MIT Biology Flashcards
What is the valency of sulfur?
2
Which five molecule types make up most of the human body (in order)?
Water, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids/fats, nucleic acids
What do you get if you combine a glycerol molecule with three fatty acids?
Triacylglycerol (triglyceride)
What is this functional group? -SH
Sulfhydryl (aka thiol) group
Which field of biological science seeks to purify and fractionate?
Biochemistry
What do you call an organic compound which contains a carboxyl group?
A carboxylic acid
How much of the human body is composed of carbon (by atom count)?
10%
What is the technical term for fats?
Triglycerides
Amino group - acid or basic?
Basic - the nitrogen has a lone pair that can accept hydrogen protons
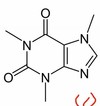
What molecule is this?

Adenosine diphosphate
How much of the human body is composed of phosphorus (by atom count)?
0.2%
How long ago did the first human-like creatures emerge on Earth?
5 million years ago
What kind of bond is this?

Hydrogen bond
What is an unsaturated fat?
A triglyceride in which at least one double bond is present between carbons
Is a sulfhydryl group polar?
Yes, weakly.
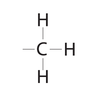
What kind of molecule does this represent?

A hydrocarbon
What is a saturated fat?
A triglyceride in which there are no double-bonds between carbons, meaning all possible bonds with hydrogen are made.
What are the three stages of cell respiration?
Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, electron transport chain
Is a water molecule polar or non-polar?
Polar
How long was it between the emergence of life on Earth, and the emergence of the first eukaryotic cells?
About 2 billion years
How long ago did the Earth cool?
4 billion years
How are oxygen and hydrogen bonded in a water molecule?
Covalent bonds
Which type of fats do not occur in nature?
Trans fats