Mega Deck Flashcards
State two conditions for any object to be in equilibrium
Resultant force zero
Resultant moment about any point zero
State three vector quantities
Any 3 of the following:
Velocity
Acceleration
Force
Displacement
Weight
Momentum
State three scalar quantities
Any 3 of the following:
Speed
Distance
Mass
Energy
Power
Temperature
How can force vectors be arranged to show that an object has constant velocity?
- Vectors make a closed shape when rearranged (by scale drawing)
- Or resolve into components and show
- Total up forces = Total Down forces
- Total left forces = Total right forces
What is the difference between a vector quantity and a scalar quantity?
Vector has a direction
Scalar does not
What is meant by centre of mass?
The point in a body where the weight of the object appears to act
Also the resultant moment about this point = 0
Define the moment of a force
Product of the force and the perpendicular distance from the line of action of the force to the point

Resolve F into its vertical and horizontal components…

FH = FcosØ
Fv = FsinØ

What mistake has been made in rearranging the vectors for a scale drawing?

6N vector has been translated (moved) but also rotated
Should be:

What are the steps in working out the resultant force using a tip-tail scale drawing?

- Set a scale
- Draw the horizontal or vertical vector first (if there is one)
- Move each vector in turn to the end of the previous one (DO NOT ROTATE THE VECTORS)
- Resultant vector goes from the very start to the very end

How is the balancing force different from the resultant force?
The balancing force brings the object into equilibrium so makes the resultant force = 0
For a scale drawing, it is the vector that closes the shape

If vectors are parallel they can be resolved by…

Adding or subtracting the values

If vectors are perpendicular they can be resolved by…

Making a right angled triangle and using trigonometry and pythagoras

What is wrong with this?

Vectors of different types can’t be combined
(Here, force and velocity cannot be combined)

How do you solve this if the object is in equilibrium?
(3 vectors with 2 unknown sizes)

- The vectors must form a closed shape
- Start as you would with a scale drawing
- But draw the third vector meeting for where it connects to the start of the first
- Draws vectors as dotted lines
(x=2.54N, y=3.89N)

The box is in equilibrium with no external forces applied
Label the forces acting on the box

Notice the angle between weight and perpendicular is also Ø

How do you calculate the resultant moment? (2 ways)

- Multiply perpendicular component of force by distance
- Multiply perpendicular component of distance by force
(First method is shown)

What’s wrong with this?

Weight must form the hypotenuse of the triangle

What is a couple?
A pair of equal and opposite coplanar forces which do not act along the same line of action

What does it mean if an object is uniform?
It has an constant density so its centre of mass acts from the physical centre point of the object
(Weight vector starts from middle of object)

When should you use moments?
Any situation that has two unknown forces acting on an object
Take moments about one of the unknown forces to find the other
Then use total up force = total down force to find the other

State the principle of moments
Sum of the clockwise moments about a point is equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments for a system in equilibrium
What is displacement and how is it different to distance?
Displacement is a measure of the line connecting the starting point to the finishing point.
Distance is a measure of the total length of the path travelled.
Also distance is a scalar and displacement is a vector.

What does a straight line on a distance-time graph represent?
A constant speed.

How is acceleration defined?
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.

How is speed different to velocity?
Speed is the rate of change of distance.
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement.

Describe the motion of this ball

Ball is moving to the right and speeding up.

Decribe the motion of this ball.
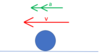
Ball is moving to the left and speeding up.

Describe the motion of this ball.

Ball is moving to the right and slowing down.

Describe the motion of this ball.

Ball is moving to the left but slowing down.

Is the ball moving to the right?

Only if the velocity vector is also acting to the right.

What does a straight line on a displacement-time graph represent?

A constant velocity.
What does a curve with an increasing gradient represent on a displacement-time graph?

An increasing velocity (acceleration)
What does a curve with a decreasing gradient represent on a displacement-time graph?

A decreasing velocity (decceleration)
What does a negative gradient on a displacement-time graph represent?

A negative velocity (travelling back to where it started)
What does a straight line on a velocity-time graph represent?

A constant acceleration.
What does a curve with an increasing gradient represent on a velocity-time graph?

An increasing acceleration.
What does a curve with a decreasing gradient represent on a velocity-time graph?

A decreasing acceleration.
What does a negative gradient on a velocity-time graph represent?

A negative acceleration.
What does this graph show?

A ball bouncing off a surface
(Dotted lines represent the bounce)
(Red lines represent the ball accelerating towards the ground)
What does the acceleration time graph of a ball in freefall look like?
Constant acceleration of 9.81ms-2

What’s wrong with this?

Displacement takes direction into account.
It should be…

Why can’t you use SUVAT’s when working with this graph?

Because the acceleration (gradient) is changing
What does it mean if an object is in freefall?
Only weight is acting on the object
It has a constant acceleration of 9.81ms-2 acting downawards (on Earth)

If one ball is dropped as another is projected horizontally which hits the ground first?
They both hit the ground at the same time…
Both in freefall so accelerate at 9.81ms-2
Vertical motion independent of horizontal motion

What’s wrong with this labelling?

Initial velocity and final velocity are not 0

In projectile motion when is the vertical component of the velocity 0?
At the peak of a parabola

Not at the start or end
How do you start a question involving angled projectile motion?

Resolve the velocity into vertical and horizontal components and fill out the corresponding SUVATs

What is wrong here?

The acceleration is only 9.81ms-2 if the object is in freefall

What does the area of a speed-time graph represent?
How about a velocity-time graph?

When can you use this equation?

When the acceleration = 0 (constant velocity)
Or to work out an average speed
When can you use SUVATs?

When acceleration is constant
Or if object has stages of constant acceleration
What is the term given to an object rotating at a steady rate?
Uniform circular motion
If an ball on a string is travelling in a circle in the vertical plane, where are the points of minimum and maximum tension?
Minimum tension at the top
Maximum tension at the bottom

Why do planes turn when at an angle?

The lift force is comprised of a horizontal and vertical component.
The horizontal component provides the centripetal force causing it to turn.

Define centripetal force
The resultant force that makes the object move in a circle
What kind of motion will a pendulum perform?
Simple harmonic motion
What is the period of oscillation?
The time for one complete cycle of oscillation.
If the graph of displacement is sin(x), what will the respective graphs of velocity and acceleration look like?
Velocity as cos(x)
Acceleration as -sin(x)
Describe a freely oscillating object
It oscillates with a constant amplitude because there is no friction acting on it.
(Its energy is constant)
What is natural frequency?
The frequency of free oscillations of an oscillating system.
What are forced vibrations?
Making an object oscillate at a frequency that is not it’s natural frequency
When does resonance occur?
When the frequency of driving force or oscillation matches the natural frequency of the system.
What is the outcome of resonance?
An increase in amplitude of the system’s oscillation.
What is damping?
The term used to describe the removal of energy from an oscillating system.
Describe heavy damping (over damping)
System not allowed to oscillate.
Slowly returns to equilibrium.

Describe critical damping
The oscillating system returns to the zero position of the oscillation after one quarter of a time period.

How do you convert degrees -> radians

How do you convert radians -> degrees

Define angular displacement
The angle through which an object in circular motion travels in a given time

What are the three levels of damping?
Light
Heavy
Critical
Describe light damping of a system
The system oscillates over a long time frame before coming to rest.
The amplitude of the oscillations exponentially decay.
What is the equation for linear velocity?
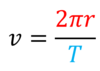
In circular motion which direction do the acceleration and centripetal force vectors act?
Always towards the centre

What is the condition for circular motion to happen?
A velocity needs to be acting perpendicular to a resultant force

What is Fcentri for an object at the top of the vertical circle?

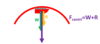
What is Fcentri for an object on top of a vertical circle?


What is Fcentri for an object at the bottom of a vertical circle?


How do you find out the minimum velocity for an object travelling in a vertical circle?

Set R=0 (or tension if ball on string)
And rearrange for v

How do you find out the maximum velocity for an object travelling over a vertical circle? (eg car over a hill)

Set reaction R=0
Then rearrange for v

When solving angled circular motion problems what are the 3 usual steps?
- Set vertical component of force = weight
- Work out horizontal component using trig
- Fcentri = horizontal component

Why can’t a ball be swung around in a circle with the string horizontal?

There must be a vertical component of the tension to match the weight
Otherwise ball is not in vertical equilibrium

What are the two conditions for SHM?
- Acceleration must be proportional to displacement
- Acceleration must be opposite to displacement

How does the time period differ for the two pendulums?

Time period is independent of amplitude

Label up the maximum and minimum velocities and accelerations on the simple pendulum…

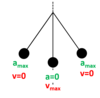
Label up the maximum and minimum velocities and accelerations on the mass spring system…


Label up the maximum and minimum potential and kinetic energies on the simple pendulum…


What are the kinetic energy, potential energy and total energy lines for one cycle of SHM?


How do you calculate KEmax or PEmax or ET in SHM?

