Male Reproductive Histology Flashcards
(40 cards)
1
Q
- Tunica albuginea thickens posteriorly to form the _ testis containing _ testis
- Tunica albuginea is surrounded by _ (which has two layers)
- First layer surrounds scrotum?
- Second layer lines tunica albuginea?
A
- Mediastinum, rete
- Tunica vaginalis
- Parietal tunica vaginalis
- Visceral tunica vaginalis
2
Q
What forms a lobule?
A
- Seminiferous tubules + Leydig cells
3
Q
- Seminiferous tubules
- What are the two cell types present?
- What cells surround them?
- Ends of tubules are located near _ of testis
A
- Sertoli cells, spermatogenic cells
- Peritubular (myoid) cells
- Mediastinum
4
Q
- Ends become _ tubules (tubulus rectus)
- Proximal-_ cells
- Distal- _ cells
- Straight tubules are continuous with _
- Rete restis= anastamosing connection w/in mediastinum (simple cuboidal or low columnar epithelium)
A
- Straight
- Sertoli
- Simple Cuboidal
- Rete testis
5
Q
- Identify the labeled structures in the following image

A
Top-tunica albuginea
- Seminiferous tubules
6
Q
- Epididymis
- Contains _ ductules that are surrounded by a thin layer of smooth muscle and aid in peristalsis
- Lies along _ and _ surface of testis
- Important for sperm _
A
- Efferent
- Superior, posterior
- Maturation
7
Q
- Head of epididymis
- What is present?
- Histo characteristics?
- Body of epididymis
- What is present?
- Histo characteristics?
- Tail of epididymis
- What is present?
*
- What is present?
A
- Head
- Efferent ductules
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- Body
- Duct of epididymis (principal cells)
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium w/ stereocilia
- Tail
- Connects epididymis to ductus deferens
8
Q
- What is a unique feature about the epididymis
A
Smooth lumen

9
Q
- Identify the following

A
1) Principal Cells
2) Basal Cells
3) Smooth muscle
4) Dense connective tissue
10
Q
- Ductus (vas) deferens
- What type of epithelium is present
- What muscle layers are present
- What surrounds them?
A
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium w/ stereocilia
- Muscular wall
- Inner and outer longitudinal layers
- Middle circular layer
- Surrounded by loose CT and adipocytes
11
Q
- _ is the dilated portion of the vas deferens leading into the prostate
- _ mucosal folds that show glandular _
- Distal end receives ducts of the _ (forming the ejaculatory duct)
A
- Ampulla
- Taller, branched, diverticula
- Seminal Vesicles
12
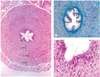
Q
- Key histological features of the ductus deferens
A
- FOLDED LUMEN
13
Q
- Spermatogenic cells
A
- Replicate and differentiate into mature sperm
- Originate from primordial germ cells in the yolk sac
- Organized in layers of progressive development between sertoli cells w/in seminiferous tubules
14
Q
- Spermatogonial phase
A
- Sperm stem cells become:
- Type A (stay as reserve stem cells or become Type B)
- Type B (enter meiosis to become mature sperm)
15
Q
- Primary spermatocytes come from _ division of Type B spermatogonia (n=?, d=?)
- Secondary spermatocytes come from _ of primary spermatocytes n=?, d=?)
- Spermatids come from _ of secondary spermatocytes n=?, d=?)
A
- Mitotic (n=2,d=4)
- Meiosis I (n=1,d=2)
- Meiosis II (n=1,d=1)
16
Q
- What are the phases of spermiogenesis?
A
- Golgi phase
- Cap phase
- Acrosome phase
- Mature phase

17
Q
- Golgi phase
A
- Hydrolytic enzymes from golgi form acrosome around the nucleus
- Creates ANTERIOR pole
- Centrioles migrate to POSTERIOR pole
18
Q
- Cap phase
A
- Acrosomal vesicle enlarges and spreads over nucleus and creates a cap
- Nuclear envelope attaches to acrosomal sac
19
Q
- Acrosomal phase
A
- Spermatid orients itself so head is embedded in Sertoli cell and points towards basal lamina
- Developing flagellum extend into lumen of seminiferous tubules
- Manchette is formed from cytoplasmic microtubules-involved in protein trafficking
20
Q
- Maturation phase
A
- Excess cytoplasm removed as residual bodies (taken up by Leydig cells) to create mature spermatozoon
- Spermatids released from Sertoli Cells into lumen of seminiferous tubules
21
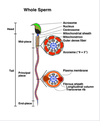
Q
- Structure of mature sperm
A
- Head
- w/ acrosome, nucleus
- Nucleus covered 2/3 by acrosomal cap (w/ hydrolytic enzymes)
- Tail
- Midpiece-mitochondria
- Principal piece-fibrous sheath
- End piece-axonemal complex (connects MTs together)
22
Q
- Sperm pathway
A
- Seminiferous tubules
- Straight tubule (tubulus rectus)
- Rete testis
- Efferent ductule
- Epididymal duct (body/tail)
- Ductus (vas) deferens
- Ejaculatory duct
23
Q
- Sertoli cells
- Epithelium type
- Function
- Bound together via _ complexes that form _ junctions and create a blood-testis barrier and basal/luminal compartment
- Secrete _
A
- Columnar w/ extensive apical and lateral processes
- Structural support/ organization to seminiferous tubules and developing spermatozoa
- Sertoli cell to sertoli cell
- ABP (binds DHT and T)
24
Q
- What cell type is indicated in the following image?

