Math & Statistics Tricks and Definitions Flashcards
(37 cards)
Multiplication Trick
If you round one number up, round
the other down to compensate
Division Trick
If you round one number up, round
the other up to compensate
Logarithmic Identities
log A x B = logA + logB
log A / B = logA - logB
log AB = B log A
log 1/A = -logA
Converting Common and Natrual Logrithms
log x = lnx / 2.303
log (n x 10m) ~ m + 0.n
Scientific Method
Determine whether sufficient background exists
and whether the question is testable
FINER Method
Determine whether a study is Feasible, Intersting.
Novel, Ethical, and Relevant
Hill’s Criteria
Help determine the strength of causal relationships.
Only temporality is necessary.
Small Sample Size
Amplifies the effects of statistical anomalies.
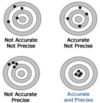
Defects in Precision and Accuracy
Create random or systematic variations in the data.
Bias
Systematic data error. Common types include selection bias, detection bias,
and the Hawthorne Effect. Minimized by proper participant selection,
blinding, and randomization.
Confounding
An analysis error that results when a casual variable is associated with two other variables
in a study but is not accounted for; may falsely indicate that the two variables are associated.
Generizability
Statistical significance and casuality do not make something generizable or a good intervention. Clinical significance and the target population must also be considered.
Mutually Exclusive
Two events that cannot occur together.
Independent
The probability of either event is not affected by the occurrence of the other.
P(A and B) = P(A) x P(B)
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B)
Null Hypothesis
A hypothesis of no difference; always the comparator.
p- value and significance level (α)
The probability that results were obtained by chance given that the null hypothesis is true.
- Compared to the selected significance level (α)- usually 0.05.
- For a directional test, if the p-value is greater than α, then we fail to reject the null hypothesis, which means there’s not a statistically significant difference between the two groups.
- If the p-value is less than α, then we reject the null hypothesis and state that there is a statistically significant difference between the two groups.
- If the alternative hypothesis is not directional, we compare the p-value to α/2 instead. Again, when the null hypothesis is rejected, we state that our results are statistically different.
Confidence Interval
A range of values believed to contain the true value with a given level of probability (confidence)
Box Plots
Contain information about measures of central tendency and distribution; may be comparative or single.
Also called box-and-whisker: the ends of the whiskers correspond to maximum and minimum value of the data set; outliers can be represented as individual points; the ends of the whiskers correspond to the largest and smallest values in the data that are still within 1.5 x IQR of the median.
Standard Deviation (σ)
A measure of how spread out values are from the mean; affected by outliers.
Approximately 68% of data points fall within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% fall within two standard deviations, and 99% fall within three standard deviations.
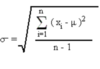
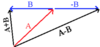
Vector Addition and Subtraction
Significance Level α
Set number we compare our p-value to in order to determine rejection or failure to reject hypothesis.
It is the level of risk we are willing to accept for incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis.
Type I Error
Incorrectly rejecting null hypothesis
Type II Error (β)
Incorrectly fail to reject the null hypothesis.
In other words, the likelihood that we report no difference between two populations when one actually exists.
Power (1 - β)
Probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis (reporting a difference between two populations when one actually exists)