What two factors affect the time period of a mass spring system in SHM?
- Mass on the end of the spring
- Spring constant (stiffness) of spring

What two factors affect the time period of a simple pendulum in SHM?
- Length between top of string and centre of bob
- Gravitational field strength

What does the graph of energy against displacement look like in SHM?

How do you deal with rpm? (revolutions per minute)
÷60 to convert to rps (revolutions per second)
Then set rps = frequency
When an SHM system is lightly damped what happens to its amplitude and time period?
Amplitude decreases (as it loses energy)
But time period remains constant

How is natural frequency determined for a mass spring system?

How is natural frequency determined for a simple pendulum?

Define frequency
The number of complete oscillations per second
Why is an object in circular motion accelerating?
Its linear velocity does not change in magnitude
But is constantly changing in direction
The graph below shows driven oscillations with varying frequencies.
Add two lines if the system is:
- Undamped (free oscillations)
- Over damped


For Barton’s pendulum which two balls oscillate?

P and Y because they have the same length
So natural frequency of y matches frequency of driving force from P

What happens if…
Fcentri > Fmax
Circular motion does not happen
(Eg car skids off the road or moves to a higher radius)
What happens if…
Fcentri max ≤ Fmax
Circular motion happens
(eg friction is large enough to keep car on track)
Define amplitude.
The maximum displacement of an obejct/particle/point from equilibrium position
When do you use?
x=Acos(wt)
When do you use?
x=Asin(wt)
x=Acos(wt) -> displacement in SHM when x=A when t=0
x=Asin(wt) -> displacement in SHM when x=0 when t=0
Does circular motion count as SHM?
When projected onto a flat surface, yes it does
What happens if the frequency of driving force is less than the natural frequency of a system?
f0
Low amplitude oscillations
With 0 phase difference.
What happens if the frequency of driving force matches the natural frequency of a system?
f=f0
Resonance occurs
Large amplitude oscillations
π/2 radians out of phase
What happens if the frequency of driving force is more than the natural frequency of a system?
f>f0
Low amplitude oscillations
With phase difference of π
What is Newton’s 1st Law of Motion?
If no resultant force acts on a body, then it will either remain at rest, or continue moving with constant velocity (no acceleration)

What is Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion?
The rate of change of momentum (acceleration) of a body is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on it
Fres ∝ a
What is Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion?
When two objects interact, they exert an equal and opposite force on each other and the forces are of the same type

If the forces acting on an object are balanced what can you say about its motion?
There is no resultant force so it will continue moving at a constant velocity. It won’t accelerate.
What’s wrong with this?

In F=ma, F must be the resultant force!!!

How does an object reach terminal velocity?
As it speeds up, air resistance increases, decreasing the resultant force.
Eventually air resistance = driving force, Fres=0 so a=0.
What two things are the case for tension?
- Tension always acts away from the contact points
- Tension is constant throughout the rope/wire/ cable

Why are objects never truly in freefall?
There will always be air resistance opposing the weight
(Apart from when v=0)

What is the condition for terminal velocity?
The drag force = driving force (or weight) so Fres=0 and so a=0

What factors the drag force on an object?
- Fluid density
- Shape of object
- Cross sectional area of object
- Velocity of object
Why does air resistance increase with velocity?
The object is colliding with more air molecules per second
What does the velocity time graph of an object reaching terminal velocity look like?

What’s wrong with this?

The acceleration is not constant so you cannot use SUVATs
Instead use area under graph
How is momentum calculated?

What’s wrong with this?

Direction must be taken into account (as momentum is a vector)

What two things is impulse equal to?
- Rate of change of momentum
- Impact force x impact time

What are the units of impulse and momentum?

What does the area under a force-time graph represent?

The change of momentum or impulse
What is the conservation of momentum?
For a system of interacting objects, the total momentum remains constant…
…provided no external resultant force acts
In any interaction, what is conserved?
Total momentum is always conserved
Total energy is always conserved
Kinetic energy is only conserved if collision is elastic
What is an elastic collision?
A collision where kinetic energy is conserved
(as well as momentum)
What is wrong here?

You have to calculate kinetic energies separately for each object

In physics terms what is an explosion?
The total momentum = 0

How do you answer flow rate questions? (momentum of a flowing liquid)
Consider the cylinder made by a liquid’s flow after 1 second
Where the length of the cylinder = velocity of the fluid
And use density equation to get volume of cylinder

How do you work out the area of a curved graph?
- Split into boxes
- Count the boxes (pairing up incomplete boxes)
- Multiply number of boxes by area of each box

What is the principle of conservation of energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred from one type to another.
How does an object gain energy from a force?
When the force does work on the object (same direction as movement)

How does an object lose energy?
By doing work against a force (usually frictional)

What’s wrong here?

In W=Fs you multiply the parallel components

When using W=Fs what must be the case?
The components must be parallel

What is the work done by the weight of this block?

0 because the weight is perpendicular to the movement
So there is no parallel component to displacement
If two objects are dropped from the same height and air resistance is negligible, which hits the ground first?
Both hit at the same time because they both accelerate at 9.81ms-2
How do you calculate the velocity the object hits the ground using GPE and KE (assuming no air resistance)

Energy equivalency (only works when air resistance = 0)

What is power?
The rate of transfer of energy
or
The rate at which work is done
(Measured in Watts [W])

What is wrong here?

For P=Fv, F is not the resultant force

How do you calculate efficiency?

If the system is not 100% efficient would this be correct?

No, because some GPE is converted to thermal and kinetic energy of the snow (working against friction)

What is 1 mole?
A collection of 6.02×1023 molecules
(Avogadro’s constant)
What is the molar mass of a substance?
The mass of each mole (every 6.02×1023 molecules)
Eg for He each mole has a mass of 4g
How do you calculate the molar mass of a compound eg NO2
Add up the nucleon numbers
(14+16+16=46gmol-1)
How do you calculate the number of molecules in a substance?
N = n × NA
(Number of molecules = moles × Avogadro’s constant)
What is the molecular mass and how is it calculated?
The mass of each molecule of the substance
m = M/N
(molecular mass = total mass / number of molecules)
How is the total mass of a substance calculated?
M = n × mr
(Total mass = moles × molar mass)
How do you convert a temperature from °C to K?
T(K) = T(°C) + 273
Define absolute zero
The point at which an ideal gas exerts no pressure
(0K, -273°C, molecules have no kinetic energy)

What is Boyle’s Law?
The pressure in a gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies
at a fixed temperature
and a fixed mass of gas
(P ∝ 1/V)
What does the P-V graph look like for an ideal gas?

How do you prove Boyle’s law graphically?
Plot a graph of P against 1/V
Should be a straight line passing through the origin

What is Charles’ Law?
Volume a gas occupies is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas
at a fixed pressure
and a fixed mass of gas
(V ∝ T)
How do you prove Charles’ law by graph?
Plot a graph of V against T
Should be a straight line passing through the origin

For an ideal gas, what does a graph of V against T(°C) look like?
Note: x-intercept represents absolute zero

What is the Pressure law?
The pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas
at a fixed volume
and a fixed mass of gas
How do you prove the pressure law graphically?
Plot a graph of P against T
Should be a straight line passing through the origin

For an ideal gas, what does a graph of P against T(°C) look like?
Note: x-intercept is absolute zero

What is the ideal gas relationship?

When can you use the ideal gas relationship?

If the mass of the gas is constant
How do you calculate the work done compressing or expanding a gas?
Calculate the area under the curve

What is the general equation for pressure?
P = F / A
(Pressure = Force / Area)
How does a gas exert a pressure on a container?
- The gas molecules collide with the container walls changing their momentum.
- This creates a force on the molecule and the wall
- Exerting a pressure

What are the 5 conditions for an ideal gas?
- Volume of the molecules must be much smaller than the volume of the gas itself
- The intermolecular forces are negligible
- The collision time of molecules with each other and the walls is much less than the time between them
- The collisions are elastic (no loss in KE)
- The molecules’ motion is random
How does Brownian motion explain the random motion of smoke?
- Air molecules are moving randomly
- They collide with the smoke changing momentum and exerting a force on the smoke particles
- If at one moment there are more collisions on one side than the other
- The smoke particle has a resultant force so accelerates in that direction

Explain Boyle’s Law using the molecular Kinetic Theory
- When volume of container is decreased
- More collisions per second
- So total momentum change bigger (▲p)
- So force exerted bigger
- So pressure bigger (From P = F/A)
Explain Charles’ Law using the molecular kinetic theory
- When temperature is increased
- Volume increases to increase the distance travelled between collisions
- Molecules have greater kinetic energy but travel further so frequency stays same
- Change in momentum (▲p) stays constant
- So pressure is constant (P = F/A)
Explain the Pressure law using the molecular kinetic theory
- As temperature increases
- The average kinetic energy of the molecules increases
- Increasing the number of collisions per second with container walls
- So greater change in momentum
- Greater force and pressure exerted (P = F/A)
How would you use this equation to work out the density of a gas?


How do you calculate crms from a list of speeds?
- Square the speeds and add up
- Take a mean of the squares
- Square root the value
How is cms calculated?
cms = (crms)2
What are the units of cms?
[m2s-2]
What does the maxwell-boltzmann distribution tell us about gases?

