Lecture 3: Female tract, oogenesis and endocrine 1 Flashcards
(17 cards)
What is oogenesis?
The formation and development of an ovum
Different stages of follicle development?
- Primordial
- Primary (30-50 for 2-3 months)
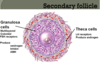
- Secondary (15-20 for 2 weeks rapid growth) -loss by atresia
- Tertiary Follicle (1-2)
- Release of a secondary oocyte within corona radiata
Oogonia/oocyte number throughout life?

Formation of oocytes from oogonia?
Following the mitotic division that forms a large number of germ cells (oogonia) , Meiosis begins but is not completed
Meiosis halts just prior to metaphase 1 at the end of prophase and these are now called oocytes
These oocytes remain arrested until ovulation (12-50 years later)
The ovarian cycle begins with?
- Three months before ovulation many primordial follicles become activated (recognisable by the number of granulosa calls that surrond the oocyte) = Follicular wave
- It takes about 85 days from activation to antrum formation
- They compete with each other to become the dominant follicle in terms of growth with the others dying.
- Ovulation occurs from one ovary at a time (unknown mechanism)
Primordial follicle structure
- Very thin almost invisible zona pellucida
- Flat granulosa cells with stromal cells surrounding

Primary and Secondary follicle structure?
- Granulosa cells proliferate slowly and then rapidly
- Theca cells develop outside the basement membrane that are LH receptive and produce androgens
- Granulosa cells are receptive to FSH and produce: oestrogen, inhibin and AMH
Steriod Pathway?
Progesterone is converted to
Androgen that is aromatosed to
Oestrogen
- These pathways can go both forward and backwards mostly
Two theories of follicular steriodogeneis?
- Theca cells in response to LH are making progesterone and androgens
- Granulosa cells then convert these to Oestrogens (most potent being oestradiol)
Tertiary Follicle structure?
- Follicular fluid filled Antrum forms
- Granulosa cells still miltilayerd and cuboidal
- Theca interna and externa visible
- cumulus oophorous - granulosa cells currounding oocyte
- mural granulosa cells lining the wall of the antrum

Zona Pellucida structure, formation and function?
- Protein ZP1 is present in primordial follicles
- ZP2 and ZP3 are added to the activated follicles
- Very important for filtering normal sperm in and blocking polyspermy as well as fertilisation from other species sperm.
Formation and role of AMH and FSH?
- AMH - Antimullerian hormone
- Produced in the granulosa cells of larger tertiary follicles
- Supresses follicular recruitment and development
- FSH drives proliferation of Granulosa cells so at the secondary and tertiarty follicular levels it becomes gonadotrophin-dependent growth (antral growth opposed to preantral) Before this (eg. primordial) is non-gonadotrophin dependent
How is the egg released?
- A dominant follicle is said to be about 15mm
- Estrogen feedback flips and causes a surge in LH
- 12-24h after LH peak you get ovulation
- A part known as the Stigma pushes out from the side of the ovary.
- The oocyte then must get into the fillopian tube and theca cells begin to leutinise
- The corpus luteum forms and produces progesterone and estrogen before regressing to corpus albicans
Fillopian tube regions?
- Infundibulum (with fimbrae)
- ampulla
- isthmus
- intramural/interstitial portion

Fillopian tube structure?
- Epithelial lining
- muscular coat -inner circular, outer longitudinal
- serosal coat
Epthelium:
- (i) Ciliated
- (ii) secretory
- Responsive to steroids
effects of E2 (estrogen) of the FT?
E2 Promotes:
- increase in cilia
- increase in secretory activity
- increase in muscular activity
Thus the early peak in E2 gets the FT ready for the oocyte
Effects of P4 (progesterone) in the FT?
P4 Promotes:
- Decreased in muscular activity
- decrease in cilia BUT increase in the beat frequency after estrogen priming
- Decrease in volume of secretions


