Lecture 4: The Neurophysiological Biomarker Toolbox (NBT) and ICA Flashcards
(19 cards)
Why do we use Neurophysiological Biomarker Toolbox (NBT)?
To understand the complex dynamics of neuronal oscillations in health and disease by using multiple biomarker algorithms
What is an algorithm?
A process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations, especially by a computer.
What are frequency domain filters used for?
To pass certain frequencies (passband), while blocking others (stopband). This, because for analysis you are not interested in the whole spectrum of frequencies in your signal.
What types of frequency domain filters are there?
Low-pass, high-pass, band-pass and band-stop.
What does the frequency domain low-pass mean (also think of what high-pass is)?
You let the low frequencies pass (e.g. <40 Hz), while blocking higher frequencies (e.g. >40 Hz).
What does the frequency domain band-stop mean?
There’s enormous amount of 50 Hz noise in your surrounding. For this you can do band-stop, so you can filter out the noise at 50 Hz.
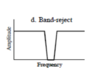
What does the frequency domain band-pass mean?
The opposite of band-stop, where you want to look at a specific frequency, e.g. alpha oscillations.

What is the cutoff frequency?
The frequency where the amplitude is reduced to 50, 70, 90, or 99%.
So to summarize:
- Low-pass is used when…
- High-pass is used when…
- Band-pass is used when…
- Low-pass is used when there’s 50 Hz (in Europe, in US 60 Hz) line noise that disturbs viewing the traces.
- High-pass is used when looking at high frequencies (< 1 Hz noise is very sensitive to movement.
- Band-pass is used when you’re interested in a specific frequency, e.g. alpha.
So the terms mentioned above (high-pass, band-pass, cutoff frequency etc.) are important for visualization of frequencies in NBT. What is the next step?
NBT pre-processing (selecting bad channels, transient artifacts removal, re-referencing to average reference etc.)
What is pre-processing?
It prepares the data for detailed inspection/visualization and removes non-neuronal sources of EEG signals (artifacts).
What is the cocktail party effect and what has it to do with independent component analysis (ICA)?
When you are at a party with a lot of noise around you and two persons in front of you are talking, you can focus on one person so that you can understand and hear them and with that ignore all the noises/disturbances around you. This is what ICA can do, ICA can pull two noises apart and analyse them independently.
How does Independent Component Analysis (ICA) work in general?
If you have two sources (S1 and S2) and 3 electrodes (x1, x2, x3) that receive electrical signals from the dipoles located in these two sources, the electrodes will receive signals from both sources. You then want to know how much S1 and S2 contribute to the electric signals received by electrodes x1, x2 and x3. Since both sources contribute differently to the different locations of the electrodes (among others distance differs), ICA can split up these electrical signals by statistical analysis (called projection) to see the original source signals.
How is ICA applied to EEG?
Many neuronal sources contribute to the signal at each electrode. In addition, you have non-neuronal artifacts that need to be removed.
What do you get if you apply ICA to multichannel EEG recording?
Scalp topographies, that you can use to distinguish sources (e.g. artifacts vs brain sources).
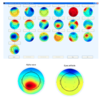
What needs to happen to get an activation time series corresponding to each source identified by the ICA?
For every time point (i.e. sample), the sample recorded at every electrode is multiplied with the factor displayed in color in the ICA topographic map and the weighted average across all channels is calculated. A topography can thus be used as a weighting factor for different EEG channels to produce a time series corresponding to the estimated independent component.
What is displayed here?

Spatial filtering of artifacts using mathematical projection (i.e. removing artifacts from the EEG). Spatial filtering has the advantage of clearly removing even large artifacts, without necessarily removing brain signals with similar frequency content.
What three steps need to be taken for analysis in NBT of neural correlates of cognition during rest?
- Effect of rest on EEG
- Effect of rest on cognition
- Association between EEG and rest.
What is the central frequency?
It’s a weighted frequency within a given frequency band (e.g. alpha band), weighted by its powers (strenght/amplitude). So the central frequency of the alpha band will go up if the power of the alpha band also goes up.



