Mixed/RO Non-Odontogenic Lesions Flashcards
Mixed/ RO Non-odontogenic lesions
Mixed 2
RO 6
- Mixed
- Cemento-osseous dysplasia
- Central ossifying fibroma
- RO
- Idiopathic osteosclerosis
- Fibrous dysplasia
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Osteoma
- Sinusitis/Mucositis
- Mucous retention psudocyst
Benign Fibro-Osseous Lesions 3
- Benign neoplasms and non-neoplastic lesions of bone with identical micro features
- Cemento-osseous dysplasia- not a neoplasm
- Ossifying (cementifying) fibroma- neoplasm
- Fibrous dysplasia- not a neoplasm
Spectrum of Cemento-osseous dysplasias
3 kinds
- Cemento-osseous dysplasia develop in areas of teeth but may represent benign fibro-osseous lesions
- Bone gets broken down and replaced with fibrous tissue
- Focal cemento-osseous dysplasia- solitary lesion, most common
- Periapical cemental dysplasia- multiple lesions usually in anterior mand
- Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia- multiple, bilateral lesions throughout the jaws
Cemento-osseous dysplasias
what are they
Do not cause, rarely
Demo, age
tx
- These are not neoplasms
- Do not cause enlargement, rarely tooth resorption
- 90% women 30-50yo
- Tx dont need to be treated
Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
Location, involving
Demo
May produce
Process
Xray2
Management

- Commonly multiple periapical lesions involving mand ant teeth
- Common in african americans
- ay produce mineralized products
- First becomes RL then mixed
- Surrounded by thin RL line
- Hard to id partly well defined, partly corticated
- Management: dx and then no addnl tx
Focal Cemento-osseous Dysplasia
Same as
Location 2
Demo
Xray 2
Tx

- Same feat as PCOD
- Occurs only in one location
- Usually post mand
- Common in caucasians
- RL with RO center
- Partly corticated
- No tx necessary
Florid Cemento-osseous Dysplasia
same as
Distribution/ xray
Location
Xray
demo
tx

- Same as PCOD
- Multiple bilateral periapical RL areas w/ formation of mineralized product
- Occurs in only 2+ quadrants
- Mixed
- Common in african americans
- No tx needed
Fibrous Dysplasia
Definition
3 diff severities
Tx
- Non-neoplastic developmental disturbance of bone growth
- Severity of disease depends when mutation occurs
- Monostotic- late
- Polyostotic- mid
- Syndrome- ealry
- Tx
- bony recontouring once it stops growing
- Lesion shout NOT be irradiated as this may cause malignant transformation
Monostotic Fibrous dysplasia
Involves
occurs during
occurrence
- Involves one bone
- 1st and 2nd decade of life
- More common than polystotic
Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia
Involves, begins, features, occurence
2 diff types- involve, app
- Involves multiple bones, begins early in life, systemic features, rare
- Jaffe syndrome
- Involves fewer bones
- Cafe au lait melanotic macules
- McCune Albright Syndrome
- Involves most of skeleton
- Endocrine abnormalities, usually precocious puberty in females
- Cafe au lait macules
Fibrous Dysplasia Xray
Specific term
Location
causes
borders
Mand and max

- Ground glass homogenous radiopacity, poorly defined, blends into surrounding bone
- Diffuse uniform RO
- Causes expansion- on mand expands buccal and lingual
- Margins of lesion blend into surrounding bone
- Monostotic only mand
- Max lesions may involve surrounding bones- craniofacial fibrous dysplasia

Central Ossifying (& Cementifying) Fibroma
What is it
Growth
can cause, and
xray/ varieties 4
tx

- True neoplasm of bone
- Persistent and progressive growth
- Can cause expansion and displacement of teeth
- Xray
- well demarcated
- May app in diff patterns
- Entirely RL
- RL with foci of RO areas
- Mostly RO
- Tx
- Must be removed
- Enucleation or curettage
Idiopathic Osteosclerosis
Aka
counterpart of
definition
Location
dx
xray 6

- AKA dense bone island, Enostosis
- Intraosseous counterpart of tori
- Focal area of cortical bone of unkown cause
- 90% post mand
- Dx can be done with xrays
- Xray
- round, well defined, sclerotic area
- Usualy at apex
- Still have PDL (unlike cementoblastoma)
- Still have lamina dura

Osteoma
What is it
4 areas it can affect
xray 3
tx 2

- Benign tumor of bone restricted to skull
- Periosteal- surface of bone
- Endosteal- medullary bone
- Osteoma cutis- within muscle or dermis
- Common in condyle (shift in midline/occlusion) and paranasal sinuses
- Xray
- Well defined
- Totally RO
- Circumscribed sclerotic mass
- Tx
- Small-observe
- Large-surgery

Mucositis and Sinusitis
What is it
caused by
Muco vs sinus
xray 3

- Inflammation of lining of sinus
- Allergy, irritation, foreign body, trauma
- Mucositis- localized- no tx
- Sinusitis- multiple sinuses- control or surgery
- Feels like tooth pain
- Xray
- Well defined
- Noncorticated
- RO band of increased radiopacity parelleling the bony wall of max sinus
Mucous Retention Pseudocyst
What causes it
Xray 5
tx
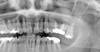
- Blockage of seromucous glands in sinus mucosa
- Mucos gets trapped btw epithelium and bone causing domeshaped swelling
- Submucosal accumulation of secretions= dome shaped swelling
- Xray
- Well defined
- Noncorticated
- Smooth
- Dome shaped
- Sessile RO mass
- No tx needed