Molecules have a range of kinetic energies.
So temperature of the gas is a measure of the average kinetic energy.

For these equations how do you calculate the internal energy of the gas?

Multiply each by the number of molecules of the gas.

How do two objects brought into contact reach thermal equilibrium?

- There is a net flow of thermal energy from the hotter object to the colder object
- Until both objects are at the same temperature
- And there is now no net flow of thermal energy

Define specific heat capacity
The energy required to increase 1kg of a substance by 1K [Jkg-1K-1]
When would you use this equation?

To calculate the mass flowing per kg of a fluid

Why does the temperature of a substance changing state not increase?

The thermal energy is used to break some of the intermolecular bonds (solid → liquid) or the rest of the intermolecular bonds (liquid → gas)

Define specific latent heat of fusion
The energy required to change the state of 1kg of a solid to a liquid at its melting point.
Define specific latent heat of vaporization
The energy required to change the state of 1kg of a liquid to a gas at its boiling point.
What is wrong with this?

Haven’t considered the change of states. Need to break it into 3 equations:

How is density defined?
The mass per unit volume. [kgm-3]

How do you convert 2,3,4 etc… units to SI units?
(eg 5cm3 to m3)
Whatever you do to the unit, you do the same to the prefix
(eg 5cm3 = 5x(10-2)3m3 = 5x10-6m3)
How do you measure the density of an irregular solid?
- Read off the volume from the beaker or measuring cylinder without and with the object submerged in water
- The difference in volumes is the volume of the solid
- Measure the mass using a balance
Calculate density using ρ=M/V

How do you calculate the average density of an alloy?
(Eg 200cm3 5kg rod of 60% copper (8960kgm-3) and 40% aluminum (2700kgm-3) by volume?)
- Work out the mass of each and the volume of each
- Add together to get the total mass and volume
- Then do the density calculation

Define Hooke’s Law
When a material is stretched, its extension is proportional to the force applied, up until the limit of proportionality
F=kx
Define the limit of proportionality
The point at which the material stops obeying Hooke’s law.
The graph is no longer a straight line.

Define the elastic limit
The point at which when stretched further the material no longer returns to its original length (there is a permanent extension)

What do the gradient and area of a force extension graph tell you for a spring.
Gradient → The spring constant (must be taken before limit of proportionality)
Area under line → The strain energy stored loading the spring or energy released unloading the spring

What equation calculates energy stored when a material is stretched?
E=½Fx
What is the difference between the elastic limit and the limit of proportionality?
Limit of proportionality is the point at which a stretched spring (or wire) stops obeying Hooke’s law.
The elastic limit is the point at which it doesn’t return to its original length when unloaded.

Will this spring return to its original length if it has been stretched to 35mm?

Yes, because it has not passed the elastic limit

What is a ductile material?
A material with a large plastic region.

What is a brittle material?
A material with a small plastic region.

What is the fracture point of a material?
The point at which a material breaks
How do you know the rubber hasn’t stretched passed its elastic limit?

It still returns to its original length when unloaded.

What is the formula for Young’s Modulus that you need to remember?

What does the gradient and area under a stress-strain graph give?

Gradient → Young’s modulus (before the limit of proportionality)
Area → strain energy per unit volume

If this box is in equilibrium how would you go about calculating the frictional force and the reaction force?


Define current (I)
The rate of flow of charge

How do you work out the number of electrons carrying a charge (eg 10C)?
Divide charge by the charge of each electron (6.25x1019)

What is the difference between conventional current and electron flow?
Conventional current flows from the +ve terminal to the -ve terminal
Electron flow shows the direction the electrons flow, from -ve to +ve

How is the current in a circuit related to potential difference and resistance?

Increasing potential difference increases the current
Increasing resistance decreases the current

What is Ohm’s law?
The current flowing through a metallic conductor is proportional to the potential difference applied across it at constant temperature

When does Ohm’s law apply?
When the component has a fixed resistance (eg a fixed resistor at a constant temperature, or a filament at a low current)

Define potential difference
The work done (energy transferred) by each coulomb of charge moving between two points
(Eg a 12V battery adds 12J of energy to each coulomb of charge passing through)

How does a circuit ‘short circuit’?
If there is an available path with 0 resistance
Current → ∞
And the circuit heats up
What is the I-V graph for a fixed resistor?


What is the I-V graph for a filament bulb?


What is the graph for a semiconductor diode?


What’s wrong with this?

Resistance is not calculated using the gradient (of a tangent) of an I-V graph!!!
Instead just use the voltage and current at that point

Explain the shape of the I-V graph for a filament

As current increases, temperature of filament increases
This increases lattice ion vibrations.
Which increases the number of collisions per second with electrons.
So resistance increases.

How does the I-V graph for a fixed resistor prove it is ohmic?

The straight line passing through the origin
proves that current ∝ voltage
Explain the shape of the semiconductor diode (in positive bias)

- As the potential difference increases weakly bound electrons in the conductor gain energy
- After the threshold pd, some electrons become free to carry a current
- The lattice vibrations still increase but this is less significant
What happens if a semiconductor diode is connected in reverse bias?

No current flows until the breakdown voltage is reached (~50V)
The diode breaks and all current flows through

What is the difference between a series and a parallel circuit?
Parallel circuits have junctions (3 or more wires connect)

Why doesn’t adding voltmeters in parallel affect the circuit? (it is still series)

Voltmeters have ~ ∞ R so no current flows through
What are the p.d and current rules for a series circuit?
P.D is shared across the components (by resistance)
Current is constant throughout
What are the p.d and current rules for a series circuit?
P.D is shared across the components (by resistance)
Current is constant throughout

What are the p.d and current rules for a parallel circuit?
P.D is same for parallel branches
Current separates at junctions (according to branch resistance)

What is Kirchoff’s 1st Law?
At any junction in a circuit the sum of the current flowing into the junction is equal to the sum of the current flowing away from it.

What is Kirchoff’s 2nd Law?
In any complete “loop” of a circuit the sum of p.d’s equals the source p.d.

How do you combine series resistors in the same branch? (no junction between them)

Add up their resistances

How do you combine resistors in parallel branches? (one junction between them)

Use the following equation…

What is the advantage of placing resistors in parallel arrangements?
The total resistance is always less than the smallest resistance

Will the current split equally?

No, because the resistance of each branch is different

Will each component receive the same voltage?

No, because the resistance of the components are different

Why would you place batteries in parallel?

- The power delivered is the same
- But they take longer to run flatter
What is a potential divider circuit?
A circuit with 2 or more resistors connected in series with a power supply. (usually one is a thermistor or LDR)

How does resistance change for an NTC Thermistor?

As temperature increases, resistance decreases

How does resistance change for a Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)?

As light intensity increases, resistance decreases

What is the advantage of setting up a rheostat as a variable resistor?

- Simpler circuit
- Current constant throughout
- But cannot get 0V across bulb
What is the advantage of setting up a rheostat as a potential divider?

- Bulb can receive full range of voltage 0V → Vsource
- Current through bulb can be reduced to 0A
- But maximum current is lower
How does changing the dimensions of a piece of metal affect its resistance?

- Increased length → increased resistance
- Increases cross sectional area → decreased resistance
- Increased resistivity (using different material) → increased resistance

How do you calculate the cross sectional area of a wire?
Assume it to be a cylinder (unless told otherwise)

A=∏r2
Why do metals with a greater cross sectional area have a lower resistance?

There are more paths for the electrons to propagate

How do you calculate the potential difference across branches?

- Work out the P.D of each component
- Make a loop connecting the branches
- Subtract the PDs of one branch from the other

What is a superconductor?
A material with 0 resistance at and below the critical temperature

Why does a material become superconducting at and below its critical temperature?
- The lattice ion vibrations reduce to 0
- So electrons can pass through without collision

What is the advantage of superconductors and name a use?
- Transmit large currents with 0 resistance
- So negligible thermal energy losses
- Used to create high power magnets → MRI machines
- High processing power circuits → Supercomputers

Define emf of a power source
The potential difference across the terminals when no current is flowing through

Define terminal potential difference of a circuit
The potential difference across the terminals when a current is flowing through

What is the lost voltage in a circuit?
The potential difference used up pushing a current through the battery (vlost = emf - TPD)

How should you work with a circuit involving internal resistance?
Treat the internal resistance as another resistor in series with the components
Then solve as a regular circuit (using ohm’s law, kirchoff’s laws, P=IV etc)

What is the photoelectric effect?
Light incident on a metal surface causes electrons to be emitted from the surface

Why are electrons emitted from this surface by shining green and blue light on it? (not red)

Blue and green light are above the threshold frequency of this metal
So the photons of light have an energy > work function (φ)

Why are no electrons emitted when red light shines on this metal?

The red light photons are below the threshold frequency
So the energy of each photon < work function (φ)

Why does making the red light brighter not cause electrons to be emitted? (Photoelectric effect)

Electrons in the metal interact with photons in a 1-1 interaction
They only absorb photons which have an energy > work function (φ)

- Why do both light source cause electrons to be emitted? (from the surface)
- What is different about the electrons emitted due to the blue light?

