Microvascular complications Flashcards
What are the sites of micorvascular complications in Diabetis?
- Retinal ateries
- Nephrophathy –> damage of Glomerular arterioles
- Neuropathy –> Damage of Vasa nervorum (tiny blood vessels that supply nerves)
What are the factors that influence the development of microvascular complications?
- Severity of Hyperglycaemia
- –> the higher the sugar, the higher the risk
- Hypertenstion
- Genetic
- Hyperglycaemic memory –> good controll is important at early stage
What is the machanism microvascular complications with high glucose levels?
High glucose –> increase production of cytokines –> inflammation

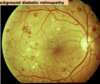
What is the most cimmonest cause of blindness in people of working age?
Diabetic retinopathy
What are the changes that can be seen in diabetic retinopathy?
Backround:
- Hard exudates (cheese colour, lipid)
- proteins leaving
- Microaneurysms (“dots”)
- sprouting of vessels
- Blot haemorrhages
Pre-proliverative
- retinal ischaemia, seen by
- •Cotton wool spots also called soft exudates (white, bright spots on retina)
Proliverative
- new vessels formed
- visible on disc or elsewhere in the eye
- may effect vision
What is maculopahty?
•Hard exudates near the macula
–> can threaten vision

What are hard exudates?
Lipid deposits in the retina
What is the management of backround diabetic retinopathy?
- improve control of blood glucose!!!
- warn patient that warning signs are present
- screening every year
What are the different stages in diabetic retinopathy?
- Backround
- Pre-prolaverative
- Prolaferative
- Maculopathy
What is the management plan for someone with pre-proliferative diabetic retinopathy?
- Pre-proliferative (cotton wool spot)
- Suggests general ischaemia
- If left alone, new vessels WILL grow
- Needs: Pan retinal photocoagulation –> laser to prevent new vessels from forming
How do you manage proliferative retinopahty in diabetic retinopathy?
- Proliferative (visible new vessels)
- Also needs:
-Pan retinal photocoagulation –> laser therapy
How do you manage maculopathy in diabetic retinopathy?
- Only have problem around macula
- Needs only a GRID of photocoagulation –> around the macula
- (NOT pan retinal photocoagulation)
What are the signs of someone with diabetic retinopathy?
- Hypertension
- Progressively increasing proteinuria
- Progressively deteriorating kidney function
- Classic histological features
What happens to someone with CKD and Diabetis?
They are at substantial risk of dying! (from macrovascular / Cardiac complications)
What are the glumerular changes in diabetic nephropathy?
- Mesangial expansion
- mesangial cells= specialised pericytes in kidney
- Basement membrane thickening !!!
- Glomerulosclerosis

How do high glucose levels and Hypertension lead to CKD?
Cytokine mediated changes –> Inflammation
What is the prevalence of CKD in Type 1 and 2 DM?
In T1: 20-30% after 30-40 years
In T2: probably the same but many people die before that from macrovascular complications
What are the clinical features of Diabetic Nephropathy
- Progessive proteinuria
- hypertension
- Renal function
How do you treat a patient with diebetic nephrophathy?
- Diabetic control!!!
- Reducing BP
- VIa: Inhibition of RAS system (ACE inhibitors) (maybe also Angiotensin 2 receptor antagonist
- Stop Smoking
What are the Vasa nervorum?
Blood vessels that supply the nerve
What different types of diabetic neuropathy are there?
- Peripheral
- most common
- Mononeuropathy
- only one nerve effected
- Mononeuritis multiplex
- areas of nerve
- Radiculopathy
- dermatomes
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Diabetic amyotrophy
- painful condition
What are the characterisitcs of peripheral neuropathy?
When does it occur?
What is the problem with it?
- Longest nerves supply feet
- More common in tall people
- Loss of sensation
- Danger is that patients will not sense an injury to the foot (eg.Stepping on a nail)
Where does peripheral neuropahty occur?
- in tall people
- with poor blood glucose controll
What are the clinical signs of peripheral neuropathy?
- Loss of ankle jerks
- loss of vibration sense (using tuning fork)
- multiple fractures on foot X-ray (Charcot’s joint) –> tender red areas, can leave permanent deformities
What is mononeuropathy?
What are the clinical features?
Loss of a single peripheral nerve leading to (depending on site o lesion)
- Usually sudden motor loss
- wrist drop, foot drop
- Cranial nerve palsy:
- –> double vision due to 3rd nerve palsy (pupil is “down and out” ) but pupils are light responsive (PNS fibres still work)
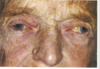
Explain the Pupil sparing third nerve palsy
- parasympathetic fibres on outside.
- Thus they do not easily lose blood supply in diabetes
(would be different in space taking lesion)
What is mononeuritis multiplex?
•A random combination of peripheral nerve lesions
–> can be very painful
What is Radiculopathy?
•Pain over spinal nerves, usually affecting a dermatome on the abdomen or chest wall.
What is Autonomic neuropathy?
•Loss of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves to GI tract, bladder, cardiovascular systemdue to diabetic neuropathy
- GI tract:
- •difficulty swallowing
- delayed gastric emptying
- constipation / nocturnal diarrhoea
- Bladder dysfunction
What are the clinical signs of autonomic neuropathy?
- Postural hypotension
- can be disabling: collapsing on standing.
- Cardiac autonomic supply
- case reports of sudden cardiac death
- Measure changes in heart rate in response to Valsalva manoevre –> increase Intra-thoracic pressure
- Normally there is a change in heart rate
- Look at ECG and compare R-R intervals


