MBE and NY Distinctions (Con Law) Flashcards
Substantive Due Process:
Pre-Viability Abortion Rights
& the Undue Burden Test

1st Amendment:
Freedom of Association
& Political Parties/Elections

Equal Protection:
Gender Discrimination Chart

Substantive Due Process: Right to Travel
& Residency Requirements

First Amendment: Freedom of Association (Fundamental)
What is required for gov’t to prohibit group membership?
Regulate private discrimination?

First Amendment:
Establishment Clause
What are the 3 elements
of the Lemon test?

First Amendment:
Regulation of Locations
for Dissemination of Speech
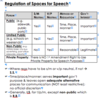
First Amendment:
Free Exercise Clause
What kind of law is immune
to challenge under the
Free Exercise Clause?
Free Exercise Clause Cannot Be Used to Challenge A Neutral Law of General Applicability
Neutral: not motivated by religious animus
General Applicability: applies to everyone, not just religious entity
State has initial burden to prove (a) neutral and (b) general applicability, then RB (or if state doesn’t prove, then SS).
E.g. gov’t cannot deny benefits to people who quit their jobs for religious reasons.
It doesn’t matter how much a neutral law
of general applicability burdens religion,
it is only subject to rational basis review.
First Amendment: Unprotected & Less Protected Speech
Incitement of Illegal Activity: speech directed to and substantially likely to cause imminent illegality
Sexually-Oriented Speech (1) prurient interest, (2) patently offensive, (3) no artistic, literary, political or scientific value
Obscenity: generally protected. 2 Exceptions: free, over-the-air broadcast media (intrusive, kids); Schools
Commercial Speech: must meet I.S. (narrowly tailored but not least restrictive) (Central Hudson)
False/Deceptive Ads: unprotected; true commercial speech capable of deception (professional trade names, in-person attny solicitation, NOT accountant)
Privacy-Related Speech: govt may limit its dissemination of info to protect privacy, can’t punish truthful broadcast of private info, IF media didn’t participate in illegality.
Defamation: depends on ID of Π (public official/figure vs. private figure).
First Amendment:
Sexually Oriented Speech
What is the test for
sexually-oriented speech?
Test to ID Sexually-Oriented Speech: (1) prurient interest, (2) patently offensive, (3) as a whole, lacks serious artistic, literary, political, or scientific value
Zoning Ordinances OK if Some Channel is Allowed
Child Porn = always obscene
Can’t punish private possession, except child porn
May seize assets of businesses violating obscenity laws (7 obscene items = OK to destroy $9 million)
First Amendment:
Symbolic Speech
When is symbolic speech protected? What is the test for regulation of symbolic speech?

First Amendment:
Defamation Liability Chart

First Amendment:
Content-Based vs.
Content-Neutral Restrictions
Content-Based Restrictions à S.S.
Subject matter restrictions (S/M)) Viewpoint restrictions (V/P)
Content Neutral Restrictions à I.S.
Applies to all speech regardless of content/viewpoint (parade in city park)
First Amendment:
Vagueness and Overbreadth
When is a law unconstitutionally overbroad or unconstitutionally vague?
Vagueness and Overbreadth
Vagueness: reasonable person cannot tell what speech is prohibited and what is allowed
E.g. “any book that corrupts morals of youth”
Overbroad: regulates substantially more speech than the constitution allows to be regulated
E.g. “all live entertainment”
Fighting words laws are always
unconstitutionally vague and overbroad.
Equal Protection: Fundamental Rights Under EP
What fundamental rights are protected by the EP Clause rather than the DP Clause?
Right to Travel
Laws that prevent people from traveling state-to-state must meet S.S.
Durational Residency Requirements: S.S. (max of 50 days for voting)
BUT foreign travel, ONLY R.B.
Right to Vote
Laws that deny some citizens: S.S. (poll taxes)
Property ownership except water dist. elect.
One-person-one-vote: same # in each district
At-Large OK: unless discriminatory purpose
Race in drawing district lines: S.S.
Counting uncounted votes w/o stds.: Fail S.S.
First Amendment:
Prior Restraints

