ligament
3. anterior cruciate ligament
4. posterior cruciate ligament
52
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. fibularis longus
2. superior and lateral surface of fibula and lateral tibial condyle; fibres converge forming a tendon which inserts onto medial cuneiform and base of metatarsal I
3. superficial fibular nerve
4. eversion and plantar flexion of foot (also supports lateral and transverse arches of foot)

53
name three hip extensors
1. gluteus maximus
2. hamstrings
3. posterior part of adductor magnus
54
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. semitendinosus
2. ischial tuberosityof pelvis; medial surface of tibia
3. tibial part of sciatic nerve
4. flexion of knee joint; extension of hip (medially rotates hip and knee)

55
1. what type of joint is the ankle
2. identify the structures indictated on the diagram

1. hinge type synovial joint
2. 1. deltoid/medial ligament: tibionavicular part, 2. deltoid/medial ligament: tibiocalcaneal part
56
name the muscles involved in dorsiflexion
1. tibialis anterior
2. extensor digitorum longus
3. extensor hallucis longus
4. fibular tertius
57
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. abductor digiti minimi
2. calcaneus; lateral base of proximla phalanx of 5th digit
3. lateral plantar nerve
4. abducts and flexes 5th digit

58
describe footdrop
arises from paralysis of muscles in anterior compartment of leg (tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, fibularis tertius).
typically due to damage to common fibular nerve which gives rise to deep fibular nerve
muscles of posterior compartment of lower leg are unopposed so get permanent plantarflexion- can affect walking (foot drags/ has to be flicked outwards when walking)
59
name three medial rotators of hip
1. anterior fibres of gluteus medius
2. anterior fibres of gluteus minimus
3. tensor fascia lata
60
name three hip flexors
1. iliacus
2. psoas major
3. pectineus
61
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. plantaris (v. thin, can be mistaken for nerve, absent in 10% people)
2. lateral supracondylar line of femur; tendon blends into calcaneal tendon (inserting onto calcaneus)
3. tibial nerve
4. plantarflexion of ankle; flexes knee (not vital for any of these movements)

62
1. what artery is the femoral artery a continuation of?
2. what vein does the femoral vein become and what vein was is previously
1. external illiac artery
2. becomes external illiac vein, used to be popliteal vein
63
name five hip adductors
1. adductor longus
2. adductor brevis
3. adductor magnus
4. gracilis
5. obturator externus
64
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. flexor digitorum brevis
2. calcaneous; middle phalanges of lateral four toes
3. medial plantar nerve
4. flexes lateral four digits and PIP joints

65
which veins do the top and bottom arrows point to?

top arrow= greater saphenous vein
bottom arrow= dorsal venous arch
66
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. adductor magnus (composed of an adductor part and a hamstring part)
2. pubis and ischium; ishcial tuberosity; femur
3. obturator nerve; tibial component of sciatic nerve
4. adducts thigh (adductor part also flexes thigh; hamstring part also extends thigh)

67
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. lumbricals
2. orginate from tendons of flexor digitorum longus; each attaches to extensor hoods of lateral four digits
3. most medial- medial plantar nerve; lateral three- lateral plantar nerve
4. flexes at MTP joint, extends at IP joints
68
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. flexor digitorum longus
2. medial surface tibia; plantar surfaces of lateral four digits
3. tibial nerve
4. flexes the laterral four toes

69
name the bones of the foot

1. talus
2. calcaneus
3. navicular
4. cuboid
5. cuneiforms (medial, intermediate, lateral)
6. metatarsals
also proximal and distal phalanxes
70
name the nerves and arteries the arrows point to
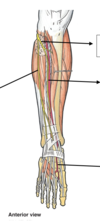
1. deep fibular nerve
2. superficial fibular nerve
3. anterior tibial artery
4. dorsalis pedis artery
71
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. biceps femoris (along with semitendinosis and semimembranosus = hamstrings)
2. long head- ischial tuberosity of pelvis; short head- posterior surface of femur; together form tendon which inserts onto head of fibula
3. long head- tibial part of sciatic nerve; short head- common fibular nerve
4. flexion at knee (also extension of hip; lateral rotation of hip and knee too)

72
What is and what causes a positive Trendelenburg sign?
Patient stands unassisted on each leg in turn. In positive sign, pelvic drop occurs on unsupported leg. E.g. if left gluteal muscle is weak, right side of pelvis will drop when patient stands on only left leg.
Caused by superior gluteal nerve damage so its muscles are paralysed- pelvis becomes unsteady.

73
Give:
1. name of muscle
2. attachment(s)
3. innervation
4. movement(s)

1. gastrocnemius
2. lateral head- lateral femoral condyle; medial head- medial femoral condyle; tendon combines with soleus to form calacneal tendon which inserts on calcaneus
3. tibial nerve
4. plantarflexes ankle joint; flexes knee


