Lecture 5: Insulin and glucagon action Flashcards
In what form is carbohydrates transported in the body
In the form of glucose
What is the effect of insulin of glucose homeostasis

- Upregulates glycogenesis in the liver and muscle
- Upregulates the synthesis of fatty acids and triglycerides
- Downregulates gluconeogenesis (in the liver)

What is the effect of glucagon on glucose homeostasis

- Upregulates glycogenolysis
- Upregulates gluconeogenesis
- Downregulates glycogenesis

What is the role of the glycogen stored in the liver
Storage for blood glucose maintainenace
Stored when blood glucose levels are high so when levels are low they can be broken down to maintain blood glucose level
What is the role of the glycogen stored in the muscle
Storage for local energy production (only used by the muscle itself)
When the glycogen is broken down it cannot go back to glucose but used for ATP because the muscle cells do not contain the enzyme G6Pase (which converts G6P to glucose)
What happens to liver glycogen metabolism in the fed state
Insulin increases glucokinase and glycogen synthase activity
Increase glucokinase activity- conversion from glucose to G6P
Increase glucogen synthase activity- therefore more glycogen formed.
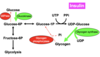
What is the effect of nor(adrenaline) on muscle glycogen metabolism, if person is in a fasted state?
- More glucose is needed as the body is in the “fight or flight” response
- Increase GLUT4 activity (to bring glucose into the muscle cell)
- Increase hexokinase activity
- Increase glycogen phosphorylase activity (breaking down glycogen into G1P)

Gluconeogenesis occurs where?
Mainly in the liver
Kidneys can contribute with prolonger starvation
How does glyconeogenesis convert glucose-6-phosphate to glucose?
By glucose-6-phosphatase

How does glyconeogenesis convert fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate?
By Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (F16bPase)

How does glyconeogenesis bypass pyruvate kinase activity?
Converts pyruvate into oxaloacetate (by pyruvate carboxylase (PCOX))
Oxaloacetate is converted to phosphoenolpyruvate (by phosphoenolpyruvate (PEPCK))

Draw the steps for gluconeogenesis from a pyruvate source

Which hormones regulate gluconeogenesis
Glucagon - Increase gluconeogenesis
Adrenaline - Increase gluconeogenesis
Insulin - Decrease gluconeogenesis
What effect does glucagon and adrenaline have on gluconeogenesis
Upregulates gluconeogenesis by:
- Decreasing glucokinase activity
- Increasing G6Pase and PEPCK activity

What effect does insulin have on gluconeogenesis
Downregulates gluconeogenesis by:
- Increase glucokinase activity
- Decrease G6Pase and PEPCK activity

Glucagon ____ glucokinase activity and ____ G6Pase and PEPCk activity. Overall ___regulates gluconeogenesis
A) Decrease
B) Increase
C) Upregulates
Adrenaline ____ glucokinase activity and ____ G6Pase and PEPCK activity. Overall ___regulates gluconeogenesis
A) Decrease
B) Increase
C) Upregulates
Insulin ____ glucokinase activity and ____ G6Pase and PEPCK activity. Overall ___regulates gluconeogenesis
A) Increase
B) Decrease
C) Downregulates
At what level does hormonal regulation have on gluconeogenesis?
Gene level
The effect of the hormones (glucagon, adrenaline and insulin) effect the level of gene expression
Influences if more/less enzyme are synthesised- however takes a while for the effect to be influence on gluconeogenesis
What is the principal action of insulin on the liver
- Increases glycogen synthesis
- Increases fatty acid synthesis
- Inhibits gluconeogenesis (PEPCK & G6Pase)
What is the principal action of insulin on the muscle
- Increases glucose transport (GLUT4)
- Increases glycogen synthesis
What is the principal action of insulin on the adipose
- Increases glucose transport (GLUT4)
- Suppresses lipolysis
- Increases fatty acid synthesis
Name the hypogylcaemic drugs available
- Sulphonylureas
- Biguanides
- Thiazolidinediones
- Incretin mimics & DPP-4 inhibitors
- SGLT2 inhibitors
Describe the mechanism of action for sulphonylureas + an example
- Hypoglycaemic drug
- Inhibits ATP-sensitive potassium channels (similar action as to the high levels of glucose, which stimulates ATP production)
- This depolarises the cells causing voltage gated calcium channels to open causing the exocytosis of insulin
- Example: Gliclazide




