Macrophages Flashcards
Monocytes
Properties:
- Round with Kidney shaped nucleus
- Phagosomes/lysosomes for phagocytosis and killing
- Circuate 3 days then enter tissues
Location:
- Bone Marrow
- Site of monocyte Production
- Blood
Function:
- Recruited to sites of tissues inflammation to become macrophages
Macrophages (M0)
Properties:
- Derived from Blood Monocytes
- Phagosomes contain killing chemicals and proteins
Location:
- see picture

Macrophage (M0) Function
Sentinels:
- Express PRRs
- Active Phagocytosis
- Trap and clear Particulate matter from circulation
Bacteria/partivle clearance from blood
Differs among species
Kupffer celss and macrophages on spleen:
- Rodents
- Dogs
Lung Pulmonary intravascular Macrophages:
- Cats
- Horses
- Ruminants
- pigs
Particle Capture by other routes
Aerosol Route:
- Nose
- Tracheal Cilia
- Bronchia & Bronchioles
- Alveolar macrophages in lung
Dermal Route:
- Antigen Trapped by macrophages/dendritic cells in skin
- Migrate to the lymph nodes
- Stimulate adaptive immunity
- Migrate to the lymph nodes
M1 Macrophage Polarization

M2 Macrophage Polarization

Microbial Killing Mechanisms of M1 Macrophages:
Oxygen Dependent
Phagosome:
- NADPH oxidase
- Superoxide anion
- Hydrogen peroxide
Phagalysosome:
- Nitric Oxide Synthase 2 (NOS)
- Oxidizes arginine to citrulline and NO
- NO combines with superoxide anion to produce NO free radicals
Microbial Killing Mechanisms of M1 Macrophages:
Oxygen Independent
Natural Resistance-associated macrophage protein (NRAMP)
- Transport divalent metals out of phagosomes
Lysozomes:
- Proteolytic enxyme degrades cell wall
Defensins:
- Make holes in pathogen cell walls
Acidic Pump:
- Add H+ ions and reduce the pH
Role of M2 Macrophages
Clean up dying/dead neutrophils
Produce Protease inhibitors neutralize neutrophil enzymes
Produce Growth Factors:
- Transforming growth Factor (TGF-b)
- Fibroblast growth Factor (FGF)
Macrophage Major Surface Receptors
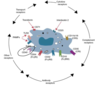
Cytokine Productn by Macrophages

Local Inflammation
IL-8: Chemotaxis of neutrophils
IL-1, TNF-a: Increase expression of selectins adn integrins
TNF-a: Enhance Killing of Virus/Bacterial infected cells and tumor cells by assembling NADPH oxidase
Positive Acute Phase Proteins
Concentration in blood Increases
- Complement proteins
- Fibrinogen
- Serum Protease Inhibitors
- Iron Binding Proteins
Negative Acute Phase Proteins
Concentration in the Blood Decrease
- Albumin
- stabilizes osmotic pressure of the blood
- Transferrin
- transport iron to tissue