Lipid Metabolism Flashcards
1
Q
Lipogenesis
A
- Storing energy in fat
2
Q
Citrate / Pyruvate Shuttle and Fatty Acid Synthesis

A
- De novo fatty acid synthesis uses acetyl-CoA to build up fatty acids
- But Fatty acid synthesis happens in the cytoplasm, while acetyl-CoA is in the mitochondria
- Acetyl-CoA is shuttled out of the mitochondria through citrate
3
Q
Fatty Acid Synthesis
A
- Addign 2 carbons at a time onto a growing fatty acid chain
- A series of steps starting with acetyl-CoA that adds 2C units to a growing fatty acid chain
- Happens in the Liver and Adipose
- Uses NADPH instead of NADH
- Carefully regulated, primarily by acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- Deactivated by Phosphorylation by AMP-Activated Kinase or glucagon signaling (low-energy situation) or epinephrine signaling (high energy mobility situation)
- Activaed by high citrate and by dephosphorylation by insulin signaling (high energy situation)

4
Q
Triglyceride Synthesis
A
- Fatty acids are further processed into triglycerides (glycerol backbone) for storage
- Glycerol comes from glucolysis dihydroxyacetone phsphate which is reduced to glycerol-3-phosphate
- 3 fatty acids are added in stepwise fashion to position 1, then 2, then 3
- If the process is stopped after adding fatty acids to only positions 1 and 2, diacylglycerol phosphate is produced and can be used for membrane lipid synthesis
- Tryiglyceride synthesis happens in Liver and Aidpose
- In adipose it is stored
- In Liver it is transported to the rest of te body by very low density lipoprotein

5
Q
Lipolysis
A
- Using energy from fat
- Step 0:
- a: Hormone sensitive Lipase/Monoacylglycerol Lipase
- b: Fatty Acyl CoA Synthetase
- Step 1: Acyle-CoA Dehydrogenase
- Step 2: Enoyl-CoA Hydratase
- Step 3: 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase
- Step 4: Thiolase
6
Q
Step 0a: Hormone Sensitive Lipase/Monoacylglycerol Lipase
and
Step 0b: Fatty Acyl CoA Synthetase
A
- Step 0a: Hormone Sensitive Lipase/Monoacylglycerol Lipase
- Main control point of Lipogenesis
- Rgulated by INsulin/Epinephrine
- Step 0b: Fatty Acyl CoA Synthetase
- Step 0 (activation) reactions happen in the cytosol, but all further steps happen in the mitochondria
- Fatty acyl CoA cannot cross the mitochondrial membrane
- How can we get FA-C into mitochondria?
- Carnitine Shuttle

7
Q
Carnitine Shuttle
A
- Carnitine binds with Acyl CoA by CPT1
- Transports across the membrane by translocase
- Carnitine seperates from Acyl CoA by CPT1

8
Q
Step 1: Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase
and
Step 2: Enoyl-CoA Hydratase
and
Step 3: 3-hydroxyacly-CoA Dehydrogenase
A
- Step 1: Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase
- Step 2: Enoyl-CoA Hydratase
- Step 3: 3-hydroxyacly-CoA Dehydrogenase

9
Q
Step 4: Thiolase
A
- Energy Totals:
- CoA Synthetase: -2ATP
- B-oxidation: 1NADH + 1FADH2 -> 4ATP
- Acetyl-CoA oxidiation: 3NADH + 1FADH2 + GTP -> 10 ATP
- For palmitate (16:0): 7 B-oxidation + 8 acetyl-CoA - 2ATP -> 106ATP

10
Q
Lipolysis/Lipogenesis Control
A
- Lipogenesis:
- Citrate: feed forward regulation of AA catabolism
- Insulin: Activates Protein Phosphatase 2A
- Dephosphorylation inhibits Hormone-Sensitive Lipase, activates AA Catabolism
- Lipolysis:
- AMP: Activates AMP-Activated Protein Kinase
- Phosphorylation activates Hormone-Sensitive Lipase, inhibits AA Catabolism
- Epinephrine: Activates Protein Kinase A
- Phosphorylation activates Hormone-Sensitive Lipase, Inhibits AA Catabolism
- Glucagon: Activates Protein Kinase A
- Phosphorylation activates Hormone-Sensitive Lipase, Inhibits AA Catabolism
- AMP: Activates AMP-Activated Protein Kinase

11
Q
Ketone Bodies
A
- Burning fat efficiently requires glucose
12
Q
Acetyl-CoA
A
- Central to multiple pathways
- Must be replenished

13
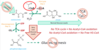
Q
Acetyl-CoA Oxidation
A
- Requires Glucose
- No TCA cycle = No Acetyl-CoA oxidation
- No Acetyl-CoA oxidation = No Free HS-CoA
14
Q
Ketogenesis
A
- Ketone Bodies are formed whe oxaloacetate/free HS-CoA have been depleted
- Oxaloacetate is used up by gluconeogenesis
- Free HS-CoA is used up by utilizing fat or ketogenic amino acids
- Ketogenesis:
- Regenerates Free HS-CoA
- Supplies energy to tissues, especially heart and brain through ketone bodies
- In Liver and Kidney
15
Q
Ketone Bodies as Energy
A
- During periods of starvation/low glucose, the brain (and other tissues) can use ketone bodies as an alternative energy source
- Liver cannot use ketone bodies
- lacks the 3-oxoacid CoA transferase enzyme
- During starvation: Liver oxidizes fatty acids and produces ketone bodies
- Ketone bodies used by other tissues for energy
- Why not just fatty Acids?

16
Q
Ketoacidosis
A
- Ketone Bodies formed any time when a large portion of the bodies energy is coming from fatty acids and/or ketogenic AA
- Normal: serum [Ketone bodies] ~0.1mM
- Ketosis: serum [Ketone bodies] >0.5mM (normal condition)
- As Ketone production increases, ketonuria (ketones in urine) balances production
- usually not/barely detectable by urinalysis strips in ketosis
- When Ketone production becomes dysregulated, ketone serum concentration can raise significantly leading to acidosis
- Ketoacidosis: serum [Ketone Bodies] > 1.5 mM (Patholigical)
- Ketoacidosis leads to reduced serum pH (<7.35) and can be easily measured by significant ketonuria


