Lecture 4: Spine & Trunk Flashcards
(43 cards)
Name the parts of the sternum

How many cervical vertebrae are there, how many thoracic, how many lumbar, how many sacrum segments and how many coccyx segments?
7 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
4 coccyx
Name the bony prominences of the vertebrae

vertebral foramen- hole in the center
vertebral body - big piece
spinous process - big point posterior
transverse process - 2 lateral points
pedicle - from body to transverse process
facet - articulating surface
lamina - between spinous process and transverse process

What are the 4 functions of vertebrae and where are the located on the bone?
Support body weight
Muscle attachment and movement
Protection of spinal cord
Restriction of movement

What is the C1 and C2 vertebrae, how do you differentiate them?
C1 = atlas (holds the world, on top)
C2 = axis (pivot joint) has spine pointing ventrally (DENS)
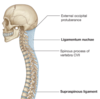
What are the 2 ligaments in the cervical and thoracic regions along the spine?
Ligamentum nuchae & supraspinous
How can you distinguish the 3 types of vertebrae?
Look at all from the sagittal view.
Cervical = mouse
Thoracic = giraffe
Lumbar = moose
What type of vertebrae has facets on the vertebral body and the vertebral foramen is large triangular shaped?
Cervical
What is the strongest cervical vertebra?
Axis
On what vertebra is the vertebral body heart-shaped?
Thoracic
Is the picture anterior or posterior? Name the bony processes of the sacrum.

S1-S5–> coccyx
Ala
1st sacral body
Sacral formina
Is the picture anterior or posterior? Name the bony processes of the sacrum.

Lateral, intermediate, median crests
Sacral canal, sacral hiatus
Sacral tuberosity
Facet and Articular surface
Sacral formina
Is this anterior or posterior this? Name the ligaments.


Is this anterior or posterior this? Name the ligaments.


What are the two parts that make of the intervertebral disc?
Annulus fibrosus, nucleus pulposus
What are the 3 different views of the intervertebral disc under relaxed, erect and later flexion states?
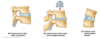
What is a tear in the outer annulus fibrosus ring known as?
Slipped disc, intervertebral disc herniation
What is the superior and inferior attachments of the intercostal muscles (external, internal, innermost)
Superior = inferior border of ribs
Inferior = superior border of ribs below
What nerve innervates the intercostals?
Intercostal nerve
What is the main action of the intercostals (hint: 2 have the same action)
External intercostal: during forced inspiration: elevate ribs
Internal & innermost intercostal: During forced respiration, interosses part depresses rib, interchondral part elevates ribs
What is the superior and inferior attachment of the subcostal muscles and what is the action?
Superior = internal surface of lower ribs near angle
Inferior = superior border of 2nd or 3rd rib below
Action: act the same as internal intercostal muscles
What are these two muscles, what are there superior and inferior attachments?

Serratus posterior superior & serratus posterior inferior
Superior attachement: Superior = nuchal ligament, spinous process of c7-T3, Inferior = inferior border of ribs 8-12 near angle
Inferior attachment: Superior = superior border of 2nd and 4th ribs, Inferior = spinous process of T11-L2 vertebrae
What is the innervation and action of serratus posterior superior and serratus posterior inferior?
Innervation: Superior = 2-5th intercostal nerves, Inferior = 9-11 intercostal nerves, subcostal nerve
Action: Superior = elevate ribs, Inferior = depresses ribs
What is the origin, insertion, innervation, and action of rectus abdominis?
Proximal = pubic symphysis and pubic crest
Distal = Xiphoid process, 5-7th costal cartilages
Innervation = Thoracoabdominal and sub-costal nerves
Action = flex trunk, compress abdominal viscera, stabilizes and controls tilt of pelvis















