Male Pelvic Viscera Flashcards
1
Q
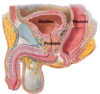
Label all:

A
2
Q
The prostate is a derivative of what embryonic structure?
A
urogenital sinus
3
Q
The vas deferens and seminal vesicles are derivatives of what embryonic structure?
A
mesonephric ducts
4
Q
The four parts of the male urethra:
A
- pre-prostatic (proximal)
- prostatic
- membranous
- spongy (distal)
5
Q
Shortest portion of the male urethra:
A
membranous portion
6
Q
Longest part of male urethra:
A
- spongy portion on ventral side of penis.
- opens externally.
7
Q
Label all:

A

8
Q
Ampulla of the Ductus (vas) Deferens:
A
- enlarged portion of vas deferens as it approaches prostate.
- stores sperm prior to emission.
- forms ejaculatory duct with seminal vesicle.
9
Q
Label all:
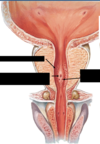
A

10
Q
Ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of:
A
ampulla of the vas and seminal vesicle.
11
Q
Seminal colliculus:
A
- elevation within prostatic urethra.
- remnant end of mesonephric ducts.
- surrounded by prostatic sinus.
12
Q
Prostatic sinus:
A
- surrounds seminal colliculus.
- where prostatic glands secrete fluid into prostatic urethra.
13
Q
Stroma of the prostate is composed of:
A
- collagen and smooth muscle.
- enlargement of stroma smooth muscle causes benign prostatic hyperplasia.

14
Q
Benign prostatic hyperplasia:
A
- increase in size/number of stroma and glandular cells in prostate gland.
- decreases size of prostatic urethra (radius) and urinary flow.
15
Q
Arterial blood supply to prostate:
A
- inferior vesicle artery.
- branch of internal iliac.





