lungs Flashcards
how do you determine if penetration is adequate in a PA CXR
YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO SEE THE THORACIC SPINE THROUGH THE HEART SHADOW Inspiration: should see at least 8-9 posterior ribs
how do you determine if inspiration is adequate in a PA CXR
Inspiration: should see at least 8-9 posterior ribs
how do you determine if rotation is adequate in a PA CXR
rotation: spinous process should fall equidistant b/w the medial ands of the clavicle
how do you determine if magnification is adequate
AP films magnify only slightly
angulation adequate?
clavical normally has an S shape and medial end superimpose onto 3rd or 4th rib
if you can not see the htoracic spine through the heart on a PA CXR it is known as
underpenetrated
erros of with underpenetration
1) L lung base may appear opaque mimicking or hiding true disease in the L lower lung field 2) Pulmonary markings (i.e. mostly the blood vessels in the lung) may appear more prominent than they actually are leading to a false impression of disease like CHF or pulmonary fibrosis
what is the solution for a underpentrated CXR that mimics LL lung dz
confirm with lateral CXR
what to do if underpenetration makes CXR look like CHF
look for other signs of CHF lateral films for the presence of increase markings airspace dz effusions at the left base that you suspect
pitfall of poor inspiration
incomplete inspiration can lead to exaggeration of lung markings and heart size ○ Lung hyperexpansion is a sign of obstructive lung disease
how do you tell the adequacy of a cxr
RIP MA rotation inspiration penetration magnification angulation
If spinous processes closer to left clavicular head what can we infer about roation in a CXR
pt is rotated to their right
f spinous processes closer to right clavicular head what cna we infer about rotation in the CXR
pt is rotated to their left
How can you tell if it’s a AP or a PA film
is it a PA or AP film? (if there’s a lateral, it’s a PA!)
what are the problems with poor rotation
significant rotation may alter expected contours of the heart and great vessels, the hila and the hemidiaphragms
when do we get a CXR
SOB Chest pain Fever Cough Weight loss Trauma Lines/Tubes Foreign bodies
What are we looking for with a CXR
Pneumonia, infection Pleural effusion Pneumothorax Pulmonary edema Cancer, mass Heart size Mediastinum Perforated viscous Much, much more…
why do you want hands on hips or suspended above the head
to avoid scapula covering thorax
Lateral decubitus film (far right) is used to see if
Lateral decubitus film (far right) is used to see if a pleural effusion “layers out” if it doesn’t layer out that means a thorsocopy probably needs to be done
minor lung fissures are more likely to be seen on the
right side
mediastinum masses will nee
lateral films is the mediastinum mass locator compartments are only used for ddx
compartments
anterior, middle, posterior mediastinal compartment superior is used to be specific
what is this