Substantive Due Process: Privacy
Chart on Scrutiny Levels for Various Privacy Rights

Equal Protection
Level of scrutiny for age, disability, wealth, economic regulation, sexual oriented classifications?
Rational Basis for:
Age
Disability (Cleburne)
Wealth
Economic Regulation (EP or DPL)
Sexual Orientation
Discrimination Against Non-Marital Children
Intermediate Scrutiny
Laws that grant benefit to ALL marital, and deny to all non-marital FAILS I.S. (except requiring all non-marital children to establish paternity during life OK)
Substantive Due Process: Economic Liberties
What protection is afforded to economic liberties through substantive due process?
Economic Liberties (employment, trade, minimum wage, consumer protection): since Lochner minimal protection: rational basis review
Takings: (1) taking for public? (2) just comp pd?
Possessory Taking = physical taking
Regulatory = leaves NO reasonable economic use
Public Use = broadly defined
Just Compensation = Loss to Owner, NOT govt gain
Contracts CL (I§10): applies ONLY to state substantial interference w/existing contracts;
Apply intermediate scrutiny: reasonably & narrowly tailored to promote important interest
Applies to state interference w/its own contracts; never to fed gov interference.
Ex post facto NOT in civil cases
Equal Protection
What level of scrutiny is applied to race, gender and alienage?
Race/National Origin (S.S)
Existence: facial OR impact + intent (but-for)
Benign Classifications: still SS; quotas ONLY clear past discrim (narrow); 1 factor for schools, but no points; aff. act. can’t disrupt seniority system
Gender Classification (I.S.)
Existence: facial OR impact + intent (but-for)
Benefit Women: NOT based on role-stereotype; BUT remedy past discrim/actual differences OK.
Alienage (Non-US Citizens)
S.S.: welfare, civil service jobs; I.S.: children (schools)
ONLY R.B.: self govt/dem. process: voting; jury; PD/probation; teacher (dem. value), NOT notary
Rational BasisàCongressional action (immigration)
Bill of Rights:
Incorporation
Selective Incorporation (Almost-Total)
B/c Bill of Rights ONLY applied to fed, individual amendments have been incorporated to the states through the 14th Amendment. The only Amendments NOT to be incorporated are:
2nd Amd. Right to Bear Arms
3rd Amd. Protection Against Troop Quartering
5th Amd. Right to GJ Indictment in Criminal Case
7th Amd. Right to Jury in Civil Cases
8th Amd. Protection Against Excessive Fines
BUT, the rest of the 8th Amd. is incorporated
Procedural Due Process
What deprivations of liberty
or property are protected by the due process clause?
Deprivation of Liberty Requiring Due Process:
Institutionalization of an adult BUT NOT a child, not prisoners, not reputation School Discipline (notice, opportunity to explain) Parental Custody (notice, hearing)
Deprivation of Property Requiring Due Process
(Intentional/reckless govt conduct (NOT negligence),
or in emergencies if conduct shocks conscience)
Welfare Benefits (notice, hearing) SSD Benefits (post-deprivation hearing) Punitive Damages (instructions to jury, jud review) Prejudgment Attach/Seize (notice, hearing; except exigencies; innocent owners ok if use w/permission) Public Employment (prior notice, opp. respond, sub. Evidentiary hearing); not probationary employees.
Procedures: balance (1) individ. Interest, (2) accuracy of procedures, (3) govt interest.
Levels of Scrutiny
What are the requirements of each of the three levels of scrutiny?
Rational Basis (R.B.): rationally related to legitimate govt purpose
purpose need only be conceivable
challenger has burden of proof
Intermediate Scrutiny (I.S.): substantially related to important govt purpose:
Actual purpose (not merely conceivable)=important Means Narrowly Tailored/Substantially Related; but NOT necessarily least restrictive alternative Govt retains burden of proof
Strict Scrutiny (S.S.): necessary to achieve compelling govt purpose
Compelling is most important ends
Necessary is narrowly tailored/least restrictive alternative
Govt retains burden of proof
If facially neutral = initial burden on P to prove discriminatory intent/purpose, then shifts to state.
State Action Doctrine

