Lipoprotein Metabolism, Cardiovascular Disease and Obesity Flashcards
3 features of atherosclerotic lesions
Fibrous cap Foam cells (macrophages full of cholesteryl ester) Necrotic core (full of cholesterol crystals)
4 examples of plasma lipoproteins from biggest to smallest
Chylomicrons VLDLs (both rich in triglycerides) LDLs (main cholesterol carriers) HDLs (HDL2 > HDL3)
Which lipoprotein is cholesterol stored in the most
LDLs

Which lipoprotein is important after a meal?
Chylomicrons important in cholesterol transport after a meal Their cholesterol content in fasted state is very small
Cholesterol absorption
Cholesterol entering the intestines comes from two sources: the diet and the bile
Most of the cholesterol coming down into the upper small intestine is derived from the bile duct
Cholesterol is then solubilised within mixed micelles (in which the major components are bile acids)
It is then transported across the intestinal epithelial brush border by NPC1L1
- Main determinant of cholesterol transport going into the lymphatics, and then to the liver
There are two transporters (ABC G5, ABC G8) that transport cholesterol back into the intestinal lumen
The balance between these three transporters determines the net amount of cholesterol absorbed

Where are bile acids reabsorbed?
Bile acids will travel all the way down to the terminal ileum before being reabsorbed.
Cholesterol metabolism in the liver: HMG CoA reductase
On arrival at the liver, cholesterol downregulates the activity of HMG CoA reductase. HMG CoA reductase is main enzyme involved in cholesterol synthesis from acetate and mevalonic acid. Therefore, the amount of cholesterol synthesised in the liver depends on the amount of cholesterol absorbed at the intestine.
People who are efficient at absorbing cholesterol have low rates of cholesterol synthesis, and vice versa.
the two fates of cholesterol in the liver
Hydroxylation by 7-hydroxylase into bile acids
- The bile acids will then be excreted via the bile ducts.
Esterified by ACAT enzyme to produce cholesterol esters
- Together with triglycerides and ApoB, cholesterol esters are incorporated into VLDL particles (which involves the MTP transfer protein).

Cholesterol packaging in the liver (MTP, VLDL/LDL/LDLr)
MTP packages cholesteryl ester to VLDL
LDLs transport cholesterol from the liver to the periphery to cells that have LDL receptors
- VLDL is the main precursor of LDL
- After circulation in the plasma for 3-4 days, LDLs are taken up by the liver via LDL surface receptors

What is the role of HDL
HDLs pick up excess cholesterol from the periphery (involves ABC A1, which mediates the movement of free cholesterol from the peripheral cells to the HDL).

What is the role of CETP (cholesteryl ester transport protein)?
CETP mediates the movement of:
- Cholesterol ester from HDL to VLDL
- Triglyceride from VLDL to HDL
Following this process, some of the HDL cholesterol ester is taken up by the liver via an SR-B1 receptor.

Trigylyceride transport: chylomicrons and VLDL
VLDL = major triglyceride transporter in fasting state, it is endogenously synthesised (from the liver)
fasting state = little triglyceride in chylomicrons, have short life-span so following a fatty meal, there will be a peak in chylomicrons, but then they rapidly disappear

triglycerides -> chylomicrons
Triglycerides are hydrolysed into fatty acids
They are then re-synthesised into triglycerides
These resulting triglycerides are transported via chylomicrons into the plasma
What happens to chylomicrons containing triglycerides?
Chylomicrons are then hydrolysed into free fatty acids (FFA) by lipoprotein lipase enzyme (present in capillaries, particularly in relation to muscles). These free fatty acids are partly taken up by the liver and partly taken up by adipose tissue.The liver resynthesises these free fatty acids into triglycerides and packages them into VLDLs. VLDLs will also be acted upon by lipoprotein lipase to liberate the free fatty acids.