lordotic view to highlihgt apex pancoast tumor
how wide should the mediastinum be?
no more than 8cm unless the pt is supine
how do you tell the normal heart size?
the cardiac width at the widest point should be less than half of the width of the entire thoracic cavity. If the width of the cardiac sillouette is more than half of the entire chest then the heart is enlarged (might be plueral effusion, cardiomegaly, spurious)
when does the heart appear falsely enlarged?
when it is squished (pregnancy)
pectus excavatum
AP
obesity
epiration
bony abnormalities: kyphosis and pectus
pericardial effusions: water bottle shape even though the heart is normal size
what view is more sensitive for lateral effusions
Lateral view is more sensitive for small effusions.
Lateral - 75ml to blunt
Anterior - 200-300ml to blunt
what are some findings you might see with a pleural effusion
Concave meniscus
Diaphragm, liver silhouetted
Fissures opacified? from fluid collecting
Loculated? Lateral decubitus
how should you approach the lungs
periphery first! do not skip ahead
then scan back and forth noodle style
describe lung opacities
Well defined (discrete) or ill defined borders?
Infiltrate? Air Space or Interstitial? Air bronchograms?
Nodule (<3cm)? Mass (>3cm)? Appear solid? Calcified? Cavitary?
Dense consolidation or patchy infiltrate?
Air-fluid level?
Unilateral? Bilateral? Multiple? Disseminated?
Where is it located??
air bronchogram
fluid is around the thing that hold the air
silhouette sign
same density of overlaping sturctures that allows you to tell the location of the infultrate on one film
if the diaphragm is obscured what can you determine about the location based on the silhouette sign
RLL and LLL infiltrates may create silhouette sign with the diaphragm (on PA, AP)
RML and Left Lingular (LUL) infiltrates may create a silhouette sign with
● RML and Left Lingular (LUL) infiltrates may create a silhouette sign with the cardiac border (on PA, AP)
● Fluid-filled lung will obscure normal border of the structure it is anatomically contiguous with (same density) this is known as a benefit of the
silhouette sign
Left heart border (left ventricle) is obscured
Lingula
Right heart border (right atrium) if obscured
Right middle lobe
Left hemidiaphragm if obscured
Left lower lobe
Progressive increase in density of spine from top to bottom on lateral CXR is known as a
spine sign
spine sign is indicative of
indicates a lower lobe process
(normally, thoracic spine density decreases - becomes less white)
● Infiltrates can be hidden behind the heart on what type of films
● Infiltrates can be hidden behind the heart on PA/AP films → always check the lateral!
look for spine sign on lateral
Lucencies are what?
Lucencies are black areas (black = air)
Lucencies are indicative of what etiologies
Possible etiologies: pneumothorax, bullae from COPD, cystic structures
Prominent vasculature in upper lobes =
“cephalization”
● Cephalization is a sign of
pulmonary venous hypertension.
Vascular Markings are seen as what on CXR
Prominent central vasculature with elevated pulmonary artery pressure
● Engorged hilar vessels, azygos
Reasons for vascular markings on film
CHF, PULMONARY EDEMA, MITRAL STENOSIS, RENAL FAILURE, SMOKE INHALATION
tip of ET tube should be where
Tip should be located in the trachea about 3-5cm above the carina (roughly half the distance between
the medial ends of clavicles and the carina)
chat are the advantages of CT of lungs
provides details about size, extent, character
indications for lung CT
Lung nodules / masses / staging of malignancies, systemic lung disease, pleural effusions, PE, aorta,
mediastinal masses, trauma
obliterated retrosternal airspace indicates
anterior mediastinal mass
an increased retrosternal space indicates
pulmonary emphysema
Thickening of the fissure by fluid is almost always associated with
other signs of fluid in the chest, such as Kerley B lines and pleural effusions
Thickening of the fissure by fibrosis is the more likely cause if
there are no other signs of fluid in the chest.
why would you see the loss of vertebral height on a CXR
Degeneration of the disk can lead to narrowing of the disk space and the development of small, bony spurs (osteophytes) at the margins of the vertebral bodies.
▪
When there is a compression fracture, most often from osteoporosis, the vertebral body loses height.
MIP stands for
MIP stands for maximum intensity projection (CT) and is a way to display certain structures of a given density, preferentially making them stand out more easily.
The normal relationship between the bronchus and its accompanying pulmonary artery is that the artery is usually ______than the bronchus. In bronchiectasis, that relationship is reversed, with the bronchus becoming ____the artery (signet-ring sign)
he normal relationship between the bronchus (solid white arrow) and its accompanying pulmonary artery (dotted white arrow) is that the artery is usually larger than the bronchus. In bronchiectasis, that relationship is reversed, with the bronchus becoming larger than the artery (signet-ring sign)

The trachea, usually oval shaped, is about ____- cm in diameter on CT
The trachea, usually oval shaped, is about 2 cm in diameter.
In most people, there is a space visible just underneath the arch of the aorta but above the pulmonary artery called the _______ and it is an important landmark because
In most people, there is a space visible just underneath the arch of the aorta but above the pulmonary artery called the aortopulmonary window.The aortopulmonary window is an important landmark, because it is a common location for enlarged lymph nodes to appear.
seen here as the white arrow in the left picture

The minor fissure travels in the same horizontal plane as an_____ CT image so that it normally is not visible, except in the ____or _____
The minor fissure travels in the same horizontal plane as an axial CT image so that it normally is not visible, except in the sagittal or coronal plane

cardiogenic interstitial edema (early) is characterized by
fluid in the fissures
kerley b LINES
PLEURAL EFFUSIONS
Peribronchial cuffing
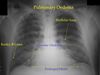
alveolar airspace edema late CHF is characterized by
bilateral fluggy pathy indistinct airspace densities
bat wing
pleural effusions commonly no air bronchogram


