Lymphoma Flashcards
lymphoma vs leukaemia classification

Lymphoid tissue - locations and B cell vs T cell location
- Normal Locations: Regional lymph nodes, tonsils + adenoids (Waldeyer tonsillar ring), peyer Patches and appendix, and white pulp of the spleen
- Locaitons of B cells: Germinal follicles in lymph nodes, peripheral areas of the spleen white pulp
- Location of T cells:paracortex (parafollicular) in the lymph nodes, periarteriolar sheath in the spleen and thymus (primary site for T cell maturation)
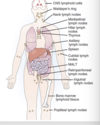
LYMPH Node organ labelled

Non-Hodgkins lymphoma -what is this and the epidemiology
Group of malignancies arising from cells of lymphocytic or histiocytic origin and thus typiclly originate within lymphoid tissue in which most often appear (eg, lymph nodes, tonsils, thymus, or Peyer Patches)
lymph nodes have a firm consistency and are fusedtogether. On cut section they have a “fish flesh” appearance
Epidemiology:
- Accounts for abotu 60% of adult lymphomas
- Greater than 80% are of B-cell oriin and derive from the germinal follicle
- Second most common cancer in AIDS
- Median age in adults is 65-70y/o
- Slight male predominance
- Approximately 1/3 arise from extranodal sites including stomacg (most common), Peyer patches, anterior mediastinum and CNS (particularly in AIDS)
- Anterior mediastinal sites can be asosicated with the superior vena-caval syndrome.
Classifications of Non-hodgkins lymphomas
Classified into low-(indolent) and high grade (aggresisve) lymphomas :
A. low grade lymphomas include follicular lymphoma )grades 1&2), chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL), small lymphocytic leukaemia (SLL) and most skin lymphomas
B. High-grade lymphomas include follicular lymphomas (grade 3B), diffuse large-cell lymphoma, mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, peripheral T-cell lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, burkitt lymphoma and acute lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukaemia
C. Diffuse large-cell lymphoma is the overall most common type of NHL (30% of cases). Second most common is folliculsr lymphoms (25% cases)
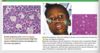
Whats this image show

- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Lymph node enlargement is typical.
- The lymph nodes have a firm consistency and are fused together.
- On cut section, they have a “fish flesh” appearance.
WHats this show

- CXR, upper anterior mediastinal mass in non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- This location can be assoicated with compression fo the SVC causing upper SVC syndrome
CHildhood Non-Hodgin Lymphoma
- Peak age is 5 to 15years
- Wheras Burkitt + small, noncleaved cell lymphoma (SNCL) predominate among those in 5-14years old, diffuse large-cell lymphomas (DLCLs) are more common among those 15-19.
- Generally more aggressive in children than adults
- As opposed to adults, most NHL that arises in childhood occur in extranodal sites (abdomen >mediastinal > outside head and neck region > Waldeyer ring, tonsils or cervical >skin ) and other sites.

What is childhood Non hodgkins lymphoma assoicated with
- ▪ Associated with congenital immunodeficiency syndromes:
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, ataxia-telangiectasia, X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome, severe combined immunodeficiency, X-linked agammaglobulinemia, severe combined immunodeficiency, and Chediak-Higashi syndrome
- ▪ Other associations include AIDS, immunosuppressive therapy, and various viruses

RFs for Non hodgkin lymphoma in children
Viruses:
- Epstein-bARR Virus (EBV): burkitt lymphoma. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma and primary CNS lymphpma (HIV)- associated with AIDS
- Human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV) Type I - Adult T-cell lymphoma or leukaemia
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV): B-cell lymphoma
Helicpbacter pylori:
- Produces malignant lymphoma of the stomach - deirves from mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) in the stomach
- Treatment of peptic ulcer disease caused by H.Pylori reduces the risk for developing this lymphoma.
Autoimmune disease
- Sjogren syndrome - salivary gland and GI lyphomas
- Hashimoto thyroiditis - malignant lymphoma arising within thyroid gland
Immunodeficiencysyndromes - Chromsoome isntability syndromes (Bloom syndrome), AIDs
Immunosuppressive therapy that is used to preent rejection in organ or bone marrow (BM) transplant patienta
High dose radiation that is used in treatment of hL
Chemical exposure (pesticides)
Follicular lymphoma schematic

Burkit lymphoma on histology
Patho of NHL

Common types of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma

Describe the basics of Precursor T-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma
- . Accounts for 40% of childhood lymphomas
(1) Primarily involves the anterior mediastinal and cervical nodes
(2) BM and CNS involvement are common - . Precursor T-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia
• Leukemic variant of T-cell lymphomas

Mycosis Fungoides (MV)
- Most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma characterised by infiltrtion of the sin by neoplastic CD4+ helper T)TH) cells
- Epidepmiology: usually occur in adults 40-60years of age
- Clinical:
- Begins in the skin (rash to plaque to nodular masses) - Metastases to lymph nodes, lung, liver and spleen
- Groups of neoplastic cells that invade epidermis are called pautrier micro-abscesses
- Sezary syndrome:
- Refrs to leukemia phase of mycosis fingoides
- Ciruclating malignant T cells are called Sezary cells.

