Lymphatics Flashcards
1
Q
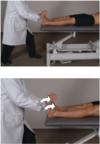
Thoracic Inlet MFR
A
Patient: supine
Physician: seated at head of table
- Hand placement: palms down over shoulders at cervicothoracic junction. Thumbs over posterior first rib, index fingers superior to clavicles at SC joints, middle fingers inferior to clavicles at SC joints.
- Assess for motion: superior/inferior, left/right, torsional
- Apply principles of direct or indirect myofasical release
- +/- release enhancing mechanisms

2
Q
Doming the Diaphragm
A
- Performed 2nd for lymphatic problems inferior to diaphragm
- Position: Pt supine with hips and knees flexed, physician at pt’s side facing cephalad
- Hand placement: thumbs inferior to xiphoid process and pointing cephalad
- Instruct pt to take a deep breath and exhale
- On exhalation, press thumbs posteriorly and superiorly
- Push further on exhalation, resist on inhalation
- Repeat 3-5 times

3
Q
Suboccipital Release
A
- 2nd for HEENT lymphatic problems
- Position: Pt supine, physician seated at head of table
- Hand placement: finger pads are placed in the suboccipital region
- Apply anterior-superior pressure
- Kneading: pressure may be slowly and rhythmically applied for 2 minutes or until tissue texture changes occur.
- Inhibition: apply a constant inhibitory pressure for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
4
Q
Ischiorectal Fossa Release
A
- 3rd for lymphatic problems in the lower extremities
- Will not be covered in this lab
- Addresses somatic dysfunction in the pelvic diaphragm
- Treatment of any sacral and pelvic somatic dysfunctions also improves pelvic diaphragm function

5
Q
Effleurage and Petrissage
A
- Treatment of upper and lower extremity lymphatic congestion
- Position: Pt supine, physician on side to treat
- Effleurage: induce stroking force distally to proximally
- Petrissage: induce a kneading/twisting force distally to proximally

6
Q
IT Band Effleurage
A
- Treatment of lower extremity lymphatic congestion
- Position: Pt lateral recumbent with the affected side up, physician on side to treat
- Hand placement: cephalad hand on pt’s greater trochanter for stabilization. With caudad hand, make a “C” shape and contact pt’s IT band.
- Start halfway between the greater trochanter and knee, stroking distal to proximal in a distal proximal fashion
- Continue to 1-2 minutes

7
Q
Tapotement
A
- Treatment of chest, thoracic, lumbar lymphatic congestion
- Position: Pt prone, physician at pt’s side
- Apply rhythmic forces to the thoracic region
- Hacking: “karate chop” with ulnar side of hands
- Cupping/Clopping: cup hands into a slight “C” shape
- Slapping: use palmar surface of hands

8
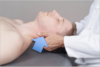
Q
Submandibular Drainage
A
- Treatment of HEENT lymphatic congestion
- Position: Pt supine, physician seated at head of table
- Hand placement: fingertips below the inferior rim of the mandible
- Direct fingers superiorly and evaluate for ease/restriction of motion
- Apply principles of myofascial release, may use direct or indirect treatment

9
Q
Cervical Chain Drainage
A
- Treatment of HEENT lymphatic congestion
- Position: Pt supine, physician seated at head of table
- Hand placement: Using caudad hand, place palmar aspect of fingers over the sternocleidomastoid (SCM) near the angle to the mandible. Use cephalad hand to stabilize.
- Gently roll along the SCM muscle in a milking fashion, working caudad
- Treat one side at a time to prevent pressing on carotid sinuses bilaterally

10
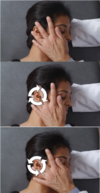
Q
Auricular Drainage
A
- Treatment of HEENT lymphatic congestion
- Position: Pt supine, physician at pt’s side
- Hand placement: using caudad hand, place 3rd and 4th fingers in front of and behind ear, respectively. Use cephalad hand to stabilize pt’s head
- Apply a clockwise and a counterclockwise motion
- Continue for 30 second to 2 minutes
11
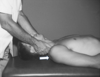
Q
Cervical Stroking
A
- Treatment of HEENT lymphatic congestion
- Position: Pt supine, physician at head of table
- Hand placement: hands along cervical paravertebral muscles
- Slowly stroke the region in a cephalad to caudad direction
12
Q
Pectoral Traction
A
- Position: Pt supine, physician standing at head of table
- Hand placement: grasp inferior to pt’s clavicles at anterior axillary fold
- Extend arms and lean back to apply cephalad traction bilaterally
- Pull when pt inhales and resist on exhale
- Repeat 5-7 times

13
Q
Rib Raising (Supine)
A
- Position: Pt supine, physician sitting on side to treat
- Hand placement: grasp ipsilateral posterior/inferior rib angles (lateral to transverse processes) by flexing fingers
- Starting with T12, apply sustained and/or rhythmic anterolateral traction by rocking backward/leaning elbows into the table. Continue up ribs.

14
Q
Rib Raising (Seated)
A
- Position: Pt seated with arms crossed, physician standing facing pt. Pt crosses arms and leans forward toward physician.
- Hand placement: grasp bilateral posterior/inferior rib angles (lateral to transverse processes)
- Starting with T12, pull superiorly and toward the physician in a rhymthmic fashion. Continue up ribs.

15
Q
Thoracic Pump (Repetitive/Oscillatory)
A
- Position: Pt supine, physican at head of table
- Hand placement: place thenar eminence of each hand inferior to clavicles with fingers spread over upper rib cage OR over the sternum. Offer women a pillow or place their hands under yours.
- Have the patient take a deep breath and exhale fully
- At the end of exhalation, apply rhythmic posterior inferior pumping. Rate should be 120x/min (2x/sec).
- Continue for several minutes.