Maternal/Perinatal Mortality Flashcards
What is maternal mortality/morbidity?
‘The death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management, but not from accidental or incidental causes’
Is the rate of maternal mortality increasing or decreasing?
The numbers of maternal deaths is reducing, and this is likely due to reduced pregnancys, but it is difficult to tell if the risk is reducing because the majority of maternal deaths are in developing countries.
[in the UK the rate has been falling but in last couple years has plateaued - likely due to obesity and immigration]
What is maternal mortality ratio? What does this represent?
- Number of maternal deaths during given time period per 100 000 livebirths during same time period
- Represents the risk associated with each pregnancy, i.e. the obstetric risk
What is the maternal mortality rate? What does this represent?
- Number of maternal deaths in given time period per 100 000 women of reproductive age, or woman-years of risk exposure, in same time period (may be at risk of mortality)
- Takes into account not only the obstetric risk, but also the frequency with which women are exposed to that risk.
What is definition of lifetime risk of maternal death? What does this represent?
- Probability of maternal death during a woman’s reproductive life, usually expressed in terms of odds
- Measure of women’s risk of becoming pregnant as well as the risk of dying while pregnant.
What is the proportionate mortality ratio?
- Maternal deaths as proportion of all female deaths of those of reproductive age—usually defined as 15–49 years—in a given time period.
What can we classify maternal deaths as?
Direct and indirect deaths.
Direct: Those related to obstetric complications during pregnancy, labour or puerperium (6 weeks) or resulting from any treatment received
Indirect: Those associated with a disorder, the effect of which is exacerbated by pregnancy (13%)

What are the main direct causes?
Haemorrhage, Sepsis, Preeclampsia, Obstructed labour or Unsafe Abortion
What are the main indirect deaths?
- Malaria is an example
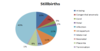
What are the main maternal deaths worldwide?

What are main maternal mortality in UK?

Please explain the 3 delay model and how this affects maternal mortality.
- Delay in decision to seek care: lack of understanding, low social status of women, socia-cultural barriers
- Delay in reaching care: geographical mountains, islands, lack of transport
- Delay in receiving care: supplies personnel, poorly trained staff
How can we prevent maternal mortality?
- Antenatal care: 4 visits, monitoring weight, BP, proteinuria, folic acid, malaria prophylaxis
- Skilled attendant at birth
- Emergency obstetric care: clean delivery, active management at 3rd stage, parental antibs/oxytocics/magnesium sulphate, manual removal of placenta. Blood transfusion, C section
Define:
- Stillbirth
- Early neonatal death
- Late neonatal death
- Perinatal mortality
- Infant mortality
- Child mortality
- Stillbirth: Birth of a dead baby after 20/ 24/ 28 weeks of gestation or weighing more than 500 g
- Early neonatal death: Death of a baby within the first week of life
- Late neonatal death: Death of a baby within the first 28 days of life
- Perinatal mortality: Includes stillbirth and neonatal mortality
- Infant mortality: Death of an infant within the first year of life
- Child mortality: Death of a child within the first 5 years of life
What is the current trend in perinatal deaths in the UK?
Reducing
What are the main causes for stillbirth?
Why do we have so many classifications?
We have so many classifications because we still cannot identify the cause of 43% of stillbirths.
What are the main points in essential newborn care?
- Ensuring that the baby is breathing
- Starting the newborn on exclusive breastfeeding right away
- Keeping the baby warm
- Washing hands before touching the baby