WHta is tumour Lysis syndrome
Complication of nHL characterised by rapdi clel breakdown leading to hyperuriceaemia, hyperkalaemia, hyperphosphataemia, hypocalacemia, and acute renal failure (ARF)

Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Def = Mlaignant lymphoma arising from germinal centre B cells. Characterised by the presence of multinucleated giant cells called Reed-Sternberg (RS) within a mixed inflammatory infiltrate.
- Epidemiology:
- Accounts for abotu 40% of adult lymphomas
- More common in males (particularly in childhood) than females . EXception is nodular scleroising type more common in female
- More common in adults that children
- More common in whites than blacks
- Biomodal age distirbution in HL. 1st large peak 15-34, second smaller peak >50 and overall more at younger ages than NHL
- Most comon site of intiial involvement is in neck region
- EBV has been identified in certain types HL (60-70& of cases of mixed cellularity HL)
- Those infected with HIV infecions have higher incidence HL relative to uninfected pop
- Increased risk in smokers
- Defects may occur in cell mediated immunity (CML) in HL. Example - defects in skinr eactions to infection of common antigens
Types Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL)

Classifications of Hodgkins lymphoma
- Lymphocyte rich classical
- Nodular sclerosing classical (Most common)
- mixed cellularity classical
- Lymphocyte depleted classical
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant
Patho of hodgkins lymphoma
- Genertic susceptibility underlies HL in children
- Acitvation of NF-lB (Nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activared b cells) is common in classical HL
- NF-KB is activated by EBV or other factors
- When activated, it tirns on genes that promote proliferation of B cells

Hodgkin disease

Pathologic findings in Hodgkin lymphoma
Pathologic findings
▪ Involves localized groups of nodes and has contiguous spread to other lymph node groups
a. Most frequently involves cervical, supraclavicular, and anterior mediastinal lymph
nodes. A mediastinal mass in a young person is most often HL.
b. Cut section of involved lymph nodes has a bulging “fish-flesh” appearance
▪ RS cell is present
a. RS cell is the neoplastic cell of HL
(1) Positive for CD15 and CD30
(2) Most (not all) RS cell cells are of B-cell origin and are derived from lymph node
germinal centres
b. Classic RS cell
• Two mirror image nuclei, each with an eosinophilic nucleolus surrounded by a
clear halo
Reed-Sternberg cells
▪ RS variant: lacunar cell
(1) Not a “classical” RS cell
(2) Lacunar cells are nonlobulated or multinucleated cells with small nucleoli and
abundant, pale cytoplasm.
(3) Cell lies in a clear space, which is an artifact of fixation in formalin-fixed tissue.
(4) Present in the nodular sclerosis type of HL (Fig. 14-10 B)
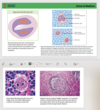
Diagnosis Hodgkin lymphoma
Presence of classic rS cell required to secure diagnosis
Hodgkin vs NHL
• HL less commonly involves Waldeyer tonsillar ring, mesenteric lymph nodes, and
extranodal sites than NHL.
Clinical findings and prognosis for Hodgkin lymphoma
▪ Constitutional signs include:
a. fever, unexplained weight loss, and night sweats (40% of cases)
b. pruritus (itchy skin)
c. Pel-Ebstein fever, an uncommon variant of fever
• Characterized by alternating bouts of fever followed by remissions
▪ Hematologic findings include:
a. normocytic anaemia (presenting symptom 40% of cases)
• Anaemia of chronic disease, immune haemolytic anaemia
b. painless enlargement of single groups of lymph nodes in the neck region
• Nodes become painful if the patient drinks alcohol
Chest pain, cough, and dyspnea usually indicate the presence of a large mediastinal mass or metastasis to the lungs.
▪ Primary factors that determine the prognosis.
a. Clinical stage is more important than the type of HL.
b. Majority have lymphadenopathy above the diaphragm (stages I and II), which
correlates with an excellent prognosis.
▪ Increased risk for developing second malignancies, usually acute myeloblastic leukaemia
(AML) or NHL
a. ↑Risk 2nd malignancies (AML, NHL)
b. Increased risk is related to treatment with radiation and alkylating agents
Progosis and treatment of hodgkin lymphoma
▪ Prognosis and treatment
- Majority are curable. Poor prognosis correlates with age >45 years, male gender, high stage, large mediastinal mass, and abnormal complete blood count (anaemia, lymphopenia)
- Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are used depending on the stage of the disease
Staging of Hodgkin lymphoma



