LFT, Resp failure, Pul HTN Flashcards
Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Diffuse pulmonary infiltrates on chest x-ray Bronchoalveolar lavage eosinophilia >25% Absence of parasitic, fungal, or other infection Absence of drugs known to cause pulmonary eosinophilia Quick clinical response to corticosteroids Failure to relapse after discontinuation of corticosteroids



Variable Intrathoracic
Causes - tumour, bronchial stenosis







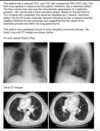
DLCO very low, normal/slightly decreased TLC
Indications for ECMO
Scoring
Resp - ARDS, Aspirtion, Pneumonia, Asthma, Post lung tx, Lung contusion
Cardia - Post AMI, Drug OD, PE, cardiogenic shock
RESP Score - prediction of survival on ECHMO. Factors - Age, Duration of lung injury
Mx of ARDS
NIV indications
Pul edema
COPD
Hypoxic resp failure
Resp Failures - Type 1–>4
Type 1 - hypoxia
Type 2 - hypoxia + hypercapnia
Type 3 - Perioperative Atelectasis
Type 4 - Shock
Elevated PAP - definition, factors
Pulmonary artery pressure >25 or >30 with exercise (but this is being debated to reduce it to 20)
Factors affecting - pulmonary artery pressure, pulmonary vascular resistance, left atrial pressure, cardiac output
Pul Htn Types 1–> 5
Sx of PAH
Ix for PAH
Vasoreactivity Test
to check if its an issue with the endothelial wall itself
if vasoreactivity test positive, can use CCB, if not then need to use meds that act as vasodilators
Inhaled NO or IV Epoprostenol
PAH - PDE5 inhibitors
MOA
Ex
C/I
Increases cGMP (which is broken down by PDE5)
Sildenafil, Tadelafil
Cant use with other cGMP stimulatns like Riociguat
Prostacyclin agoniss
IV - Epoprostenol, iliprost
Oral - Selexipag
Only class with possible survival benefit
Endothelin Receptor Antagonists
potent vasocontrictor
- Non selective (A + B)
- Bosenten, Macitentan
Selective
-ambrisentan
CTEPH
Dx - diagnostic feature
Mx
Dx - reduced DLCO out of proportion to spirometry
VQ scan - PROX pul HTN (unlike group 1 pul htn which is distal)
Mx - Warfarin, thromboendarterectomy, pul balloon angioplasty, meds if inoperable/persistent sx
Normal A-a gradient
Formula
Causes of increased A-g gradient
5–10 mmHg
A-a gradient = (FiO2 - PCO2/0.8) - PaO2
Causes raised DLCO
Alveolar haemorrage
Polycythaemia
Obesity
L –>R shunt
Exercise


