Lecture 7: Hemiacetals and Acetals in carbohydrates: Furanoses, Pyranoses, and Glycosidic Linkages Flashcards
How does a linear glucose molecule create a hemiacetal?
Through a nucleophilic addition rxn: the O attached to the second to last C (which becomes the anomeric C), attacks the carbonyl C, creating a ring with the hydroxy O becoming a member of that ring. The carbonyl O becomes a hydroxyl group.
How many chiral centers does linear glucose have? In cyclic form?
Has 4 chiral centers in linear form, but 5 in cyclic form
As the linear monosaccharide cyclizes, the carbonyl C becomes a hemiacetal, which is now called the _____ C
anomeric
the anomeric C is C# ___ for aldoses, and C# ___ for ketoses
C1 for aldoses and C2 for ketoses
What are anomers?
epimers in which the molecules differ only in configuration at anomeric C1
alpha-D-glucose and ß-D-glucose are ____ of each other (what type of isomer?)
anomers (a type of epimer)
In cyclic form, the alpha form of a monosaccharide has the anomeric OH ____(up/down); whereas the ß form of a monosaccharide has the anomeric OH ____(up/down)
alpha = down if drawn as a flat molecule, and axial if drawn in the chair conformation
beta = up if drawn as a flat molecule, and equitorial if drawn in the chair conformation
Why is there more ß-D-glucopyranose found in a solution compared to alpha-D-glycopyranose when that solution is at equillibrium?
Because the ß-D-glucopyranose has a more stable chair conformation compared to the alpha. The ß confirmation has all the OH gorups and the CH2OH group in an equitorial position, whereas the alpha confirmation has the anomeric OH in the axial position.
What is a 5 membered and 6 membered ring called?
5 membered ring = furanose
6 membered ring = pyranose
aldo hexoses form ___ membered rings when C5 attacks C1
6
ketohexoses form ___ membered rings when C5 attacks C2
5
Aldopentoses form ___ membered rings when C4 attacks C1
5
What is mutarotation?
Refers to the spontaneous interconversion of anomers (via linear form) in aqueous solution via rapid ring opening and cyclization
Why does D-glucose not exist in a 50/50 mixture of beta and alpha confirmations?
Because of steric hinderance. ß-D-glucose has less steric hinderance than alpha
In linear fischer projection form for glucose, which OH groups on the chiral carbons are positioned to the R? to the L?
R, L, R, R
C1 = R
C2 = L
C3 = R
C4 = R
In cyclic form, which positions (up/down) are each of the OH/CH2OH groups on the cyclic C?
up, down, up, down, up
C1 OH = up
C2 OH = down
C3 OH = up
C4 OH = down
C5 CH2OH = up
1) In oxidation, you ___ O, ____ e-, and/or _____ H
2) In reduction, you ___ O, ____ e-, and/or _____ H
1) oxidation: gain O, lose e-, or lose H. (oxidation state increases)
2) reduction: lose O, gain e-, or gain H. (oxidation state decreases)
Glucose and other aldoses are called _____(oxidation or reducing) sugars because their free aldehyde can undergo _____
called reducing sugars because their free aldehyde can undergo oxidation
Oxidation of an aldose at C1 converts it to the corresponding ___ acid
aldonic acid
i.e. ß-D-glucose that undergoes oxidation becomes ß-D-gluconic acid
What is the structure of D-glyceraldehyde?

What is the structure of L-glyceraldehyde?

What is the fischer projection structure of D-ribose?

What is the fischer projection of 2’-deoxyribose?

Distinguish between the cyclic structure of ribose and 2’-deoxyribose
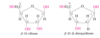
Distinguish between the fischer projection of D-arabinose and L-arabinose

D-fructose fischer projection structure

ß-D-fructofuranose cyclic structure

D-glucosamine cyclic structure

D-glucosamine fischer projection structure

Fischer projection structure of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine

N-acetyl-D-glucosamine cyclic structure

Glycosidic linkages are stable in aqueous solution under __1___ or __2___ conditions, but can be hydrolyzed under __3___ conditions. Fill in the blanks, with acidic, basic, and neutral.
1) neutral
2) basic
3) acidic
a glycosidic linkage is a monosaccharide ______(hemiacetal or acetal)
acetal
monosaccharide acetal = ______ linkage
glycosidic
Glycosidic bond between 2 monosaccharides always connecs __1___ C on one monosaccharide to an __2__ on the other monosaccharide
1) anomeric C
3) OH
Maltose is made of what 2 monosaccharides?
2 glucose monosaccharides
Maltose is a disaccharide made of 2 glucoses. Specify the type of linkage between these 2 glucoses: alpha or beta, and carbon numbers
the linkage is an alpha 1 → 4 linkage
What is the systemic name for maltose?
alpha-D-glucopyranosyl1(1→4)-D-glucopyranose
or
Glc(alpha1→4)Glc
Note that the first glucose suffix = “syl” because it is considered a substituent to the other molecule
1) Is a sugar that has a hemiacetal anomeric C capable of acting as a reducing sugar?
2) Is a sugar that has an acetal anomeric C capable of acting as a reducing sugar?
1) yes
2) no
What must the anomeric C have in order to be a reducing sugar?
must be a hemiacetal (cannot be an acetal)
What type glycosidic linkage constitutes lactose? alpha/beta and carbon numbers
ß1→4 linkage between C1 of galactose and C4 of glucose
(galactose is the nonreducing end and glucose is the reducing end)
What is the systemic name for lactose?
ß-D-galactosyl1-(1→4)-D-glucopyranose
or
Gal(ß1→4)Glc
How are glycosidic linkage hydrolyzed?
via a strong acid i.e. 6M HCl
Can lactase that hydrolyzes a ß1→4 linkage between galactose and glucose also break down a ß1→4 linkage between 2 glucoses
NO!
What is the type of glycosidic linkage in sucrose? alpha/beta and carbon #
ß-D-fructofuranosyl2-(2→1)-alpha-D-glucopyranoside
(can also be written vice-versa)
or
Fru(2ß→alpha1)Glc
(can also be written vice-versa: Glc(alpha1→2ß)Fru
Why is sucrose not a reducing sugar?
because the anomeric C of glucose (C1) is linked to the anomeric C of fructose (C2)- hence both are acetals; there are no hemiacetals and, therefore, no reducing end.
What is a key to analyzing whether a cyclic ß-D-fructose drawing is right side up or upside down?
Look at the anomeric C of fructose (which has the OH and OR attachment)
If the anomeric C has it’s OH facing up, it is right side up (the anomeric C will be on the R side of the drawn structure)
If the anomeric C has it’s OH facing down, its upside down (the anomeric C will be on the L side of the drawn structure)
How many anomeric C are there in a monosaccharide?
one
Why do some sugars taste sweeter than others?
because the proteins on our taste buds bind with much higher affinity with some sugars compared to others. The closer the binding, the sweeter the sugar will taste
What 2 monosaccharides make up trehalose? Is this a reducing or non-reducing sugar?
2 glucose molecules; trehalose is a non-reducing sugar (because the 2 anomeric C of each glucose bond with eachother, forming an acetal and leaving no hemiacetal to undergo mutarotation or oxidation)
Trehalose: Glc(alpha1→1alpha)Glc
A reducing end of a sugar is a free __1__ carbon, which can undergo __2__ to interconvert between anomers and become __3__ while in the aldehyde form
A reducing end of a sugar is a free anomeric carbon, which can undergo mutarotation to interconvert between anomers and become oxidized while in the aldehyde form


