Mid-medulla Flashcards
Name this and state its function.

Inferior cerebellar peduncle.
- Posture maintenance and balance.
- integrating proprioceptive sensory input with vestibular motor function.\
Name this and state its function.

Dorsal efferent(motor) nucleus of Vagus.
- Provide input afferents pulmonary, digestive and cardiovascular, affecting blood pressure and blood gas levels.
Name this and state its function.

Hypoglossal nucleus.
- Somatic efferent, innervating tongue musculature.
Name this and state its function.
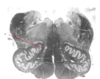
Hypoglossal nerve.
Name this and state its function.[5 marks overall].
Tract involved.
Pathway specific to function.
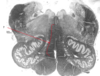
Medial lemniscus.
- Second order neurons of Dorsal-column medial lemniscus pathway(DCML), of conscious proprioception.
- Spinothalamic information:
- caudal medulla*–>*thalamus*–>*somatosensory cortex.
Name this.

Fourth ventricle.
Name this and state its function.
Nerves involved.[3 marks].

Medial longitudinal fasciculus.
- Integrating eye movement and the head.
- involves:
oculomotor, trochlear and abducens.
Name this and state its function.
Neurotransmitters involved?

Nucleus Tractus solitarius(NTS).
- Generates peristaltic activity of the gastrointestinal tract during swallowing.
- Release of inhibitory(GABA) and excitatory(Glutamate).
- controls motor pattern.
Name this and state its function.

Inferior olivary nucleus.
- Fine motor and co-ordination. project to the ICP( to Cerebellar cortex and deep cerebellar nuclei).
Name this.

Medial vestibular nuclei.
Name this.

Inferior vestibular nucleus.
Name this, state its function, divisions and pathway.

Pyramidal tract.
-
Composed of :
- Corticospinal + Cotricobulbar tracts.
- Descending tract:
- Carrying motor fibres from cortex—>spine/brainstem.
Voluntary control.
Name this and state its function within its 2 parts.

Olive.
Inferior: integrates motor and sensory function
- Relays between spine and cerebellum.
Superior: sound localisation.
- Sound localisation, and relay between cochlear nuclei and inferior colliculi.
Name and state its function in each hemisphere.

Arcuate fibres.
Left hemisphere:
- Language processing.
Right hemisphere:
- visuospatial processing.