What are the 4 main dyslipidaemias?
Hypercholesterolaemias
Hypertriglyceridaemias
Mixed hyperlipidaemia
Hypolipidaemias
What is the cause of primary hypercholesterolaemia
NOT SECONDARY to any other disorder
usually implies a GENETIC bases
most important to consider is familial hypercholestolaemia
Familial hypercholesterolaemi (type II)
Which genes
Increases risk of premature coronary disease by 5-10%
Dominant mutations of:
- LDL receptor
- ApoB gene (major protien in LDL)
- PCSK9
Recessive very rare = LDLRAP1
Clinical feature of familial hypercholesterolaemia
Homozygous = corenal arcus
Heterozygous (common)
- corneal arcus
- xanthelasma
- tendon xanthomata (achilles tendon is thickened and roughened)
Atheroma of aortic root in familial hypercholesterolaemia homozygote
atherosclerosis affecting aortic root
impinges on coronary ostia (entries into coronary arteries)
these patients would pass away in teenage years due to coronary infsufficiency
LDL receptor function (in what cases is FH more severe)
The phenotype of the mutation will depend on which part of the LDL receptor is affected by the mutation (e.g. if there is a large mutation in the ligand-binding region of the receptor, the disease will be more severe.
PCSK9 mutation (FH)
chaperone protein = bind to LDLr to promote its degradation
gain of function mutation in FH -> increased breakdown of LDLr -> high LDL levels
Other types of primary hypercholesterolaemias
Polygenic hypercholesterolaemia:
- another form of primary hypercholesterolaemia that is caused by multiple gene mutations (NPC1L1, HMGCR and CYP7A1)
Familial hyperalphalipoproteinaemia:
- an increase in HDL which is caused by deficiency of CETP:
- relatively beign
- risk of premature coronary disease is not as pertinent – this is associated with longevity
Phytosterolaemia:
- a disease in which plasma concentrations of plant sterols are increased (namely sitosterol and campesterol). It is due to mutations in ABC G5 and ABC G8
- rare
- the main function of ABC G5 and ABC G8 is to prevent the absorption of plant sterols
- premature atherosclerosis is very common in this condition – plant sterols are just as atherogenic, if not more so, than cholesterol itself
Primary hypertrigyleridaemia: Familial Type I
cause
mechanism
test tube
what sign can you see in some patients
deficiency in LPL/ApoC II (activates LPL)
LPL degrades CM
refrigerate overnight -> CM layer
eruptive xanthomatosis: when very high cholesterol/lipids. Firm, yellow, waxy, pea-like bumps on the skin are surrounded by red halos and are itchy

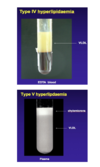
Primary hypertriglyceridaemia: Familial Type IV and V
mx for Type I, IV and V
Familial Type IV: caused by increased synthesis of triglycerides
- The cause is unknown
- This test tube shows whole blood – there are no chylomicrons here
- The white substance is primarily VLDL (chylomicrons can float to the top, whereas VLDLs don’t)
Familial Type V: due to deficiency of ApoA V
- This is a more severe version of Type IV
- After overnight standing, there is a mixture of chylomicrons and VLDL
- Chylomicrons have floated to the top
Mx: reduce uptake of fat (diet)
Primary mixed hyperlipidaemia: familial dysbetalipoproteinaemia (type III)
what gene
signs
rare
aberrate form of ApoE 2/2 (normal type is ApoE 3/3) = homozygous phenotype
yellowing of the palmar crease (palmar striae) and eruptive xanthomas on elbows

Other primary mixed hyperlipidaemias
Familial combined hyperlipidaemia
- Some people in the family will have high cholesterol and other will have high triglycerides (it is uncertain why this happens).
Familial hepatic lipase deficiency
- Another type of mixed hyperlipidaemia.
Secondary hyperlipidaemia causes
Pregnancy
- In pregnancy, there is always an increase in lipoproteins. A patient with the Type I Primary Hypertriglyceridaemia (lipoprotein lipase deficiency) and then fall pregnant, this can become a major problem (may lead to pancreatitis and infant/maternal death).
Exogenous sex-hormones
- These can cause increases in lipoproteins (particularly, oestrogen-containing compounds cause an increase in triglycerides).
Diabetes
- Diabetes is often associated with hypertriglyceridaemia (as with all the other metabolic secondary causes in the table). Diabetic patients may have eruptive xanthomas all over their bodies. Another metabolic disorder associated with hypertriglyceridaemia is progressive partial lipodystrophy.
Nephrotic syndrome (CHOLESTEROLAEMIA)
- The loss of protein in the urine in combination with a low serum albumin _activates LDL synthesis -> very high cholesterol level_s in the nephrotic syndrome. If you ever have a patient with a markedly increased cholesterol, check the urine protein content.
Chronic renal failure, on dialysis or post-transplant
- This gives rise to triglyceride disorders.
Obstructive liver disease (CHOLESTEROLAEMIA)
- This can give rise to a particular form of hypercholesterolaemia. Primary biliary cirrhosis can give rise to xanthelasmas.
Excess alcohol consumption
- Alcohol consumption in excess is a very common cause of hypertriglyceridaemia.