Full Faith & Credit
When do the requirements of FF&C apply to a judicial action?
Full Faith and Credit
Courts in one state must give FF&C to judgments of another state as long as:
Court that rendered judgment had PJ/SMJ
Judgment was on the merits
Judgment was final.
Dormant Commerce Clause (DCC)
What is the definition of the dormant commerce clause (DCC)?
Dormant Commerce Clause
Negative implication of the commerce clause: prohibits state regulation from imposing undue burden on interstate commerce (even w/o explicit Congressional action).
Privileges & Immunities
Clause of Art. IV

State Regulation of Interstate Commerce: Flow Chart

Federal Executive Power:
Foreign Policy
POTUS Foreign Policy Power: Broad
Treaties: negotiated by POTUS/ratified by Senate
Prevail over state laws
Conflict betw. treaty and statute: most recent
But, conflict w/Constitution: treaty falls
Exec. Agreement: signed by POTUS/foreign leader
Prevail over conflicting state laws
No ratification; can be for any purpose
BUT, federal law/Const. preempt agreement
C-I-C Power to Use Troops is Nearly Unlimited
Either political Q, or
Based on POTUS broad foreign affairs powers.
Federal Executive Power:
Domestic Affairs & Liability
POTUS: Federal Powers and Liability
Appointment: Congress can vest appointment of lower officers in POTUS, or depts., judiciary, but NOT in itself
Removal: POTUS may fire any exec. Branch officer, BUT Congress can limit removal to good cause where independence from POTUS is desirable (Indep. Pros.).
Impeachment: officers/judges can be impeached and removed for high crimes/misdemeanors; impeach in House (majority) and trial in Senate (2/3 for removal).
POTUS Civil Liability: absolute immunity from $ damages for in-office acts (Nixon), but not before office (Clinton).
POTUS Executive Privilege: privilege will yield to other interests (e.g. criminal evidence – Watergate)
Pardon: federal crimes, BUT NOT impeachment, civil actions, state crimes
Federal Legislative Power
What limits exist on Congress’ ability to delegate its powers to the executive/judiciary?
Non-Delegation Doctrine
Formal requirement: is that Congress must provide intelligible standards, but no delegation has been struck down since 1936; virtually unlimited.
Limitations:
NO legislative veto (less than bicameralism & presentment)
NO line item veto for POTUS
Congress CANNOT delegate executive power to itself or its Officers
(e.g. Act struck down à required that if executive doesn’t cut budget, Comptroller (Congressional Officer) would impose across-the-board cuts).
Federalism: Preemption
and the Supremacy Clause
Supremacy Clause = Federal Laws Preempt State Laws
Express Preemption: federal statute says that federal law wholly occupies area where Congress has authority, even if state law doesn’t conflict.
Implied Preemption: text is silent BUT: (1) laws conflict, (2) state law impedes fed objective, (3) clear Congressional intent to preempt.
States may not tax or regulate fed gov activity
E.g. taxing federal banks (McCulloch)
E.g. can’t require fed gov to adhere to state standards (e.g. military base and state air stds).
BUT, states can tax private enterprise on fed land and can impose a general tax on a service provided to the fed government (telephone svc).
Federal Legislative Power
Chart w/ Examples of
Congressional Powers

