Lecture Four - On why plants and animals are the same Flashcards
(12 cards)
What forces shape the planet’s surface?
Tectonic plates.
Oceanographic.
Atmosphere.
Biotic factors - other life.
How did forests evolve?
The evolution of lignin and tracheids.
Tracheids are a type of water-conducting cell in the xylem which lacks perforations in the cell wall.
Lignin is a complex organic polymer deposited in the cell walls of many plants, making them rigid and woody.
Lignification allowed structures to be more solid, and thus allowed plants to become land plants (from aquatic plants), and then to increase in height, eventually giving rise to tall trees.
This caused the evolution of other plants which now have to fight for sunlight, when taller trees block this.
What are the constraints of evolution?
Organic life evolves subject to a variety of constraints.
A constraint is any physical or biological process that limits the phenotype possible for evolution.
Organisms must obey thelaws of chemistry and physics - biomechanics and thermochemistry.
Tradeoffs amoung functions - allocation of energy and zero sum dynamics (energy in = energy out).
Some more obvious contraints are temperature, atmosphere (pressure), gravity and resources for metabolism.
What are some of the differences between animals and plants?
Locomotion.
Foraging for resources.
Defence.
Social behaviours.
What are some of the similarities between plants and animals?
RNA.
Mitochondria.
Genes.
Distribution of resources within the organisms. E.g. the vascular systems in plants and animals are very similar in look and function.

What is Fick’s first law of diffusion?
To exchange resources with the envoronment, plants must follow diffusion laws.
Solute particles more from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
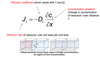
What are some constraints to plants caused by air, regarding their ability to evolve?
The density of oxygen in air is much higher than that in water.
Gases can diffuse 10,000 times more quickly into and out of a plant growing in air.
Good for CO2 gain, bad for O2 loss.
Aquatic plants, no advantage in getting larger.
Every cell can absorb CO2 and nutrients.
Minimum of surface area lost to intercellular connections.
What is the equation used for the resistance of fluid flow in plants? Hagen-Poiseuille equation.
Less resistance is better.
Resistance decreases linearly with decrease in length.
But it decreases as the fourth power of radius increases.

Define cavitation and embolism.
Cavitation - negitive water potential exceeds cohesive strength of water molecule.
Embolism - air bubble that fills in break in water collumn and impedes water flow.

What is the relationship between height and volume, and the pro’s and con’s of having these characteristics.
As height increases, mass is disproportionaltly increasing.
You would need a very well developed distribution network is you were very big.
Challenges would include heat dissipation, neuronal controls, blood pressure, quick movements and food consumption.
What is surface area, weight, wind resistance and terminal velocity proportional to, respectively?
Surface area ~ length ^2.
Weight ~ length ^3.
Wind resistance ~ surface area.
Terminal velocity ~ weight.
Define allometric scaling.
Allometry describes how characteristics of an organism change with body size.
Y = aX^b or logY = loga + blogX
Where X and Y are measures of body size and a and b are fitted parameters.