- Both light sources have frequency above the threshold frequency (f0) of the metal
- The electrons emitted due to the blue light have a greater maximum kinetic energy (because blue photons have a greater energy from E=hf)

What does threshold frequency (f0) of a metal mean?
The minimum frequency of the incident light needed to cause electrons to be emitted from the surface

- What can you say about the green light incident on this metal?
- What difference does the brighter lamp make?

- The green light is above the threshold frequency so the photelectric effect happens
- The brighter lamp causes more photons of light to collide with electrons so more photons are emitted per second (But the electrons have the same maximum kinetic energy)

You are shining a light (above f0) on a metal. How do you:
- Increase the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons?
- Increase the number of emitted electrons per second?
- Increase the frequency of the light source
- Increase the brightness of the light source

This is a graph for the photelectric effect. What information do the 3 features of the graph provide?
- Y-intercept
- X-intercept
- Gradient

- Y-intercept = - work function
- X-intercept = threshold frequency
- Plancks’ Constant

This is the photoelectric effect graph for a metal
Plot a line on this graph for a metal with a higher threshold frequency

- Y-intercept (φ) decreases
- X-intercept (f0) increases
- But the gradient (h) is constant

If you shine a really bright light on a metal but the light is below the threshold frequency why will electrons never be emitted?

Electrons interact with the photons in a 1-1 interaction
But only if the photon has an energy > work function
No red light photons have an energy > work function
So electron emission will never occur

What is the definition of the work function (φ) of a metal?
The minimum energy required to liberate an electron from the surface of a metal

How is the work function (φ) related to the threshold frequency (f0) of a metal?

When light (above f0) is incident on a metal surface how is the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons calculated?

Difference between the energy of each photon and the work function (φ)

For the gold leaf experiment (to show the photoelectric effect):
- How do you make the gold leaf rise?
- Why does the gold leaf fall?
- A charged rod transfers additional electrons to the plate causing repulsion between the stem and gold leaf
- Electrons are liberated from the metal surface (by light above f0) so the stem and leaf become neutrally charged again

Define the electron volt
The kinetic energy gained by 1 electron passing through a potential difference of 1 volt

How do you convert between electron volts and Joules?
eV → J : multiply by 1.6x10-19J
J → divide by 1.6x10-19J

How is the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons (emitted during the photoelectric effect) measured?
- Connect the system to a circuit
- Place a battery opposing the current produced by the emitted electrons
- Measure the stopping potential when the total current = 0
- Ekmax = eVs

During the Photoelectric effect why are electrons with a range of kinetic energies emitted?
Electrons deeper down require more energy to rise to the surface before being liberated
(Electrons at the very top of the surface are emitted with maximum kinetic energy)

What are the 3 types of line spectra and how are they produced?
- Continuous - Produced by blackbody
- Emission - Produced by an excited gas
- Absorption - Produced by a continuous spectrum passing through a cold gas

What are the key ideas of the Bohr model of the atom?
- Electrons can only travel in allowed orbitals (energy levels)
- Electrons can emit or absorb energies to instantaneously transition between orbitals
- Electrons cannot exist between orbitals

How could an electron excite from the n=2 → n=4 energy level?

It must absorb an energy = the difference between levels (By photon or electron collision)

How could an electron de-excite from n=3 → n=1 energy level?

It must emit an photon of energy = the difference between levels

How is the energy of a photon calculated?


Why do different gases (made of different elements) have different emission spectra?

- Each element has a different set of orbitals (with different energy levels)
- So each element has a different set of electron de-excitation energies
- The different de-excitation energies produce photons with different frequencies (E=hf)

How would you show the 488nm hydrogen emission line corresponds to a de-excitation from n=4 → n=2?

- Calculate then energy difference between the energy levels
- Convert energy difference to Joules
- Convert to f or λ (E=hf or E=hc/λ)

What is the ionisation energy of an atom?
The energy required for an electron to to become liberated from an atom

Equal to the energy of the ground state
What is wrong with this?

Never use work function when talking about energy levels. Ionisation and work function are different.

How is excitation by photon different from excitation by an electron?

- Photon energy = Difference between energy levels
- Electron energy ≥ Difference between energy levels

How many photons (of different wavelengths) can be emitted from this hydrogen atom?

6 possible transition so 6 different photons

Why is this mercury vapor in the fluorescent tubes kept at low pressure?

So a large enough current (of incident electrons) can be sustained

How does fluorescence work in a tube light?

- Mercury atoms excite by absorbing electrons from the current
- When the Mercury atoms de-excite they emit UV photons
- UV photons are absorbed by and excite the phosphor coating
- When the phosphor coating de-excites it emits visible light

When do particles exhibit properties of waves? (refraction, diffraction and polarisation)
When their Debroglie Wavelength is similar to the size of the gap they are passing through

What does this experiment show?

Wave-Particle duality
Electron diffraction through graphite to form maximas (bright rings) and minimas (dark rings)

How is the Debroglie wavelength λdb of a particle calculated?

Which part of the atom has the largest specific charge and why?
The electron
(It has the same magnitude of charge as the proton but a much smaller mass)

Why do the proton, neutron and electron deflect differently in a magnetic field?

Neutron → 0 specific charge so zero deflection
Electron → Greatest specific charge so greatest deflection
Proton → Smaller deflection in opposite direction as specific charge smaller and opposite

How do you calculate the specific charge of a nucleus?
Divide the total charge of the protons by the total mass of nucleus
(Protons + Neutrons)

How do you calculate the specific charge of an ion?
Charge of the ion (Protons - Electrons) divided by total mass of ion

What is an isotope?
An atom with the
- same number of protons
- Different number of neutrons

When will an isotope undergo radioactive decay?
If the nucleus has:
- too many or too few protons
- Too many nucleons
- Too much vibrational energy

What happens in alpha (α) decay?
A nucleus ejects a helium nucleus (2 protons and 2 neutrons)
Decreasing its nucleon number by 4
And its proton number by 2

What happens in Beta Minus (β-) Decay?
A neutron turns into a proton
Ejecting a fast moving electron (β-) and an anti-electron neutrino

What happens in Beta Plus (β+) Decay?
A proton turns into a neutron
Ejecting a fast moving positron (β+) and an electron neutrino

What is wrong about this Beta Decay equation?

The nucleon number must not change

Why do the α, β-, β+ and γ deflect differently in a magnetic field?
α and β+ → Deflect in same direction but β+ larger (greater specific charge)
β- → Equal and opposite deflection to β+ (Equal and opposite specific charge)
γ → No deflection (no specific charge)

What is an antiparticle?
A particle with the:
- Same mass
- But equal and opposite charge

What happens during Annihilation?
A particle collides and annihilates with its correspond antiparticle
And their mass energy (E=mc2) is converted to radiation energy
Producing at least 2 gamma photons

Why do at least 2 photons need to be created during annihilation?

To conserve momentum
Before annihilation ptotal = 0
AFter annihilation ptotal = 0 (can’t be achieved with one photon)

What happens during pair production?
A gamma photon (with energy ≥ 2 × mass energy)
spontaneously creates a particle, anti-particle pair

What condition must pair production meet?
The energy of the gamma photon ≥ Mass energy of the particle anti-particle pair
(Any excess energy is used a kinetic energy for the particles produced)
How was the anti-electron neutrino discovered?
During Beta decay the emitted β- had less energy than expected so another particle carried the rest of the energy

What are the four fundamental forces and their approximate ranges?
- Strong
- Weak
- Electromagnetic
- Gravitational

What does the strong force do?
What is the exchange particle of the strong force?
Holds nucleons together in the nucleus
- By opposing the electromagnetic repulsion of the protons
- By attracting nucleons at small distances but repelling the, at very small distances
Gluons (between quarks), or pions (between hadrons)

Describe the nature of the strong force
Very repulsive over short distance (0-0.5fm)
Attractive over larger distances (0.5fm < d < 3fm)
Negligible beyond 3fm

What does the electromagnetic force act between and what is its exchange particle?
Acts between all particles with charge

Exchange particle is the photon
What does the gravitational force act between?
Particles or objects with mass

What particles does the weak force act on and what does it do?
Acts between leptons and hadrons and causes the decay of hadrons (by changing quark structure)

What are fundamental particles that make up the standard model? (that you need to know)
NOTE: Each of the leptons and and quarks has an corresponding anti-lepton and anti-quark

What is the quark structure of a proton?
Up, Up, Down

What is the quark structure of a neutron?
Up, down, down

How is a muon different from an electron?
Both are leptons, muon is much heavier than the electron, produced in cosmic ray showers

What are hadrons?
Particles that are made up of quarks

How are baryons and mesons different?
Both are hadrons (made up of quarks)
But Baryons are made up of 3 quarks
And Mesons are made up of 1 quark 1 anti-quark

What are the similarities and differences between W bosons and photons?
Both are exchange particles
But W bosons mediate the weak force, Photons mediate electromagnetic
W bosons carry charge of +1 or -1, Photons have no charge
W bosons have mass, Photons are massless
What are the similarities and differences between gluons and pions?
Both mediate the strong force
But gluons act between quarks, Pions act between hadrons (to keep the nucleus together)
Gluons have no mass, Pions have mass

What does the Higgs Boson do?
It creates the Higgs field
Which gives mass to particles

What quantities are always conserved in every interaction?
- Total momentum
- Total energy
- Charge
- Baryon
- Lepton number
NOTE 1: Kinetic energy is conserved in elastic collisions
NOTE 2: Strangeness is conserved in all interactions apart from weak
What must you know about k-mesons? (kaons)
They are made of 1 quark and 1 anti-quark (mesons)

They have non-zero strangeness
Produced by strong interactions, Decay (into pions) by weak interactions
What must you know about π-mesons? (pions)
They are made up of 1 quark and 1 anti-quark (mesons)

They have strangeness = 0
What is the most stable lepton and what is the most stable hadron?
(That other isolated particle will eventually decay into)
The electron and the proton
What are polar satellites used for?

