M2: Tissues with Lab Image Identification Flashcards
Tissue Classification & Identification of Lab Images Covers some of the locations but isn't comprehensive (28 cards)
Just some tips:
- ‘Epithelial shapes’ are defined by the plasma membrane (not the nucleus)
- When classifying, start large and then work small (in regards to categories and sub-categories)
- Know FULL NAME; e.g. “if you’re looking at adipose, you need to know this is connective tissue, in the proper category, loose in nature, and it’s adipose”
What type of tissue is this?

Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissue
Hint: look at the plasma membrane shape. It is very squished/squashed looking.
What type of tissue is this?

Columnar Epithelial Tissue
Hint: Elongated column-like shape; no cilia
What type of tissue is this?

Cuboidal Epithelial Tissue
Hint: square/cube-like plasma membrane shape
Side-note: mainly glanduar; those concentric rings are cuboidal cells making up glands/ducts
What type of tissue is this?

Supportive__Connective Tissue__Fibrous Cartilage
(fibrous cartilage = fibrocartilage)
Hints/Characteristics: wavy lines (bunch of collagen fibers)
What type of tissue is this?

Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissue
What type of tissue are red blood cells (erythrocytes), WBC (leukocytes), and platelets?
Fluid Connective Tissue
What type of tissue is this?

Skeletal__Muscle Tissue
Note: big, multinucleated, obvious striations
cardiac muscle is branched, skeletal muscle is not
Where is transitional epithelial tissue found?
bladder and ureters
- Bonus Notes:*
- ureters are the tubes that transport urine from the kidney to the bladder*
- translational epithelial is unusual because it tolerates cycles of stretching*
What type of tissue is this?

Simple__Squamous__Epithelial Tissue
What type of tissue is this?

Connective Tissue Proper Loose Areolar
Hints:
- presence of fibers but not many, so this is loose and not dense in nature.
- Some of the fibers are long/straight. So you can rule-out reticular, because reticular fibers have a branched/root-like system appearance.
- You can rule-out adipose, as adipose has no fibers.
What type of tissue is this?

Connective Tissue Proper Dense Regular
Side Note: densely packed primarily parallel collagen fibers
What type of tissue is this?

Connective Tissue Proper Loose Reticular
Hint: fibers are those dark lines; the pink stuff are just various cells. So if you strip away all those cells, you don’t have many fibers left; so this is loose.
Reticular fibers are branched, they have a root-like system appearance similar to roots or branches
What type of tissue is this?
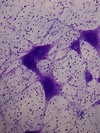
Nervous Tissue or more specifically Motor Neuron
- Bonus Side-Notes:*
- the large purple body is the cell body of a nerve cell, which has extentions coming from it that are axons/dendrites*
- motor neurons are in the PNS*
Fill-in-the-blank
When classifying/describing tissue types by the number of layers:
simple = ____ layer
stratified = ______ layers
When classifying/describing tissue types by layers:
simple = one layer
stratified = multiple layers
What type of tissue is this?

Connective Tissue Supportive Compact Bone
What type of tissue is this?

Connective Tissue Proper Loose Adipose
What type of tissue is this?

Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelial Tissue
Hint: looks similiar to columnar in it’s elongated shape, but the the give away/key-difference is all the cilia.
- Note: the professor once said he might use a different image, but if he did it would a be a better one that is more obvious*
- Reminder: review where found*
What type of tissue is this?

Supportive Connective Tissue Elastic Cartilage
Hints: lots of (elastic) fibers weaved between the chondrocytes
What type of tissue is this?

Supportive Connective Tissue Hyaline Cartilage
Side-Note: hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage.
Hints/Notes:
(1) you see really spaced out areas between cells (this space is called the matrix). Hyaline cartilage has “fluidy” matrix, where there are no obvious fibers in between the cells. Good for adding cushioning.
What type of tissue is this?

Cardiac__Muscle Tissue
Hints: branched, intercalated discs (those lines where cardiac cells connect)
Side-note: both cardiac and skeletal muscle have striations, but skeletal muscle cells are much larger with very obvious striations
What are the three types of Connective Tissue Proper that are Loose in nature?
areolar
reticular
adipose
Fill-in-the-blanks to finish the names of the epithelial tissue in the figure. (Click image to enlarge)

1 Simple Squamous
(Click image to enlarge)

- Where is simple squamous epithelial tissue found?
- Where is stratified squamous epithelial tissue found?
- simple squamous epithelia: lines blood vessels & air sacs in the lungs (aka alveoli or alveolar sacs)
- stratified squamous epithelia: the epidermis; outer layers of skin, mouth, vagina


