Melanocytic lesions Flashcards
1
Q

A
JUNCTIONAL NEVI
- Uniformly pigmented (quite flat)
- Light to dark brown in colour
- Melanocytes located in the dermoepidermal junction
2
Q
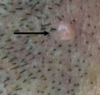
A
INTRADERMAL NEVUS
- Skin-coloured papule, often seen on the face
- Can resemble a basal cell carcinoma
- Melanocytes located in the dermis
3
Q

A
COMPOUND NEVUS
- Pigmented papule, often seen on face or body
- Melanocytes located in the dermoepidermal junction and dermis
- Can contain skin coloured areas within it (variation in pigment but uniform in size)
4
Q

A
CONGENITAL NEVI
- Onset at birth or within first year of life (95% of the time they don’t change)
- Typically larger in diameter compared to other nevi, but can be macular
- Some have a more warty or papillomatous appearance
- Stable over time
5
Q
Describe the size classifications of congenital nevi
A
- Small = <1.5cm
- Medium = 1.5-19.9cm
- Large “Giant” = >20cm
6
Q
What is the concern regarding giant congenital hairy melanocytic nevi?
A
Malignant transformation risk
7
Q
What is required for a diagnosis of congenital melanocytic nevus syndrome?
What is the genetic mutation?
A
≥1 giant congenital melanocytic nevus at birth +/- neuromelanosis
Genetic mutation: somatic mutation in NRAS
Can be associated with dysmorphic features of a prominent forehead and short nose
8
Q

A
BLUE NEVUS
- Macule or papule
- Uniform, blue colour (can have some subtle white areas, like central pallor)
- Often seen on hands, feet, face or scalp
- If seen in an older person, treat with more suspicion (activating mutations GNAQ, GNA11)
- There is a cellular variant (nodule or plaque) that has had metastatic behaviour described
9
Q

A
HALO NEVUS
- White halo around central symmetrical nevus
- Consider melanoma if multiple present
- Associated with vitiligo
- Concerning if older onset +/- asymmetrical nevus within it or mole changing rapidly
10
Q
What are the 4 stages of a halo nevus?
A
- Stage 1: nevus surrounded by a rim of hypopigmentation
- Stage 2: nevus turns pink
- Stage 3: nevus disappears, leaving depigmented area
- Stage 4: re-pigmentation over months to years
11
Q

A
SPITZ NEVUS
- Pink papule, symmetrical + lacking in pigment
- Concerning if older onset
- Epithelioid cells on histology
12
Q
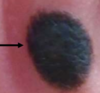
A
SPINDLE CELL NEVUS OF REED - SPITZ NEVUS VARIANT
- Deeply pigmented, flatter lesion
- Spindle cells on histology
- History to distinguish from melanoma (more inclined to excise if >12yo)
13
Q

A
MEYERSON’S NEVUS
- Patch of eczema around nevus → pink, inflamed area circumferentially
- Central nevus is symmetrical, usually solitary
- Settles with topical steroids (moderate potency)
14
Q
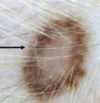
A
ECLIPSE NEVUS
- Pigmented rim surrounding uniformly lighter centre
- Typically occurs on scalp
15
Q
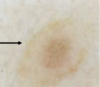
A
EN COCARDE NEVUS
- Bull’s eye appearance (pigmented symmetrical rim with intervening lighter area and pigmented centre)
- Often co-occurs with eclipse nevi





