Mechanics/ biomechanics - unit 1 deck 1 Flashcards
(46 cards)
Describe what is meant by saying ‘the choice of scale for a unit’
This is referring to the size range of any particular type of unit.
e.g. the main metric unit of distance is the metre but you have a choice of also using micrometres, millimetres, centimetres or kilometres. These different choices is a choice of scale
What is the single system of units referred to as ?
System Internationale d’Unites - known as SI units
This is just a system which came up with the standard units you should use
What are the 3 main base units in Systeme Internationale (SI) relevant to this module ?
- The metre (m) - the standard unit of length
- The second (s) - the standard unit of time
- The kilogram (kg) - the standard unit of mass
What is the 4th base SI unit which we should know about relevant to the biomechanics module?
kelvin (K) - the standard SI unit of temperature.
What is the relevant supplementary unit in the SI system which is relevant to this module ?
The radian (rad) - the standard unit of angle
What are the units other than the base SI units and supplementary SI units referred to as and how are they formed ?
The are referred to as derived units and are formed by combining base units
e.g. the newton (N) is equivalent to kilogram metres per second squared (kg m s-2 )
What do each of the following scale factors that you should remember stand for:
- mega (M) -
- kilo (K) -
- centi (c) -
- milli (m) -
- micro (µ) -
- mega (M) - x106
- kilo (K) - x103
- centi (c) - x10-2
- milli (m) - x10-3
- micro (µ) - x10-6
What are the 3 rules you need to remember to follow when using units ? i.e. m, cm, km, s, etc etc
- Write prefixes without a space, e.g. cm (there is no space between the c and the m)
- Leave a space between symbols for units e.g. m s-1 (metres per second) not ms-1 as this reads as ‘‘per millisecond’’
- Never pluralise units, e.g. 10ms means 10 milliseconds not 10 metres
What are the 4 basic physical quantities and state their SI units that we should know about in mechanics and biomechanics
- Time - SI unit is seconds (s)
- Distance - SI unit is meters (m)
- Angle - SI unit is radian (rad), note that the common unit of angle is the degree
- Temperature - SI unit is kelvin (K)
What are the common units of temperature used ?
Degrees Celsius, represented by the symbol °C
What is the Celsius scale based on ?
The melting and bioling point of water
- 0 degrees = melting point of water
- 100 degrees = bioling point of water
What does 0K represent and what is this the equivalent of in degrees Celsius ?
0K = abolsute zero, the point at which matter has no energy, this is equal to -273 degrees Celsius
Define the radian (rad)
One radian is encloses an arc which has a length equal to the circle radius
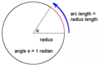
What is the relationship of radians to a full revolution (360 degrees)?
2π radians = a full revolution (360 degrees)
Note for maths purposes ignore the names and have it as 2π = 360
What does pi represent ?
It represents a constant, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, it is the same for all circles
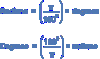
What is the equation for converting between radians and degrees ?
The more formal equation is in page 4 of mechanics binder
What is the difference between scalar and vector quantities
A scalar is a quantity that has a magnitude only
A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and direction
Describe the difference between distance and displacement
- Distance is simply the total distance travelled regardless of direction; it is a scalar quantity
- Displacement is a straight-line distance and a defined direction; it is a vector quantity

Describe the difference between angular distance and angular displacement
- An angular distance is simply the total angle turned through
- Whereas angular displacement has a magnitude (the angle it is turned through) and direction (the direction of the rotation about an axis); it is a vector quantity e.g. consider a bath tap if you instructed someone to turn a bath tap you would tell them both the direction and the angle through which to turn it
How are scalar quantities added together ?
They can be added using simple rules of arithmetic, there is nothing new to learn for this
e.g. 1kg + 2kg = 3kg
What are the two main methods for adding or subtracting vectors together ?
- Combining vectors graphically
- Resolving using trigonometry
What is the term used to describe the vector produced when two or more vectors are added or subtracted ?
The resultant vector
Describe the basic idea behind using trigonometry for resolving vectors
- The basic idea is to replace each vector with a pair of vectors ar right-angles to each other.
- This is called resolving the vector into its components, the resolved vectors along each direction can then be added to give the components of the resultant vector
Why do you often work in degrees when using trigonometry when the SI unit for angles is radians ?
Because it is easier to visualise degrees and calculators are naturally set to work in degrees not radians