- Communication for high latitude regions (close to the poles)
- Espionage (spying)
- Meteorology (weather)

What is the formula for a muon decaying into an electron?

What is the feynman diagram for an electron-electron collision?

What is the feynman diagram for β- Decay?

What is the feynman diagram for β+ Decay?

What is the quark feynman diagram for β- Decay?

What is the quark feynman diagram for β+ Decay?

Identify the unknown particles in this feynman diagram for electron capture


Identify the unknown particle in this feynman diagram for the electron proton collision


Identify the unknown quark in the feynman diagram for electron capture


Identify the unknown exchange particle in the quark feynman diagram of electron proton collision


Which particles have a baryon number = +1?
Which have a B = -1?
Which have a B = 0
Baryons = +1
Anti-Baryons = -1
All other particles (including mesons) = 0

Which particles have a Lepton number = +1?
Which have a L = -1?
Which have a L = 0
Leptons = +1
Anti-Leptons = -1
All other particles = 0

What is the muon lepton number of an electron?
0! Only muons and muon neutrinos have Lmuon = +1

What is the electron lepton number of a muon?
0! Only electrons and electron neutrinos have Lelectron = +1

How are these two gravitational fields similar? How are they different?

Both are uniform (constant field strength)

Closer field lines represent stronger field
How are radial and uniform fields different?
Radial fields have a decreasing field strength
(Field lines increasing in separation)
Uniform fields have a constant field strength
(Field lines constant\ separation)

In gravitational fields when can you use the equation EP = mgh?
Over small distances
When radial fields are approximately uniform
And g is approximately constant

Why can’t SUVATs be used for radial gravitational fields?

SUVATs need a constant acceleration
Radial fields have a variable field strength and so a variable acceleration

What are equipotentials and how are they related to field lines?
An equipotential has the same potential along that line
(So no work is done moving along the equipotential)
They are always perpendicular to field lines

What is Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation?
Force acting between two bodies is:
- Directly proportional to the product of their masses (F∝m1m2)
- Inversely proportional to the square of their separation (F∝1/r2)

Define gravitational field strength and state its units
The force acting per unit mass on an object in a gravitational field
[NKg-1] or [ms-2]

In the gravitational field strength equation what does M represent?

The mass of the object creating the field

If the Earth is exerting a force on the rocket of 5000N,
What force is the rocket exerting on the Earth?

5000N also. An equal and opposite force from Newton’s 3rd Law
(Which has little effect on the Earth because it has so much more mass)

How do you calculate the resultant gravitational field strength at a point between two bodies?

- Calculate the field strength for each body in turn (ignoring the other one)
- Calculate the difference between the field strengths (g is a vector)

How do you you calculate the field strength (or force) neutral point between two bodies in a gravitational field?


What is the definition of and the equation for absolute potential energy in a gravitational field?
The work done moving an object from infinity to that point in the field

Why is gravitational potential energy always negative?

- Gravitational potential energy is 0 at infinite distance
- And decreases inwards as you move towards object creating field
- (So must go negative)

What is gravitational potential?
The work done per unit mass moving an object from infinity to that point in a field

In this equation for gravitational potential what object is represented by mass M?

The mass of the object creating the field

Which astronaut has a greater loss in gravitational potential energy?

Neither. Potential energy (and potential) are scalar quantities so are unaffected by the path

Both decrease by 1440MJ
What is the mistake here?

In the second stage the mass of the satellite must be used
(Not the Earth’s mass again)

If a gravitational fields question uses the word ‘height’ what must you do?

Height is the distance above the surface
So you must add on the radius of the planet/star/object

Why can’t two objects have a neutral point for gravitational potential? (or GPE)

Gravitational potential from both is negative
So they combine
To increase the magnitude of the potential

When can you use these proportionality equations in Gravitational fields?

When the mass or masses are constant

In gravitational fields What does a force-separation graph look like?
And what else does the graph tell you?
The area under the curve is the change in potential energy moving between the two separations

In gravitational fields What does a field strength-separation graph look like?
And what else does the graph tell you?
The area under the curve is the change in potential moving between the two separations

In gravitational fields What does a potential energy-separation graph look like?
And what else does the graph tell you?
The gradient of a tangent is the magnitude of the force at that point

In gravitational fields What does a potential-separation graph look like?
And what else does the graph tell you?
The gradient of a tangent is the field strength at that point

What is the equation for gravitational field strength within a planet?
(r ≤ R)
This part of the graph is linear as g ∝ r

How do you derive the equation for gravitational field strength inside a planet?

- Use general equation for density (M/V)
- With V as the volume of a sphere (4/3πr3)
- Sub into general equation for field strength

How do you derive Kepler’s 3rd Law? (r3 ∝ T2)
- Equate centripetal force to force due to gravity
- Substitute in angular speed formula (from circular motion)
- Rearrange

How do you derive the formula for the velocity of a satellite orbiting a planet or star?

- Equate centripetal force to force due to gravity
- Rearrange

Which planet has the greatest orbital velocity and why?

Mercury
It is closest to Sun so smallest r

How do you derive the formula for the escape velocity of a planet or star?

In these 3 equations what does the mass refer to?

The mass of the object creating the field

Why does a satellite not need to be above the escape velocity to reach low Earth orbit?

- Escape velocity only applies to objects without engines (that can’t increase their KE)
- Satellite isn’t escaping the field (so doesn’t need as much KE)

How do you calculate the Kinetic Energy of a satellite orbiting a planet?

Substitute orbital velocity into equation for kinetic energy

How do you calculate the total energy of an orbiting satellite?

Add the kinetic and potential energy together…

What is the difference between a geosynchronous and geostationary orbit?
Both have orbital periods of 24 hours (the same as the Earth)

How are geostationary and polar satellites different?
Geostationary satellites orbit above the same point of the equator and have an orbital period of 24 hours
Polar satellites orbit over the North and South pole with an orbital period of much less (around 2 hours)

What are Geostationary satellites used for?

- Satellite television
- Mobile Phone Communications
- GPS

Why can’t this muon decay happen like this?
(What’s the mistake with the logic in the table?)

When electron and muon type particles are involve each lepton number must be considered separately

What 4 things do magnetic fields affect?

- Charges moving in the field
- Conductors with a current passing through
- Other magnets
- Magnetic materials

What do the field lines for a bar magnet look like?

Field lines always act North → South

What do the field lines look like between two opposite poles?

Field is uniform between the poles

What do the field lines look like between two like poles?


How are field lines represented ‘going into the page’?


How are field lines represented ‘coming out of the page’?


This conductor in a magnetic field has a current passing through
But doesn’t experience a force
Why?

Because it is parallel to the field lines

When do you use Fleming’s Left hand Rule?

- Looking at DC motors
- Looking at charges moving in a magnetic field

How do you calculate the force on a conductor placed at an angle in a magnetic field?

First use trigonometry to calculate the perpendicular component of its length

Why does the reading on the balance increase when a current runs through the conductor?

The magnetic field pushes up on the conductor
So the conductor pushes the magnets down (Newton’s 3rd Law)

How can you increase the mechanical energy produced by the DC motor?

Increase the torque by:

What do the commutator rings do in the DC motor?

Switch connections of the bars every 180°
So direct current is produced

What happens if the commutators are removed from the DC motor?

Force on each bar won’t change
So coil will reach equilibrium in vertical position
And won’t continue spinning

Why does an electron move in a circular path in a magnetic field?

Force from magnetic field perpendicular to velocity of electron

How do you apply Flemming’s left hand rule to a negative charge moving in a field?

Current acts opposite to the velocity

How do you apply Flemming’s left hand rule to a positive charge moving in a field?

Current acts in the same direction as the velocity

When should you use each equation?

F=BIL on a conductor in a magnetic field (with current)
F=BQv on a charge in a magnetic field (moving)

How do you calculate the radius of the orbit of a charge moving in a magnetic field?

Equate the magnetic and centripetal forces

How do you explain the different curvatures of radiation () passing through a magnetic field?

Greater the specific charge → Smaller r (Bigger deflection)

How do you calculate the speed of a charged particle accelerated through an electric field?