A
- Sertoli cells
25
* Tunica/Lamina Propria
* What happens to this during aging?
* What is associated with excessive thickening of this layer at a young age?
* Layers of myoid cells, create peristaltic waves helping move spermatozoa and testicular fluid
* Thickens, decreased rate of sperm production and reduced size of seminiferous tubules
* Infertility
26
* Myoid cells are located in the \_
* Spermatogonia are located on the _ side of the seminiferous tubules
* Spermatids are located on the _ side of the seminiferous tubules
* Lamina propria
* Basal
* Luminal

27
* Leydig cells
* Located in the \_
* Secrete _ and \_
* Histological features
* Interstitium
* Testosterone, Insulin Like Protein 3
* **Large, polygonal eosinophilic cells containing lipid droplets**
* **Crystals of Reinke-rod-shaped cytoplasmic crystals of androgenic hormones**

28
Functions of Testosterone during the following periods of development:
* Embryo
* Puberty
* Adulthood
* Embryo
* T needed for gonad development
* INSL3-descent of testes
* Puberty
* T-sperm production, accessory sex gland secretion, 2ndary sex characteristics
* **INSL3-**promotes meiotic divisions in seminiferous tubules
* Adult
* T-mainetenance of spermatogenesis, 2ndary sex characteristics, accessory sex glands
* Secrete **oxytocin** to stimulate contraction of myoid cells and move sperm towards efferent ductules
29
* What are the accessory sweat glands?
* Prostate
* Seminal Vesicles (2)
* Bulbourethral Glands (2)
30
* What is shown in the following image?

* Bulbourethral glands
31
* Seminal vesicles
* Paired _ glands on posterior surface of urinary bladder
* Parallel to _ of ductus deferens
* Excretory duct joins with ampulla of ductus deferens to form \_
* Layers?
* Secretion:
* pH
* Contents
* Tubular
* Ampulla
* Ejaculatory ducts
* Layers:
* Mucosa-folded to increase secretory surface area
* Smooth muscle-contraction during ejaculation
* Fibrous coat
* ***Pseudostratified columnar NON CILIATED***
* *Basal side: Short round cells*
* *Luminal side: Tall, non-ciliated columnar cells*
* Secretion
* Alkaline
* Fructose, AAs, ascorbic acid, prostaglandins to nourish sperm

32
* Bulbourethral glands
* Paired pea sized glands in **urogenital diaphragm**
* Joins with initial portion of spongy urethra
* **Simple columnar epithelium**
* **Secretions:**
* ****Alkaline
* Clear, mucus like with galactose, sialic acid, methylpentose
* Main portion of preseminal fluid
* **lubricares spongy urethra and neutralizes traces of acidic urine**
33
* Prostate
* Epithelium present
* Secretion
* Zones
* **Simple columnar or pseudostratified epithelium**
* Clear, slightly alkaline (7.29) to neutralize acidic environment of vagina
* 4 Zones
* Peripheral-palpable on DRE (prostate cancer)
* Transitional (BPH)
* Central
* Periurethral (right next to urethra)
34
* ***Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia***
* Occurs in Transitional zone (will develop in periurethral zone later in the disease)
* Nodular masses of epithelial cells
* Sx:
* Inability to void bladder
* Urinary frequency
* Nocturia
* Difficulty starting/stopping stream
* Excessive dribbling
* Dysuria
* 50% will show sx

35
* ***Prostate Cancer***
* Prostatic adenocarcinoma
* **Tumors occur typically in peripheral zone** (DRE makes this easily palpable)
* PSA (Prostate specific antigen) test used to monitor the progress of the disease
* Most cases are asymptomatic until late stages of the disease:
* Urinary freq
* Dysuria
* Hematuria
* Low back pain (metastasize to lower lumbar vertebrae)
36
* Semen is made up of secretions from what structures?
* pH =?
* How many sperm released per ejaculation?
* Testes, epididymis, ductus deferens, prostate, seminal vesicles, bulbourethral glands
* 7.7-neutralizes spongy urethra and vagina
* 300 mil, 20% abnormal, 25% immotile
37
* Pathway of sperm transport
* SEVEN UP
* Seminiferous tubules
* Epididymis
* Vas deferens
* Ejaculatory ducts
* nothing
* Urethra
* Penis
38
* Erectile tissue
* Comprised of irregular, interconnected _ with fibrocartillagenous stroma
* Deep a. of penis runs within the R/L \_
* Branches into Helicine arteries
* Blood fills sinuses-increases size and rigidity
* Sinuses anastamose with veins allowing blood drainage
* Engorgement of sinuses (during erection) compresses and restricts \_, blood trapped in sinuses, mainetenance of erection
* Vascular sinuses
* Corpus Cavernosum m
* venous outflow
39
* Erection is a _ response
* Comes from signals from _ nerves
* Stimulates release of _ and activates Gt and activates \_
* Leads to smooth muscle _ and increased bloodflow into sinusoids of erectile tissue
* Increased blood flow leads to _ compression in penis
* Compression of _ leads to swollen (tumescent) and rigid penis
* Parasympathetic
* Pelvic splanchnic
* NO, cGMP
* Smooth muscle relaxation (decreased concentration of Ca2+ in smooth muscle cells)
* Venous
* Veins
40
* _ initiates termination of erection (detumescence)
* Activation leads to _ of smooth muscle and _ blood flow to sinusoids of erectile tissue
* Decreased blood flow to the sinusoids, leads to opening of _ and release of blood from sinusoids
* _ breaks down cGMP and leads to _ in smooth muscle relaxation
* _ inhibitors used to treat ED
* Sympathetic nervous system
* Contraction, increased
* Veins
* **PDE (phosphodiesterase**
* **PDE inhibitors used to treat ED**


