Mechanics/ biomechanics - unit 1 deck 2 Flashcards
(43 cards)
Refer to figures 21 & 22 in binder to see the independent 3 translations and 3 rotations
What is each translation and each rotation defined as ?
A degree of freedom
How many degrees of freedom does an object which is free to move in all directions said to have ?
six degrees of freedom
The 6 different degrees of freedom are independent of eachother - T/F and explain ans
True - this is because the x, y, z axes are at right-angles to eachother
Refer to fig 23 of the binder to help get your head around rotatory degrees of freedom
Define what linear motion is
This is motion in a straight line
What are the 4 parameters used to describe linear motion ?
- Time
- Displacement
- Linear velocity
- Linear acceleration
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
- Speed is the rate of change of distance travelled i.e. distance travelled divided by time
- Whereas velocity is the rate of change of displacement i.e. speed and direction of travel ==> it is a vector quantity
What are the SI units of velocity ?
m s-1 - metres per second
What are the 2 types of velocity that we are concerned with ?
- Average velocity - this is the displacement travelled divided by the time taken (note how its the displacement not distance because velocity is concerned with direction as well)
- Instantaneous velocity - this is the velocity at an instant in time
What is the equation for average velocity?
average velocity = change in displacement/ time taken
v = Δs / t OR v = s - so / t
- v = velocity
- Δs = change in displacement
- t = time taken for the change to occur
- s = the final displacement relative to a reference point
- so = the original/ initial displacement relative to a reference point
How should a displacement-time graph be plotted and what are they used to calculate ?
It should be plotted with time on the x-axis and displacement on the y-axis
These graphs are used to calculate velocity
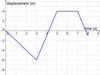
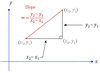
How is the gradient of a straight line calculated ?
For a straight-line graph, pick two points on the graph. The gradient of the line = (change in y-coordinate)/(change in x-coordinate)
What can be stated in general is the relevance of the gradient of a displacement-time graph ?
The gradient of a displacement-time graph is the velocity
It is useful to refer to and read over pages 19&20 in the binder
How is the instantaneous velocity calculated on a displacement-time graph if the graph is curved ? (like in figure 25 page 20 in the binder)
You can calculate it by drawing a tangent to the curve at a particular point, you then basically use the numbers from the plotted points immediately before and after the point on the graph you want to calculate the instantaneous velocity for.
Refer to fig.26 on pg.20 in the binder for visual explanation
Define acceleration
It is the rate of change of velocity
e.g. a car starting from rest, it must build up its velocity from 0 to say 50 km per hour. To do so it must accelerate
It is a vector quantity
What are the SI units of acceleration ?
m s-2 - meters per second squared
Define average acceleration and instantaneous acceleration
- Average acceleration is the change in velocity divided by the time taken
- Instantaneous acceleration is the acceleration at an instant in time
What is the equation used to calculate average acceleration?
acceleration = change in velocity/ time taken
a = Δv / t OR a = v - v0 / t
- a = acceleration
- Δv = the change in velocity
- t = the time taken for the change to occur
- v = the final velocity
- v0 = the initial velocity
How should a velocity-time graph be plotted and what are they used to calculate ?
Should be plotted with time on the x-axis and velocity on the y-axis
They are used to calculate acceleration
Refer to fig.27 on pg.21 in binder

How is the gradient of a velocity-time graph calculated and what does the graident repesent ?
The gradient is calculated the exact same way as in displacement-time graphs depending on if it is a striaght or curved line
The gradient (velocity/ time taken) in this graph represents the acceleration
When does deceleration occur ?
This occurs when an object is slowing down, during deceleration the calculated acceleration is negative since the change in velocity will be negative
What is the difference between the value you would get if an object is deccelerating rather than accelerating ?
You would calculate it the same way but a decceleration would give out a negative number since the change in velocity will be negative, whereas acceleration the value will be positive

Describe rotary motion
This is when an object can be rotating about a point on itself e.g. an ice skater performing a spin
OR when an object is rotating around an external fixed point e.g. a gymnast swining on a horizontal bar as shown in fig.28