How much work does a magnetic field do on a moving charge?

0J because the force and velocity vectors are perpendicular
So the charge does not increase its kinetic energy

In a mass spectrometer how does the velocity selector work?

Unless an ion’s velocity = E/B, it will travel in a parabola and miss the gap

In a mass spectrometer how does the mass separation work?

The ions have the same velocity (from the velocity selector)
So deflect by specific charge

In a particle accelerator why are both magnetic and electric fields needed?


In the cyclotron what is the purpose of the alternating current and magnetic field?

Alternating current → Electric Field between ‘Dees’ → Increases kinetic energy
Magneti Field → Moves particle in circular path in ‘Dees’ → Containing particle

In the cyclotron why is the frequency of the alternating current constant?

As the charge speeds up → Travels further in each Dee → So takes same time

How do you calculate the AC frequency of the cyclotron?

Note: f is independent of v
So the frequency is constant

What is a progressive wave?
Oscillations that have a resultant transfer of energy in one direction

How are mechanical and electromagnetic waves different?
Mechanical waves require a medium to oscillate through
Electromagnetic waves don’t require matter (oscillate through electric and magnetic fields)

What makes a wave transverse?
Oscillations are perpendicular to the transfer of energy

What makes a wave longitudinal?
Oscillations are parallel to the transfer of energy

What 2 properties do all electromagnetic waves possess?

- Always transverse
- Propagate with velocity of 3×108ms-1 through vacuum

Name 3 longitudinal waves
- Sound
- P-waves (Earthquakes)
- Water waves (beneath surface)

Name 3 transverse waves
- E-M waves (Light, X-rays, UV etc)
- Waves on string
- S-waves (Earthquakes)
- Water waves (surface)

List in order all waves on the E-M spectrum

How are displacement and amplitude of a wave different?
Displacement → Current distance of a point from the equilibrium position
Amplitude → Maximum distance a point reaches from equilibrium position

Why do all points on a progressive wave have the same amplitude?
All points have the same maximum displacement from equilibrium position

What is the time period of a wave?
Time taken for each particle to complete one full oscillation
(Return to same position)

How is frequency of a wave defined?
The number of complete oscillations per second

What is the wavelength of a wave?
Distance between two adjacent corresponding points on a wave
(Same displacement, no phase difference)

What is the phase difference between A and B on this progressive wave?

360° ∼ 0°
2π∼ 0π

What is the phase difference between A and B on this progressive wave?

180°
π ∼ Antiphase

What is the phase difference between points A and B on this progressive wave?

540° ∼ 180°
3π ∼ π ∼ antiphase

How is phase difference calculated in degrees?


How is phase difference calculated in radians?


How do you convert from degrees → radians?


What is the phase difference between A and B on this progressive wave?

420° ∼ 60°
14π/6 ∼ π/3

How are frequency and wavelength related?

What are the 2 key features of longitudinal waves?

Compressions and rarefactions

Why can’t sound waves be polarised?

Only transverse waves can be polarised
(Sound is longitudinal)

What is the final intensity?

- Light vertically polarised through first grating
- Vertically p[olarised light can’t pass through horizontal grating
- Final intensity = 0

What is the final intensity?

- Light vertically polarised through first grating (intensity halves)
- Vertically polarised light passes through second grating
- Final intensity = ½

How do sunglasses reduce glare?
- When sunlight reflects off surfaces it is polarised
- Sunglasses have filter to block polarised light
- Only unpolarised light passes through

What is the refractive index of a material?
Ratio of speed of light in a vacuum : speed light passes through material
(The greater n > the more light slows down)

How does θ2 compare to θ1?

θ2 > θ1
(Light speeds up and bends away from normal)

How does θ2 compare to θ1?

θ2 < θ1
(Light speeds up and bends towards normal)

Is the light refracting here?

Yes
It hasn’t bent towards or away from normal
But it has slowed down

How does refraction affect the frequency of a wave?

Frequency does not change
(But wavespeed and wavelength do)

What is dispersion?
Different wavelength refract by different amounts
So light passing through a prism separates into wavelengths

What is wrong here?

In Snell’s law θ1 is the angle between normal and incident ray

What are the 2 conditions for total internal reflection?

- θ1 > θc
- n2 < n1

How is the critical angle calculated?


How do you calculate the angle of incidence in the fibre?

Using basic geometry (angles in triangle add to 180°)

Why are optical fibres better than copper cables?

- Information transmission faster
- More information can be transmitted
- Less energy loss (copper heats up)

In optical fibres what does cladding do?
- Protects the core from scratches and spills
- Stops data loss to adjacent fibres
- Increases critical angle (reducing modal dispersion)

What is modal dispersion and how is it combatted?
Different modes (angles) take different amount of time to propagate through an optical fibre
Leads to pulse broadening
Combatted by making core narrow and using cladding with low n (increasing θc)

What is spectral (material) dispersion and how is it combatted?
Different wavelengths (colours) of light refracted by different amounts
Leads to pulse broadening
Combatted using monochromatic light

How do these two progressive waves interact when they overlap?

Form a superposition
Displacements combined (added or subtracted) at each point

What happens when these two pulses overlap?

Constructive interference (Displacements combine)

What happens when these two pulses overlap?

Destructive interference (Displacements cancel)

How does a stationary wave form?
- Progressive wave reflects off a fixed point
- Two progressive waves propagating in opposite directions (with same c,f,λ,A)
- Waves overlap and interfere forming superposition

On a stationary wave how are nodes and antinodes different?

Nodes → Points of 0 amplitude
Antinodes → Points of maximum amplitude

How are progressive waves different from stationary waves?

- All points on a progressive wave have same amplitude (Stationary waves have range)
- Progressive waves resultant energy transfer (Stationary waves have 0 resulatant)

How is the wavelength of a stationary wave calculated?

Each loop = ½λ

How is the frequency of the nth harmonic of a stationary wave calculated?

- Calculate the frequency of the 1st harmonic
- Multiply f1 by n

On this stationary wave why do points A and B have different amplitudes?

A and B have different maximum displacements

On this stationary wave what is the phase difference between A,B,C and D

0° → All points on same side of equilibrium are in phase

On this stationary wave what is the phase difference between A,B,C and D

A and B → 180° → All points on oppsoite side of equilibrium are in anti-phase
C and D → 180°
A and C → 0° → All points on same side of equilibrium are in phase
B and D → 0°

How can the frequency of the first harmonic on this string be decreased?

- Decrease tension (reduce mass)
- Increase distance between end points
- Use string with greater density (greater μ)

What 2 conditions are required to produce an interference pattern?
- Sources must be coherent (same frequency, constant phase difference)
- Sources must be monochromatic (one wavelength)

When will two sources interfere constructively?
When their path difference = nλ
So phase difference = 0°
Maxima forms

When will two sources interfere destructively?
When their path difference = (n+½)λ
So phase difference = 180° (∏ rad or antiphase)
Minima forms

When does maximum diffraction occur?

When the wavelength is close to the size of the gap the wave passes through

What does the interference pattern of the single slit look like?

Large central maxima
Intensity decreases exponentially
Each maxima has half width of central

For the single slit how is the central maxima width affected by λ?
W ∝ λ

For the single slit how is the central maxima width affected by the gap size?
W ∝ 1/a

For the double slit, how can you increase the widths of the maximas?

- Increase λ
- Increase slit to screen distance D
- Decrease slit separation s

How does the intensity graph look for the double slit interference pattern?

Intensity decreases linearly
Width of maximas constant

How is the 1st maxima formed for the diffraction grating

between adjacent slits Path difference = 1λ
So phase difference = 0°

How is the 3rd maxima formed for the diffraction grating?

between adjacent slits Path difference = 3λ
So phase difference = 0°

How do you calculate the slit separation for a diffraction grating?


How do you calculate the maximum number of observed maximas for the diffraction grating?

nmax = d/λ
Round Down!!!

How do charges interact in these situations?

- Like charges repel
- Opposite charges attract

Which direction will these charges move?

Electric field lines shows direction of Force on +ve charges
(-ve charges are opposite)

How are radial and uniform electric fields different?
- Radial fields have a varying field strength (weaker when further apart)
- Uniform fields have a constant field strength

For electric fields, how are are equipotentials related to the field lines?

Equipotentials always perpendicular to field lines

How can you change this situation to increase the force on the charge?

- Increase field strength
- Increase magnitude of charge

What field lines are produced by…
a) +ve charge
b) -ve charge

Field lines always act…
- Away from +ve
- Towards -ve

How do the field lines look for these two interacting oppositely charged particles?


How do the field lines look for these two interacting like charged particles?

NOTE: Field lines never cross

What is the electric field strength at the following points?

Field strength is constant between parallel plates (capacitor)

E1 = E2 = E3
What is the electric potential at the following points?

Electric potential linearly increases between parallel plates (capacitor)

Define Coulomb’s Law


Define electric field strength

Force per unit charge acting on a small positive charge

What force would act on a 5C charge placed at 6NC-1?

F=Eq → 5x6 = 30N

What is wrong here?