Federal Legislative Power
What are the 5 main categories of federal legislative power?
Congressional Powers
Necessary & Proper Clause: any means not otherwise prohibited to carry out any proper authority.
Tax/Spend Power: for the general welfare; can support spending for any public purpose
Commerce Power: (1) channels (places e.g. highways); (2) instrumentalities, persons, things (e.g. trucks, radio waves), (3) substantial effect: broad power for economic effects, even in aggregate (wheat for personal consumption); narrow power for non-economic activity (DV, guns) and NO cumulative effects.
14§5: Congress may NOT create new rights or expand scope; may only prevent remedy violations of rights recognized by USSC proportionate/congruent
Police Power: usually a red herring; ONLY M-I-L-D: Military, Indian Reserv., Lands (Fed/Territories), DC
11th Amendment
Sovereign Immunity
When and how can federal or state courts hear suits by private parties against state governments?
11th Amendment Sovereign Immunity
Prohibits fed courts from hearing suits by private parties against states
Alden v. ME: includes state govts/federal agencies
3 Exceptions
Explicit state waiver
Pursuant to 14§5 Laws
Fed Gov can sue State Govs
Suits vs. State Officers OK: Injunctive relief, personal damages, NOT retroactive damages paid from state treasury; municipalities are NOT included.
Abstention: fed cts may NOT
enjoin pending state proceedings
10th Amendment Limit on Constitutional Powers
How and when can Congress compel state regulatory or legislative action?
10th Amendment: powers NOT given to fed are reserved to the people/states
Generally, Congress CANNOT compel state action, but CAN induce states through spending programs if requirements to receive funds are:
Clearly stated, AND
Relate to the purpose of the spending program
Fed cannot tax essential state activities, but can tax proprietary functions (state trying to make $).
Example: 21drinking age for highway funding
Justiciability:
Political Question
Political Questions
Questions constitutionally committed to another branch or incapable of judicial resolution.
Examples:
Republican Form of Govt. Clause (usually state or local govt. practice)
President’s conduct of foreign policy
Impeachment and Removal Process
Non-reviewable power of Congress
Amendment/Ratification
Electoral College (b/c of 12th amd.)
Supreme Court Review
What is an independent and adequate state grounds of decision?
Independent and Adequate State Grounds
When state SC decision rests on an independent and adequate ground of state law, such
that even if Π wins on the federal grounds,
it will not change the result, it is NOT justiciable.
NOTE: If state law is adequate but the law is interpreted identically to a federal law, the state law is not independent b/c the federal reinterpretation changes state interpretation
Justiciability: Mootness
What does it mean for
a case to be moot?
What are the 3 exceptions
to this basic rule?
Mootness
Mootness: events after filing of suit end Π’s injury b/c cases require a live controversy.
3 Exceptions:
Wrong capable of repetition but avoiding review
Voluntary cessation, but free to resume
Class action suits: mootness of named Π does NOT moot action, if injury ongoing to other Πs.
Supreme Court Review
What are the 2 types of cases that do NOT come to the Court through a Writ of Cert?
Supreme Court Review
All appeals from state courts and federal courts of appeals come to the USSC on writ of certiorari.
Exceptions:
Appeals from 3-judge federal district courts
Suits betw. states (original/exclusive jurisdiction)
Note: By statute, Congress can change the USSC’s appellate jurisdiction, but NOT original jurisdiction
Justiciability:
3rd Party Standing
What is the rule regarding
3rd Party Standing? What are the 3 exceptions to the rule?
3rd Party Standing
General Rule: Δ’s cannot assert claims of 3rd party injuries not before court (not personally suffered).
3 Exceptions:
Close relationship between Π /3rd party (e.g. docs/abortion; bartenders/3.2% beer ).
Injured 3rd party unlikely to assert own rights (e.g. jurors excluded on race)
Organization on behalf of members, if (1) members would have standing, (2) interests are germane to org’s purpose, (3) claim/relief do not require member participation).
Justiciability:
Ripeness
Ripeness
Rule: Π is NOT entitled to review of a statute or regulation before its enforcement.
Exception: Pre-Enforcement Review IS OK IF:
Π will suffer immediate hardship, AND
Issues on record are fit for judicial review.
Justiciability: Standing
What are the 3
requirements for standing?
3 Requirements for Standing in Federal Court
Injury: actually, personally suffered; injunctive or declaratory relief requires likelihood of future harm (Lyons chokeholds)
Causation: (1) Δ caused the injury,
Redressability: favorable court decision likely to redress harm
Justiciability: Standing
Generalized Grievances
Generalized Grievances
Π cannot sue solely as citizen/taxpayer interested in having the government follow the law.
N Caution: does NOT include a harm that a large group of people actually and personally suffers.
Exception: taxpayer CAN challenge government expenditures as violating Establishment Clause


