Molluscs Flashcards
(40 cards)
What is the first offshoot of conchifera?
Monoplacophora
Describe the class monoplacophora
- single shell valve
- multiple pairs of ctenidia
- multiple pairs of dorsal attached ventral muscle
How did the shell evolve as a protective retreat from a
monoplacophoran-like ancestor?
- Gradual dorsal-ventral visceropallial elongation
- Visceropallial coiling
*no modern gastropods have a symmetrical shell
How does assymmetrical coiling work? How has this impacted the shell?
- migrates down the central coiling axis (the column of CaCO3)
- has transformed shell from dorsal shield to protective retreat
What is the central coiling axis called?
The collumella
How do they close the shell opening? What does this do?
With an operculum
-provides protections, prevents desiccation
What is the operculum made of?
Hard, proteinaceous material, sometimes with CaCO3 salts
How do you get from monoplacophoran to hypothetical intermediate?
- Reduction of:
- shell aperture, # shell muscles, # ctenidia - Elongation of shell
- Lateral mantle cavities became single one confined to posterior end
How do you get from hypothetical intermediate to gastropod?
180 degree rotation of entire visceroapallium relative to cephalopodium
What are two characteristics that support the rotation hypothesis?
Cross-over of visceropallial nerve chords (in adults)
Ontogenetic torsion in basal gastropods (larvae themselves exhibit torsion during development, in span of 12-15hrs)
What is the typical larvae of gastropods? What are the two types?
veliger
feeding/non-feeding
How do the larvae of gastropods swim?
By beating their ciliated velar lobes
What are 3 main body parts of a veliger?
- Velar lobes
- Foot
- Shell
Difference of operculum being pulled in before and after torsion
Before: foot pulled in first, velum last, no way for operculum to seal aperture
After: velum pulled in first, foot pulled in last, operculum can seal opening
Solutions to fouling in keyhole limpets
Water flow in mantle cavity, passes over ctenidia, then over anus and out perforation
Solutions to prevent fouling in coiled gastropods
- Loss of right ctenidium
- Anus moved to right side
Water flow in coiled gastropods
Oblique flow pattern
- In mantle cavity
- Passes over osphradia
- Over single monopectinate ctenidia
- Out over anus on right side
What do some gastropods use to search for prey?
- Their siphon (an outgrowth of mantle epithelium)
- looks for chemical effluent of prey item
What is the alternative hypothesis for a gastropod body plan?
Bilateral mantle cavity-> unilateral loss
Problems with cross-over of visceropallial nerve connective
If torsion evolved as 180 deg rotation, must have occurred rapidly->no functional intermediates
Evidence of cephalization in gastropods (general)
- Labial tentacles
- Eyespot
- Mouth
How do vetigastropoda feed?
-herbivorous grazing
How do caenogastropoda feed?
- herbivorous grazing
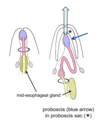
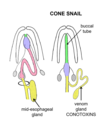
- some have proboscis and are predatory
Where is the proboscis stored when not in use?
In the proboscis sac at the anterior end.