Electric field strength ≠ acceleration

How do you calculate electric field strength outside a conducting sphere?

Treat it as a point charge

How do you calculate electric field strength inside a conducting sphere?

E=0 everywhere!!!

What is the graph of electric field strength for a conducting sphere?


How is electric field strength calculated here?

For parallel plates calculate E first if possible

How do you work out the resultant field strength between charges?

- Work out field strength from each
- Label vectors
- Add or subtract field strengths

Can you use SUVATs here?

Yes!
Field strength constant → Acceleration constant

Why is potential energy here +ve?

Ep = 0 at ∞
Increases as charge moves closer

Why is potential energy here -ve?

Ep = 0 at ∞
Decreases as charge moves closer

Why is potential energy here +ve?

Ep = 0 at ∞
Increases as charge moves closer

Why is potential energy here -ve?

Ep = 0 at ∞
Decreases as charge moves closer

Define electric potential
Work done per coulomb moving positive charge from infinity to that point

Why does the moving charge’s potential energy increase?

Equipotentials show the change in potential of a +ve charge
If +ve charge → decreases
If -ve charge → increases

How are these charges different?

Q is the charge creating the field
q is the charge moving in the field

What is wrong here?

Electric potential is scalar
But they are opposite → must be subtracted

How do you calculate the neutral electric field strength (or force) point between charges?


How do you calculate the neutral electric potential point between charges?


What is the graph of electric force for a conducting sphere?

Same as field strength graph

What is the graph of electric potential for a positively charged conducting sphere?


What is the graph of electric potential for a negatively charged conducting sphere?


What two situations produce a uniform electric field?
- Radial field over a short distance
- Field between 2 parallel plates

Define Capacitance

Charge stored per unit Volt [F]

What do the gradient and area under this graph represent?

Gradient → Capacitance
Area → Work done (Energy Stored)

What is wrong with this?

C = capacitance → not the charge!!!

When building a capacitor how do you maximize the capacitance?

- Increase the area of the plates
- Decrease the plate separation
- Place dielectric between plates

What does it mean if the relative permittivity of a dielectric (εr) is 5.0?
The capacitor stores 5x more charge with the dielectric between the plates!

How does adding a dielectric increase the capacitance of a capacitor?

- Dielectric contains polarised molecules
- They align with the field between the plates
- Bigger negative charge attracts more electrons onto negative plate
- Repels more electrons away from positive plate
- V same but Q has increased

What happens if the dielectric is removed?
(Capacitor still connected to battery)

- Polarised molecules removed
- Some electrons leave negative plate
- Attracts more electrons to positive plate
- Q has decreased but V same
- C decreases (C=Q/V)

What happens if the dielectric is removed?
(When the Capacitor is disconnected from battery)

- Polarised molecules removed
- But charge is trapped on plates
- Same Q but with lower C
- V increases (V=Q/C)

How does this capacitor charge?
(When switch 1 is closed)

- Electrons flow from the negative terminal of the battery
- To the connected parallel plate (right plate)
- Electrons are repelled from the opposite plate (left)
- And attracted to the positive terminal of the battery
- Charge across Parallel plates

How does this capacitor discharge?
(When switch 2 is closed)

- Electrons flow from the negative plate (right)
- Through the resistor
- To the other plate (left)
- Decreasing charge difference across plates

Define time constant

Time constant is how long it takes for a capacitor to…
- Charge to 63% of max charge (0.63Q0)
- Discharge 63% of Q0 (down to 0.37Q0)

What factors affect the time constant of a circuit?

- The resistance of the components in the circuit (Capacitor R=0)
- Capacitance of the capacitor

Complete this discharging curve for a capacitor


Complete this discharging curve for a capacitor


Complete this discharging curve for a capacitor


Complete this charging curve for a capacitor


Complete this charging curve for a capacitor


Complete this charging curve for a capacitor


How do you read off the time constant from this graph?

Read off time when charge (or current or voltage) has decreased to 37% initial

How do you read off the time constant from this graph?

Read off time when charge (or current or voltage) has increased to 63% final

Explain why the I-t graph is exponential when a capacitor discharges

- Potential difference across capacitor drives large current through resistor
- Charge across plates decreases
- Potential difference across the plates decreases
- Current gets smaller and smaller

Explain why the I-t graph is exponential when a capacitor charges

- Battery drives current round circuit
- Charge build up on capacitor plates
- Potential difference builds up across plates
- Difference in PD between battery and capacitor gets less
- So smaller push on electrons
- Smaller current

What is wrong here?

80% is the decrease in charge (∆Q)
So it discharges to 20% of initial Q=0.2Q0

How do you make a capacitor charge/discharge at a constant rate?

Use a variable resistor
Decreasing resistance
To keep charging/discharging current constant

How do the graphs change if a capacitor is charging at a constant rate?

Current → Constant
Voltage and Charge → Linear

How do the graphs change if a capacitor is discharging at a constant rate?

Current → Constant
Voltage and Charge → Linear

How do you show Q=0.37Q0 after 1 time constant?

Set t=RC

What is wrong here?

Capacitor is discharging at a constant rate
So current is constant

How does the potential difference of the resistor change as the capacitor charges?

NOTE: VR+VC=V0

How does the potential difference of the resistor change as the capacitor discharges?

NOTE: VR+VC=V0

For a discharging capacitor, what does the gradient of the Q-t graph give?

Current at that instant

For a charging capacitor, what does the gradient of the Q-t graph give?

Current at that instant

For a discharging capacitor, what does the area of the I-t graph give?

Charge lost in that region

For a charging capacitor, what does the area of the I-t graph give?

Charge gained in that region

How is magnetic flux calculated?
Magnetic flux density x Perpendicular area

How do you calculate the effective flux through this coil?

Must take component of field perpendicular to surface
(Or component parallel to normal of surface)

How does the number of turns in a coil affect its flux?

Flux doesn’t change
But flux linkage increases

How do you find the flux linkage through this coil?

Must take component of field perpendicular to coil
(Or component parallel to normal of coil)

How do you induce an emf in this coil?

Moving the magnet in and out of the coil
Causes a change in flux linkage
(Faraday’s Law)

If the magnet is stationary why is there no emf induced?

Emf only induced if the flux linkage is changing
(Faraday’s Law)

Which way does the current act in this coil and why?

Current acts to create a magnetic field opposing the increase in flux linkage
(Tries to keep magnet from entering)
Due to Lenz’s law

Which way does the current act in this coil and why?

Current acts to create a magnetic field opposing the decrease in flux linkage
(Tries to keep magnet from leaving)
Due to Lenz’ law

Why does moving the magnet faster induce a larger emf?

The rate of change of flux linkage is greater
(Faraday’s law)

What is Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction?

The magnitude of the emf is proportional to the rate of change of flux linkage

What is Lenz’ law?

The direction of an induced emf tends to produce a current which opposes the
change causing it

Why can’t the current act in this direction?

The magnetic field produced attracts the magnet
Increasing its kinetic energy
Energy has been created out of nothing!!!
(Against Lenz’ law)

What is the right hand grip rule?

A current in a coil produces a magnetic field as shown

What is wrong here?

Flux linkage becomes negative when coil flips!!!

How is the induced emf related to the graph of flux linkage?

(From Faraday’s law)

What is the corresponding graph of induced emf?

emf = -ve gradient

If the coil moves across the field at a constant speed what do the flux linkage and emf graphs looks like?

emf = -ve gradient

How do you calculate the emf induced between the ends of this conducting bar moving across a magnetic field?


When do you use Fleming’s Right Hand Rule

For generators!!!

For the AC generator when is the max emf induced?

When change in flux linkage is max
(When flux linkage = 0)

For the AC generator when is 0 emf induced?

When change in flux linkage is 0
(When flux linkage = max)

What is the corresponding emf graph for the AC generator?


How is the max induced emf calculated for the AC generator?


How do you increase the max induced emf of the AC generator?

Increase any of the terms in the equation:

How is the AC generator different to the DC motor?

Generator: Kinetic energy -> Electrical energy
(Motor: Electrical energy -> Kinetic energy)
Generator: Slip rings keep each side of coil connected to same side of circuit
(Motor: Commutator ring switch polarity every half cycle)

What are eddy currents?
Currents produced in a conductor by magnetic fields
(Lenz’ law in conductors)

Why does the magnet take longest to fall through the full copper pipe?

- Magnet in freefall
- Plastic not a conductor so no eddy currents (still in freefall)
- Copper pipe incomplete so can’t create eddy currents (still in freefall)
- Eddy current reduce acceleration

How are eddy currents created in this copper pipe?

- Flux linkage decreasing above -> current creates attracting field upwards
- Flux linkage increasing below -> current creates repelling field upwards

How does eddy current braking work?
- Part of disk leaving field -> current creates attraction to electromagnet
- Part of disk entering field -> current creates repulsion to electromagnet

When can eddy current braking not be used?
To hold a car stationary on a slope
(no change in flux linkage)

How does the oscilloscope trace look for an AC current?
(When the time base is switched on)


How does the oscilloscope trace look for an AC current?
(When the time base is switched off)


How does the oscilloscope trace look for an DC current?
(When the time base is switched on)


How does the oscilloscope trace look for an DC current?
(When the time base is switched off)


For AC supply what is Vrms and how is it calculated?

