Midterm Flashcards
World Cultural Realms

Functional region
a region marked less by it’s sameness than it’s dynamic structure
- a spatial system focused on a central core
- A region formed by a set of places and their practical integration
(also known as nodal region)
Relative Location
In relation to something else, ex: “he’s closer to the desk than me”; qualitative
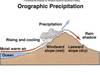
Convergent Lift

Biosphere
Atmosphere, lithosphere and lithosphere combined
- Resources (opportunities) vs. Tolerance (constraints)
- Biogeography
- studies the geographic distribution of living organisms
Biomes
global scale ecosystem classification sceheme (climates, soil etc.)
Transition Zone
- An area of spatial change where the peripheries of two adjacent realms or regions with
- marked gradual shift (rather than a sharp break)
Map
A 2-D representation of the Earth’s surface that is:
- Projected
- Reduced
- Generalized
- Explained
- Concept of ________ is inseperable from location
- Aid in understanding of patterns in space
- Visual means of communications of these relationships
Third World
Everyone Else. (Not Economically stable, not fitting into 2nd world because it’s less devel.)
First World
West. Europe, USA + Canada, New Zealand, South Korea, Japan
Equal Area Map
Area is preserved in this type of projection
Periphery vs. Core
_________ ex: Farms
__________ ex: Downtown
______ supports the _________
Conformal Map
Shape is preserved in this map projection
Absolute location
Quantitative (number attached) ex: “he is 10 metres from the desk”
- Graticule
- Latitude + Longitude
Thematic map
based on a topic/theme
Line scale

What are some concepts in Human Geography?
Location, distribution, process + interrelationships
What is a Natural Landscape?
the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture
Culture VS Environment
The environement does not control culture and innovation
Reaction to opportunities and constraints, people are the deciding factors not environements
Peters Projection

Stream discharge possible factors
- Climate
- Precipitation (amount and timing)
- Temperature (evaporation + seasonality)
- Vegetation
- Geology
- Bedrock (porosity permeability)
- Groundwater
Generalized map characteristics
- Detail through simplification, selection, combintion or smoothhing
- May be a result of necessity (i.e. scale reduction)
- May be the mapmakers choice (i.e. information converged)
Realm
the result of interaction between human societies and natural elements
geographic _________ change over time
clusters of humans
Koppen Climate System

Word scale
ex: 1cm to 1km
What is Systematic Geography?
Examines the topic with little regard to location
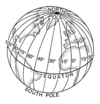
Longitude
measures positions east & west (meridians)
- Starting point for longitude in Greenwich, England
- “Prime Meridian”
What is a topographic map?
A detailed map of the surface features of land

Change in distribution suggests what?
Processes
Convective lift
heat energy

Place Attributes are always changing
No ______ is static, they evolve
Solar Radiation

Global pressure and wind belts
- NE + SE trade winds
- Intertropical convergence (ITC)
- Westerlies
- Subtropical highs
- Subpolar lows
- Cordis
- Weather comes from west to east (Westerlies)
- Tropics have trade winds from East
- Clouds close to Equator (lots)
- Lift -> cloud -> precipitation
- 4 types of lift (convergent, mechanical, convection and frontal)
What is a bathymetric map?
A bathymetric chart is the submerged equivalent of an above-water topographic map. Bathymetric charts are designed to present accurate, measurable description and visual presentation of the submerged terrain.

Second World
Soviet Union, China, Eastern Europe (communist and socialist)
What is culture?
Learned attitudes and behaviours
Cultural traits: language, games, objects and techniques
Cultural complex: language and religion
Cultural region: spatially defined
Largest cultural realm: several related regions considered together
Carrying capacity + logistical strategy
S-Shaped chart

Graticule
a network of lines representing meridians and parallels, on which a map or plan can be represented.

Reduction (Reduced)
- Linear distances must be made smaller then reality by means of scale reduction
- Scales can be word, line or representative fractions
- Small scale map vs. large scale map
- Small: larger area covered (country shown vs. town)
- Large: more detail, way zoomed in (towns shown vs. country)
Regions
The criteria we use to identity and define them
- Each _______ is a product of the processes and interactions that define them
- Formal vs. functional
- Location + spatial extent
- Hierarchy
Representative Fraction (RF) Scale
1: 50,000
Global Realm
Based on a spatial criteria
Largest geo. units, the inhabiyed world can be divided into them (based on physical and human aspects)
Sense of place
- Subjective/emotional response to a place
- Behavioural response to a place
- Territory + boundaries (boundaries surround our territories)
- Ex: Tourism
Mathusian Population Chart

Mercator Projection

Global human regions
Deals with the human landscape
ex: population or cultural geography
Terrestrial Radiation
Infra-red radiation, long wave, outgoing
- Water vapor (invisible)
- CO2
- Methane
Without the radiation processes, the earth would be 30 degrees cooler

Human enviro. interaction
Some suggest this is the crux of geo
Opportunities vs. Constraints
What are the 5 main themes of Geography?
Location, Place, Movement, Human/Environement Interaction, Regions
What is Dualism?
The first natural subdivision of geography (physical vs. human)
Topographical map
Indication of how land rises and falls (i.e. relief/elevation)
Explained map characteristic
- Marginal information provides additional information
OR
- helps decode the map
- i.e. legend/key (colour has meaning)
Low pressure system
- Divergence in upper atmosphere
- Convergence in lower atmospehere

What is Geography?
A field of science devoted to the study of the lands, the features, the inhabitants, and the phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be “to write about the earth”.
What is a unifying concept in Geography?
Space
Major Concepts with “Place”
- Place attributes are always changing
- Mental Maps
- Sense of Place
- Places interact
Ecosystem
inclues both abiotic and biotic matter
Latitude
Measures the position north or south (parallels)
- Starts at the equator

Formal region
marked by a certain degree of similarity in one or more phenomena
High pressure system
- Clear skies, cold air (winter), warm temp (summer)
- Convergence in upper atmosphere
- Divergence in lower atmosphere

Places interact
- An understandable or at least identifiable ways
- Spactial interaction
- Distance
- Linear
- Time distance
- psychological distance
- Distance decay
- interaction tends to decrease with increasing distance from something
- Accessibility of places
- Physical/psychological/cultural limitations
- Connectivitity of Places
- Quantity + quality of routes between places
Location
The foundation of Geographic thought, where?
- Relative vs. Absolute location
- Latitude & Longitude
- Maps (& map projections)
- Topographical vs. Thematic
What is regional geography?
Attention is paid to unique characteristics of a particular region such as natural elements, human elements, and regionalization which covers the techniques of delineating space into regions.

Polyconic Projection

Place
LOCATION describes SITE whereas _______ describes SITUATION.
- Location & site describe internal characteristics
- ______ & Situation describe external characteristics + relationships with other places
- _______ the combination of human features and physical features that gives relative geographic characteristics
EXAMPLE:
- Regina:
- Site: Latitude & Longitude
- Flat glacial lake plain 573 m above sea level (ASL)
- Situation: Southern SK