Lower Limb: Proximal Neurovasculature Flashcards
(42 cards)
What are the motor functions of the sciatic nerve?
Tibial portion:
- Posterior compartment of thigh excl. short head of biceps femoris
- Hamstring component of adductor magnus
- All muscles in posterior compartment of leg and sole of foot
Common fibular portion:
- Short head of biceps femoris
- All muscles in anterior and lateral compartments of the leg
- Extensor digitorum brevis.
What are the sensory functions of the sciatic nerve?
Tibial portion:
- Skin on posterolateral and anterolateral leg
- Sole of foot
Common fibular portion:
- Lateral leg
- Dorsal aspect of foot
What does the pudendal nerve innervate?
What are its nerve roots?
S2-S4
Motor:
- Skeletal muscles of perineum
- External urethral sphincter
- External anal sphincter
- Levator ani.
Sensory:
- Penis
- Clitoris
- Skin of perineum
What nerves are produced from the lumbar plexus?
What are their nerve roots?
Subcostal nerve: T12
Iliohypogastric nerve: L1
Ilioinguinal nerve: L1
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh: L2, L3
Femoral nerve: L2,3,4
Genitofemoral nerve: L1, 2
Obturator nerve: L2,3,4
Lumbosacral trunk: L4,5

Describe the course of the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh
What does it innervate?
What are its nerve roots?
Where can it be compressed?
What are the symptoms of this?
- L2-L3
- Emerges superficial to the sartorius muscle under the inguinal ligament.
- Enters enterior thigh close to ASIS where it can be compressed (often by underwear, belts etc) = meralgia paraesthetica
- Innervates anterior and lateral skin of thigh
Symptoms:
- Paraesthesia to anterior lateral thigh
What passes through the femoral triangle?
Lateral to medial:
- Femoral Nerve
- Femoral Artery
- Femoral Vein
- Lymphatics
(NAVL)
What are the borders of the femoral triangle?
Superior: Inguinal ligament (ASIS to pubic tubercle)
Lateral: Sartorius muscle
Medial: Adductor longus muscle
How is the femoral artery located in the femoral triangle?
Femoral artery enters at mid inguinal point (halfway between pubic symphysis and ASIS) +/- 1cm
Femoral vein sits roughly 1cm medial
Nerve sits roughly 1cm lateral
What is the adductor canal?
What are its borders?
What does it contain?
Canal extending from the apex of the femoral triangle to the adductor hiatus of the adductor magnus. Runs deep to sartorius.
Borders:
- Anterior: sartorius
- Lateral: vastus medius
- Posterior: adductor longus and adductor magnus
Contains:
- Superficial femoral artery
- Femoral vein
- Saphenous nerve
Describe the blood supply to the lower limb

What could be at risk in a pelvic ring fracture?
Laceration of iliac arteries
What artery is the main blood supply to the lower limb?
How does it travel down the lower limb?
Femoral artery
- Enters femoral triangle at 1.5cm medial or lateral the mid inguinal point
- Exits at the adductor canal at the apex of the femoral triangle
- Passes through the adductor hiatus to the popliteal fossa where it becomes the popliteal artery.
What can anterior compartment syndrome cause?
Occlusion of the femoral artery causing no distal arterial supply to the lower limb- ischaemia
Describe the inguinal lymph nodes
What do they drain?
Superficial inguinal lymph nodes:
- Horizontal group sit below inguinal ligament
- Vertical group follow proximal part of great saphenous vein
Deep inguinal lymph nodes:
- Located in femoral canal (Cloquet’s nodes) and medial to femoral vein
Drain:
- Lower limb
- Perineal region
- Penis
- Lower anal canal
- Lower vagina
- Anterior labia majora/ scrotal skin

What can the great saphenous vein cause in the femoral triangle as it runs to meet the femoral vein?
Saphena varix
Label the parts of the tibia and fibula on the diagram
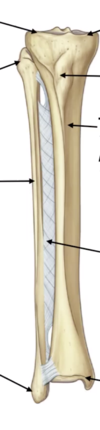
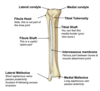
Label the compartments of the leg, bones and neurovasculature on the diagram


What gait could patients adopt if they have damage to the anterior compartment of their leg?
Damage to anterior compartment = foot drop
Circumduction gait
High stepping gait with toe landing
What is the arterial supply of the anterior compartment of the leg?
Anterior tibial artery
What is the arterial supply to the lateral compartment of the leg?
Fibular artery
What is the arterial supply to the posterior compartment of the leg?
Posterior tibial artery
What type of joint is the knee?
What movements is it capable of?
Modified synovial hinge joint
- Flexion
- Extension
- Rotation (medial and lateral)
Where is the knee joint line palpable?
Palpable posteriorly
(Sits approx 2cm distal to the skin crease)
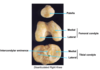
Which 3 bones form the knee joint?
What are the articulations?
Patella
Femoral condyles: medial and lateral
Articulations:
- x2 femero-tibial
- x1 femero-patellar