European Geo (Post-Midterm) Flashcards
(37 cards)
Europe subdivisions
Northern, Eastern, Alpine, Balkan, Mediterranean and Western

Relative Location: Europe and it’s Perks
- At the heart of the land hemisphere
- Maximum efficiency for contact with the rest of the world
- Every part of ________ is fairly close to the sea
- Fairly moderated climate (warmer winters and cooler summers)
- Good for trade; good for fishing
- Navigable waterways
- Moderate distances

Europe VS USA/Canada size/location

Climate of Europe

Physical Realm of Europe

Political Realm of Europe
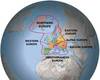
Europe Physical Landscapes
- Alpine System
- Greece, Balkins, Italy
- Western Uplands
- Ibirian Pennisula, Scandanavia, British Isles
- Central Uplands
- North European Lowland

von Thünen Rings (Europe)
Black dot = central city
Orange= Intensive farming + dairying
Red= Forest
Green= Increasingly extensive field crops
Yellow= Ranching, animal products

Europe Co-Location of Resources
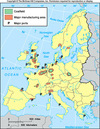
Iron Ore + Coal
Weber predicts: Manufacturing

Europe - Coal, Ports, Manufacturing areas
Europe Diversity
Europe Population Pyramid
** look at gif

Microstates of Europe
- Small sovereign political entities
- Dependent on surrounding states

von Thünen Rings
The city is located centrally within an “Isolated State” which is self sufficient and has no external influences.
The Isolated State is surrounded by an unoccupied wilderness.
The land of the State is completely flat and has no rivers or mountains to interrupt the terrain.
The soil quality and climate are consistent throughout the State.
Farmers in the Isolated State transport their own goods to market via oxcart, across land, directly to the central city. Therefore, there are no roads.
Farmers act to maximize profits.
In an Isolated State with the foregoing statements being true, Von Thunen hypothesized that a pattern of rings around the city would develop.
There are four rings of agricultural activity surrounding the city. Dairying and intensive farming occur in the ring closest to the city.

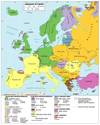
European Supranationalism
- A venture that involves three or more states
- Political, economic, and/or cultural cooperation to promote shared objectives
- “Euro” currency
- Image below:
- EU Members
- Non-members
- Prospective members

Europe - Supranationalism 1957-1987

Agrarian Revolution
- Began in Europe in the 1750’s
- Based on new agricultural innovations
- Increased food production
- Enabled sustained population increase
- Lay the groundwork for the industrial recolution
Industrial Revolution
- Developped in the UK between 1750-1850
- Evolved from technical innovations that occured in British industry
- Proved to be a major catalyst towards increased urbanizaion
- Created a huge demand for labour
- Produced a distinct spatial pattern in Europe
- Location of raw materials were factor in where people lived
Europe - Devolutionary Issues 2004

Industrial Location Theory
- Alfred Weber published in 1909
- Examined the influences that affect industrial location

Political Revolutions
- Pre-dates both the agrarian and industrial revolutions
- A general trend towards parlimentary representation and democracy
- Peace of Westphalia (1648)
- French Revolution (1789-1795)
- Impact of nationalism (which continues today)
Political Geo Key Terms
- Nation
- a large aggregate of people united by common descent, history, culture, or language, inhabiting a particular country or territory
- State
- a nation or territory considered as an organized political community under one government
- Nation-State
- a sovereign state whose citizens or subjects are relatively homogeneous in factors such as language or common descent
- Centrifugal vs. centripetal forces
Nation
a large aggregate of people united by common descent, history, culture, or language, inhabiting a particular country or territory
State
a nation or territory considered as an organized political community under one government