The equivalent DC voltage that would supply the same average power

For AC supply what is Irms and how is it calculated?

The equivalent DC current that would supply the same average power

Label V0 and Vp→p on this AC oscilloscope trace


What is wrong with this calculation?

When using electricity formulas must use rms values for voltage (and current)

How does a step up transformer work?

- AC current flows through primary coil
- Magnetic field flows through secondary coil
- Changing flux linkage in secondary coil larger
- Greater emf induced (so bigger voltage)

How does a step down transformer work?

- AC current flows through primary coil
- Magnetic field flows through secondary coil
- Changing flux linkage in secondary coil smaller
- Smaller emf induced (so smaller voltage)

Why does a transformer only work with AC supply?

If supply is DC
Flux linkage in secondary coil doesn’t change
So emf isn’t induced (Faraday’s law)

How do you calculate the voltage (rms) in the secondary coil?

This equation always works (no matter what efficiency)

How do you calculate the efficiency of a transformer?

(The voltages and currents must be rms values)

What are the main causes of thermal loss in a transformer?

- Large Eddy currents in magnet (P=I2R)
- Large currents in primary and secondary coils
- Hysteresis losses (magnet’s resistance to change in flux linkage)
- Flux losses (not all flux passing through secondary coil)

How are the main causes of thermal losses in a transformer reduced?
- Large Eddy currents in magnet
- Large currents in primary and secondary coils
- Hysteresis losses
- Flux losses

- Laminate the core
- Use wire with low resistance
- Use soft iron core for magnet
- Wind primary coil over secondary coil

Why are step up transformers used to transport electricity over long distances?

Smaller currents = smaller energy losses to thermal
(P=I2R)

What happened in the Rutherford scattering experiment?

- Most alpha particles passed through gold leaf undeflected
- Some were slightly deflected
- A tiny proportion (1 in 8000) reflected

What did Rutherford’s experiment reveal about the atom?

- Atom is mostly empty space
- Centre of atom is small, dense and positively charged (nucleus)

Compare the ionising power of the three main types of radiation

- *Alpha most ionising**
- *Beta medium ionising**
- *Gamma least ionising**

Compare the penetrative power of the three main types of radiation

- *Gamma most penetrating**
- *Beta medium penetrating**
- *Alpha least penetrating**

Compare the range of the three main types of radiation

Alpha = 3-7cm Beta = 0.2-3m Gamma = Very long distance

What are the main sources of background radiation?


How does a Geiger-Muller tube detect radiation?

- Radiation ionises gas in tube
- Negative ions attracted to metal rod
- Positive ions attracted to casing
- Small current generated in circuit

How is radiation used to control the thickness of metal?
Why can’t alpha radiation be used?
If detector count too low -> metal too thick -> Rollers move closer together
If detector count too high -> metal too thin -> Rollers move apart
Alpha won’t be detected

What materials can shield the three main types of radiation?

- *Alpha = Paper**
- *Beta = Aluminum**
- *Gamma = Lead or several meters of concrete**

How is radiation used in a smoke detector?

Alpha radiation ionizes air between detector
Ionized air causes current to flow
Smoke blocks ionization of air
Current stops
Alarm sounds

If the detector is moved 3x further away what will happen to the count rate?

9x smaller
Gamma radiation follows inverse square law

How should you safely use radiation?
- Minimise exposure time
- Maximize distance from source
- Store in shielded containers
- Don’t consume food or drink near source

How is radiation used for medical imaging?
Medical tracer with short half life injected
Tumors absorb radionuclides and emit gamma
Gamma detected outside body

How is radiation used to destroy tumors?
Gamma radiation focused on tumor
High energy breaks apart tumor
Low levels through other tissue

Sketch the graph of nuclear stability

On this graph of nuclear stability highlight regions of the decays…
- α
- β-
- β+
- Proton emission
- Neutron emission


What makes a nucleus unstable? (and radioactively decay)
- An incorrect balance of protons and neutrons (off line of stability)
- Too many nucleons
- Nucleus in excited state

What is electron capture and what is it’s equation?

Proton captures inner shell electron and becomes neutron

What two forms of radiation are released after electron capture?

X-ray → electron de-excites to fill inner shell
γ → Nucleus reorders and de-excites

How does distance of closest approach work?
KE at distance → PE closest
Use to get rough size of nucleus

What two graphs could you plot to prove this relationship?


What does r0 represent?

Average radius of each nucleon

How do you calculate the average density of a nucleus?


Why is the average nucleus density so large? (∼2.3x1017kgm-3)
Atom is mostly empty space

How was electron scattering used to determine nuclear diameter?

Graph plotted
First minima used to calculate diameter
(Don’t need to know equation)

How is electron scattering better than alpha recoil to determine nuclear radius?

Alpha Recoil
- Closest approach so only an estimate
- Recoil of nucleus not considered
- Effect of strong force not known
Electron Scattering:
- Not affected by strong force (leptons)
- Electron λdb tunable

Define the decay constant λ
The probability that an unstable isotope decays in one second

Define the activity, A, of a radioactive sample
The total number of unstable isotopes that decay after one second

What does the activity, A, of a radioactive sample depend on?
- The decay constant λ
- The number if unstable isotopes N

Define the half life, T½, of a radioactive sample
Time taken for either…
- Activity of sample to halve
- Number of unstable isotopes remaining to halve

How do you derive the half life T½ equation?

Set N as 0.5N0

How do you prove this graph is exponential?

Find multiple T½ and compare

What’s wrong with this calculation?

Activity and time must be the same units

- Derive the equation of this graph
- What are the gradient and y-intercept?


What is the gradient of this graph?

r0 → average radius of nucleon

What do the gradient and y-intercept of this graph represent?

where r0 → average radius of nucleon

When should you treat the neutron and proton as having slightly different masses?

Dealing with fusion or fission
(Calculating mass defects, binding energies or mass difference)

Define mass defect (∆m)
Mass lost when nucleons (protons and neutrons) come together to form nucleus

Define binding energy
Energy released when nucleons (protons and neutrons) come together to form nucleus

How is binding energy related to mass defect (∆m)?


Define 1 atomic mass unit
Mass of 1/12 of a carbon-12 atom
(1.661x10-27kg)

What’s the next step here?

Multiply by 931.5MeV

What’s the next step here?

Use E=mc2

Sketch the binding energy per nucleon graph

Label the fusion and fission regions
Why are they there

Energy only released if binding energy per nucleon increases

Define metastable state in radioactive decay
Long-lived excited state of nucleus
Eventually it de-excites emitting γ

How many possible decays are there?

2β- and 3γ

What is nuclear fission?
Heavy nucleus splits into two lighter nuclei releasing energy and neutrons

What are the 2 main isotopes used as fuel in nuclear reactors?

U-235, U-238

How do you calculate the energy released in this fission reaction?

Calculate the mass difference (∆mdiff)

How do you calculate if a reaction is possible?

If mass difference is positive reaction is possible

What are the main components of the nuclear reactor?

- Fuel rods - U-235
- Control rods - Boron
- Moderator - water or graphite
- Coolant - CO2 or water

What does the moderator do in a nuclear reactor?

Reduce neutrons’ speeds to thermal speeds
(More likely to be absorbed by U-235)

What do the control rods do in a nuclear reactor?

Absorb some neutrons
Stop chain reaction occurring

What are the main safety features of the nuclear reactor?

- Reaction happens inside thick walled concrete vessel
- Control rods fully inserted if meltdown starts
- Reactor flooded with water to remove thermal energy if meltdown starts

In nuclear reactors how are spent fuel rods disposed?
- Removed remotely from reactor
- Stored in cooling ponds for up to 1 year
- Vitrified by mixing with molten glass
- Sealed in barrels
- Stored in mountains or deep underground

What is nuclear fusion?
Two lighter nuclei are combined to form one heavier nuclei and release energy

Why is nuclear fusion so difficult to achieve?
Requires incredibly high temperatures and pressures
- To ionise the isotopes
- To bring isotopes close enough to overcome electromagnetic repulsion

In fusion how close do the ionised isotopes need to get?
Close enough for the strong force to be larger than electromagnetic

(<1fm)
What are the two main fusion isotopes in stars (in their main sequence)
Deuterium → H-2
Tritium → H-3

What does the coolant do in a nuclear reactor?

Transfer heat from fuel rods to the water that spins the turbines

How is 1 Tesla defined?

The magnetic field that applies a force of 1N to a 1 metre conductor with a 1A current flowing perpendicular to the field (B=F/IL)

If this unstable isotope of caesium decays by α emission where does it end up on the graph?

N → neutron number
Z → Proton Number

If this unstable isotope of caesium decays by β- emission where does it end up on the graph?

N → neutron number
Z → Proton Number

If this unstable isotope of caesium decays by β+ emission where does it end up on the graph?

N → neutron number
Z → Proton Number



