MSK 1 - Upper Limbs 1 Flashcards
What shape is the axilla?
The axilla is roughly pyramidal in shape and has an apex, base, and 4 walls.

What are the following walls of the axilla formed by:
- anterior
- posterior
- medial
- lateral
- Anterior
- Pectoralis major and pectoralis minor
- Posterior
- Subscapularis, tere major and latissmus dorsi
- Medial
- Thoracic wall and serratus anterior
- Lateral
- Intertubercular of the humerus
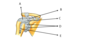
What is A?

Brachial plexus
What is B?

Axillary lymph nodes
What is C?
Axillary vein

What is D?

Axillary artery
The axillary artery is the continuation of which artery?
Subclavian artery
At what anatomical point does the axillary artery begin?
Lateral border of first rib
The axillary artery continues beyond the axilla as which vessel?
Brachial artery
At what anatomical point does the name of the axillary artery change?
Lower margin of teres major
The enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes is common in what?
The enlargement of axillary lymph nodes is common in infection of the upper limb, and in malignant processes involving the breast tissue.
What can happen to the axillary artery in response to perfuse bleeding of upper limb?
The axillary artery is a point where vasculature can be compressed (via a tourniquet) in response to profuse bleeding to the upper limb – for example after tissue trauma
Brachial plexis is formed by the ventral rami of what?
C 5 to T 1
What are the different trunks of the brachial plexus?
Upper trunk
Lower trunk
MIddle trunk
What nerve roots form the upper, middle and lower trunks of brachial plexus?
- Upper
- C5 and C6
- Middle
- C7
- Lower
- C8 and T1
What can the brachial plexus be further subdivided into?
Roots > trunks > divisions > cords > terminal branches

What is A?

Roots of brachial plexus
What is B?

Trunks of brachial plexus
What is C?

Divisions of brachial plexus
What is E?

Cords of brachial plexus
What is E?

Terminal branches of brachial plexus
The cords of the brachial plexus are named according to what?
their position in relation to the axillary artery in the axilla.
Injury to the upper trunk of brachial plexus causes what?
Erb’s palsy
What is the presentation of Erb’s palsy?
- Waiters tip appearance of upper limb
- Medial rotation of the arm and wrist flexion