Micro Lectures 1-4 Flashcards
primary mode of ATP gen for bac
glycolysis
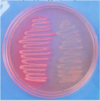
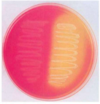
gram stain
g(+) = purple - thick cell wall
g(-) = pink - thin cell wall
method:
- crystal violet
- iodine: stab violet
- alcohol: wash out pruple: leaves the g(-) leaving it clear
- safranin: pink
peptidoglycan
repetitive horizontal NAG and NAM with verticle peptide bridge help together @ 3rd peptide
- can have pentaglycine cross bridge
- L-ala
- D-glu/D-gln
- m-DAP/lys
- D-ala
- D-ala
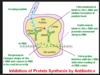
pep-gly synth
- cytoplasmic
- assembly of NAG and NAM and pentapeptide side chain
- inhib:
- fosfomycin: (-) NAM assembly
- cycloserine: (-) L-ala (~) D-ala, inhib formation of D-ala – D-ala
- “flip flop”
- bacterprenol carries across membraine
- inhib by bacitracin
- extracytoplasmic
- transpeptidation via PBP
- inhib:
- beta-lactam: inhib PBP enz (transpepsidase/carboxypeptidase): unable to linke NH2 (3rd) – C=O (4th)
- vanco: bind 4th and 5th D-ala’s together to prevent removal of 5th D-ala
otitis media
common cause of middle ear infection in peds
- strep pneumoniae
amoxicillin pen middle ear well
addn cell wall cmps of G(+)
teichoic acid
- repeating sugar-(P)
mycolic acid
- waxy lipid: stains with acid fast
- mycobacterium leprae, TB
addn cell wall cmpts of G(-)
outer membrane
- porins
- LPS (endotoxin) –> STRONGEST assoc with sepsis
periplasmic space
- site of beta-lactamases
- in G(+) and G(-) but MORE for G(-)
LPS
lipid A
- does all the toxic work: some G(-) contraindicated to tx with antibio due to this (EHEC)
- released as by-prod of bac cell dealth
core oligosacc
- branched polysacc essential for struc and viability
o-ag
- long linear polysacc
- LPS w/o this called LOS
- antigenic and highly variable
gram staining for meningitis
fast!
- lumbar puncture –> CSF
- major mening
- g(+) = s. pneumo
- g(-) = n. meninigitis
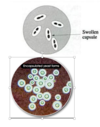
structures outside bac cell wall
- glycocalyx
- slime layer = loose = biofilm
- capsule = antiphago
- india ink
- quellung rxn
- fimbraie/pili
- sticky: pilin protein –> UTI (e.coli)
- g(-)
- conjugation
- flagella
- motility
PM
lipid structure WITHOUT choles (except mycoplasma.pneumoniae)
- bilayer
- fx sim to euk cell wall
nucleiod and plasmid
nucleoid = one circular chr
- NO histones! –> structure maint by polyamines
plasma: extrachr –> toxins/ resistance to antibio - can be txfed via conjugation

ribosomes
70s: 30 + 50
endospores
mostly G(+)
- bacillius, clostridium
what place in the body has the most bac?
colon: anaero or facul anaero = g(-)
- e.coli
- bacteriodies
bacterial interference
competitiions with normal flora and pathogens can clear foreign bac
what med gives high risk for c.dff?
clindamycin
- STRONG antio –> kills off other bac in colon
- allows c.diff to prolif
zoonotic
cap of infecting wide range of hosts
fx of virulence factors
- colonize
- invade
- evade host imm
- dmg
***aided by toxins
endotoxin fx (5)
- (+) macp –> TNF –> (+) T cells
- inflamm
- sequester iron
- (+) endothelial cells –> incr vasc permeability
- mast cells –> histamine, proinflam med
- aggregate platelets
- PMN
- hypoglycemia
*** ALL G(-)
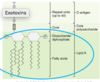
exotoxin
soluble
heat-labile
types:
- serotoxins = neurotoxins
- A/B: active/binding = MOST
- multiprotein delivery system
*** highly antigenic (specific)
usualy gets from plasmid conjugation