Lecture 9: AS and psoriatic arthritis Flashcards
Radiographic features of PsA in the hand:
Distribution usually DIP and PIP joints
Ray Pattern where all three articulations of a single digital ray (finger), including MCP, DIP and PIP. Diagnostic sign of psoriasis.
Erosions and deformity:
- At joint margins (fluffy periosteal new bone formation) (mouse ears)
- Progresses to whittled articular end of phalanx.
- Whittled end erodes into adjacent cortical surface giving pencil and cup deformity.
- Subsequent shortening of digits.
- Arthritis mutilans
Joint space: Initially widening due to erosion, with 15% progressing to ankylosis.
What are the general radiographic findings of AS?
Bilateral symmetrical osteoporosis, erosions and reactive sclerosis
Eventual bony ankylosis
Characteristic sites:
SIJ
Facet
Costovertebral
Pubic symphysis
Discovertebral junctions
Manubriosternal
Distinctive sequence:
Early bilateral SIJ involvement
Ascending spinal changes
Earliest cervical changes C2-3 and C6-7
What are the major radiographical findings in AS in the peripheral joints:
Hip:
- Uniform loss of joint space
- Axial migration of femoral head
- Protrusio acetabuli
- Subchondral cysts; small osteophytes
- Eventual ankylosis
- Erosion, periostitis at trochanters and adj. ischial tuberosity caused by enthesopathy
Shoulder:
- Lateral humeral hear erosion
- Elevated humeral head due to rotator cuff tear
- Distal clavicle erosions; eventual resorption
Calcaneus:
- Erosions, local osteoporosis and periostitis at achilles and plantar aponeurosis
What are 4 common non-marginal syndesmophytes?
4 common non-marginal syndesmophytes.
- Complete: attached to mid body of two contiguous vertebrae.
- Incomplete: Comma shaped. (teardrop)
- Bagpipe: bulkier base attached to mid body.
- Floating Unattached ossification bridging disc space.
What are the signs of enthesopathy on xray in AS
Bone/ligament entheses are most prominently affected at the iliac crest, ischial tub, femoral trochanters, spinous processes and calcaneal plantar surface
Cortical erosions, sclerosis, peristeal ‘whiskering’ extending from bone to ligament or tendon
What condition is this? Why?

AS
Dagger sign
Trolley tracks
Marginal syndesmophytes
Ghost sign
Star sign
Widespread osteopoenia
What condition is this a hallmark sign for?

AS
Shiny corner sign
A result of reactive sclerosis to a rommanus lesion
What is this condition? What is this hallmark sign called and what causes it?
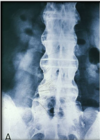
AS
Bamboo spine - multiple marginal syndesmophytes
What are the radiographic changes of late AS?
Bony ankylosis
Genersalised osteoporosis - disappearance of reactive sclerosis
Ghost joint: joint margin (visualisation of articular cortex through ankylosed joint)
Star sign: ossification of superior sacroiliac ligaments, creating triangular radioopacity
What condition is this?

AS
Uniform loss of joint space
Axial migration of femoral head
Protrusio acetabuli
Ankylosis of the joint
Erosion, periostitis at trochanters and adj ischial tuberosity caused by enthesopathy
Subchondral cysts
What are the major radiographical findings (hallmark findings) in AS in the spine and SIJ
Bony ankylosis
Rosary bead: articular erosions in SIJ
Genersalised osteoporosis - disappearance of reactive sclerosis
Ghost joint: joint margin (visualisation of articular cortex through ankylosed joint)
Star sign: ossification of superior sacroiliac ligaments, creating triangular radioopacity
Rommanus lesion: Lucent corner erosion
= reactive sclerosis/ reactive bone growth to counter rommanus lesion plus widespread osteopaenia leads to shiny corner sign
May see Andersson lesion (florid disc) which can lead to vertebral body collapse
Marginal syndesmophyte formation: ossification of annulus
multiple syndesmophytes = bamboo spine
Barrel vertebrae: squaring of vertebral body as a result of reactive bone deposition to counter the rommanus lesion
Dagger sign: ossification of supraspinous ligaments
Trolley tracks: Ankylosis of the facet joints
Gibbus deformity: Sharp angulation of # of vertebrae
Ballooned disc: vertebral end plate increased concavity due to osteoporosis
What are the common radiographic findings in the Spine in PsA
X-ray signs off psoriatic arthritis in spine: Thoracic and lumbar affected in 60%
Coarse asymmetric non-marginal syndesmophytes (paravertebral ossification’s)
Apophyseal joints are spared in this area
Non marginal syndesmophytes most common T11 – L3.
Ossification lateral to and separate from vertebral body in early stages.
What condition is this a hallmark sign for?

AS
Barrel vertebrae
Repair of rommanus lesion creates a convex margin “barrel shaped vertebrae”.
What is this condition? What can we see here that indicates this?

AS
Black arrows - rommanus lesions
White arrow - reactive sclerosis (shiny corner sign)
We can also see some signs of osteopaenia
What are the radiographical changes in the feet in PsA
Early change characteristic at big toe
Soft tissue swelling, erosions, fluffy periostitis
Widened joint space, normal bone density
Lysis at metatarsal heads and distal tuffs.
Sometimes ivory phalanx at distal tuft
Calcaneus: erosions, periostitis at Achilles and plantar lig insertions
What are the radiographic findings of AS in the SIJ?
- First sign might be subtle widening of the SIJ
- Bilateral and symmetrical
- Pannus formation over lower 2/3 of SIJ
- Finding on ilial side first, later becoming both ilial and sacral sides
- Erosive changes
(Almost sclerotic change appearance but body can’t deposit bone fast enough.)
What are the general radiographic features of psoriatic arthritis
Asymmetric distribution
Prominent soft tissue swelling (earliest sign, digits)
Lack of osteoporosis, normal bone mineralisation.
Cortical erosions
- Early are marginal
- Over time give tapered bony end.
Fluffy periostitis adjacent to marginal erosions, at lig and tendon insertions.
Fluffy spiculated bone growth (mouse ears).
What are the radiographic changes in the SIJ in PsA
30-50% of psoriasis patients have SI involvement. More commonly unilateral.
Iliac surface of joint shows erosions, sclerosis, hazy joint margins.
Enthesopathy creates erosive changes and periostitis at iliac crest, ischial tuberosity, femoral trochanters.
Infrequently, femoral head erosion with protrusio acetabuli may mimic RA
What condition is this?

DISH
- difficult to differentiate from AS, however DISH has paramarginal syndesmophytes in which the ALL is being ossified. We will often see a thin, radiolucent line between the vertebral body and the syndesmophyte if it is the ALL that is being ossified, where as in AS, it is the outer aspect of the annulus that is being ossified
What are the radiographic changes of early stage AS (sacroiliitis)?
- Articular erosions (rosary beads)
- Diminished joint space
- Loss of articular cortex definition (pseudowidening)
- Patchy reactive sclerosis
- Subchondral osteoporosis