4 types of hypolipidaemias
A-lipoproteinaemia (LDL/VLDL)
- A rare, autosomal recessive disorder
- The patient has extremely low levels of cholesterol (particularly LDL and VLDL cholesterol)
- This is due to an inherited deficiency of MTP (microsomal triglyceride transfer protein)
Hypo-lipoproteinaemia (LDL)
- An autosomal dominant disease involving mutations of the ApoB gene -> truncated ApoB protein
- Causes low levels of LDL
Tangier Disease (HDL)
- Tangier disease involves an HDL deficiency
- Caused by mutations in ABC A1 (mediates movement of cholesterol from peripheral cells into HDL)
Hypoa-lipoproteinaemia
- Sometimes caused by mutation of ApoA1
Atherosclerosis = LDL mechanism
Atherosclerosis is particularly associated with increases in LDL (other risk factors too)
The LDL becomes oxidised once it has penetrated the vascular wall
Once oxidised, it gets taken up by macrophages
Inside the macrophages, the cholesterol within the LDLs becomes esterified à foam cells
The cholesterol in the arterial wall is often separated from the lumen by a thin, fibrous cap. This cap can easily rupture under some abnormal stress (e.g. intense exercise). This results in a thrombus.
3 fates of a thrombis
Heal
- When the fissure heals, the thrombus is ‘buried’ and this increases the overall size of the plaque.
Become a mural thrombus
- A mural intraluminal thrombus/intraintimal thrombus does not fully occlude the artery, but partially occludes it.
Become an occlusive thrombus
- This will block the artery and give rise to a myocardial infarct.

Lipid regulating drugs (5)
Statins (e.g. atorvastatin) are the main way of reducing LDL cholesterol
- Up to a 50% reduction with a decent dose of an appropriate statin
- Slight increase in HDL and modest decrease in triglycerides
- Statins have been around since 1989
- They reduce total and coronary mortality by 12% and 19% respectively
- They reduce major vascular events by 25% for every 1 mmol/l reduction in LDL cholesterol
- A large part of the 50% reduction in CVS mortality in England can be put down to statins
Nicotinic acid showed potential as it causes a significant increase in HDL
- Lowers LDL slightly, increases HDL significantly and reduces triglycerides
- However, it has now been removed from the market due to its side-effect profile
Fibrates (e.g. gemfibrozil) are not brilliant at modifying levels of LDL or HDL
- However, they are very good at lowering triglycerides
Ezetimibe is a cholesterol absorption blocker (blocks NPC1L1)
- doesn’t have much of an effect on HDL and LDL levels
Colestyramine is an anion-exchange resin that binds to bile acids and reduces their absorption
- Bile acids cannot be reabsorbed, and the liver sense this
- The liver produces more bile acids (which are made from cholesterol)
- This stimulates cholesterol catabolism, and an overall reduction in circulating LDLs

Lipoprotein A importance
Lipoprotein A
- large lipoprotein made by the liver.
- it is a cardiovascular risk factor
- should be measured once (using isoform insensitive assay) in subjects at intermediate/high CVD/CHD risk, including FH, or with premature/statin-resistance CVD).
- a desirable level of lipoprotein A is <500 mg/L.
- treatment should primarily be nicotinic acid, 1-3 g/day. In refractory cases, weekly LDL-apheresis is effective.
Treatment of obesity
Hypocaloric diet and exercise (require willpower and commitment)
Iatrogenic malabsorption (Orlistat 120 – 360 mg daily)
- NOTE: this is a pancreatic lipase inhibitor
- Fat is not hydrolysed -> passes through the digestive system unabsorbed
- Consequence: steatorrhea
Bariatric surgery (if BMI > 40)
Major forms of bariatric surgery (3)
Gastric banding
- The size of the stomach is reduced using a band; the patient feels full even after a small meal
Roux- en-Y gastric bypass
- The upper jejunum is sectioned, and the distal part of the jejunum is anastomosed to the stomach. A portion of the jejunum is no longer absorbing anything, because the bile acids and pancreatic enzymes mediating absorption of lipid are introduced lower down in the tract.
Biliopancreatic diversion
- A reduced size in the stomach, much of the jejunum that is no longer in circuit. There is a lot of jejunum that is no longer doing anything (so for this portion of the intestine, nothing is being reabsorbed). A connection is made straight from the stomach to the terminal ileum, at which point absorption can take place.

Benefits and risks of bariatric surgery
Definition of surgical success: > 50% reduction in excess weight (the difference between actual and ideal).
- Reduces diabetes risk (by 72%)
- Reduces serum triglycerides (by 50 – 60%)
- Increases HDL levels (by 13 – 47%) – NOTE: low triglycerides often cause an increase in HDLs
- Reduces fatty liver
- Reduces HYPERTENSION
- Post-operative mortality is relatively small = 0.1 – 2%
Bariatric surgery and Hba1c
HbA1c (measured in obese diabetics) is reduced more with gastric banding than with medical therapy.
The biggest reduction of HbA1c is seen with biliopancreatic diversion surgery.


