Lecture 2: meninges and orbit Flashcards
(20 cards)
What are the meninges and what is their purpose?
They are the membranes the evelop to brain and protect the brain
- dura mater (outer periosteal attached to the skulll and inner meningeal layer that is the sole intraspinal dura mater layer)
- arachnoid mater
- pia mater
Label


Blood supply to the skull?
Most is supplied from the MMA (ant and post b.) through the foramen spinosum
anterior: anterior menangial a from the eethmoidal arteries + ant branch of MMA
middle: MMA
Posterior: Meningeal branch of occipital artery and vertebral artery + post branch of MMA
Innervation of meninges?
Comes from V1 ,2 and 3 of the trigeminal

Intracranial venous structures?

Flow from the inferior to superior sagittal sinus to the straight sinus. From there to the confluence of sinuses and down the transverse sinus (R + L). More sinuses drain into this before it drains into the important cavernous sinus. All eventually flow to the jugular vein.

Whats the big deal about the cavernous sinus?

CNx 3,4, 5 (V1 and 2) run within the wall ad CNx 6 and internal carotid artery run though the sinus.
Opthalmic vein drains into the cavernous sinus and is a site for bacteria to get in and cause cavernous sinus thrombosis (ED MATTER!) Eg. anyone with periorbital celllulitis

What is racoon eyes and how does it develop?
Is when the periorbital layer of the dura is damaged around the eye allowing blood to flow into a potential spaces in the eye. Can be caused from fractures of the bone damaging the dura.

Venous drainage into the sinuses?
Cerebral veins from the brain itself drain into the sinuses through the meningeal layer. Emissary veins flow from outside the skull to inside the skull (potential for bacteria entry). Diploic veins also flow form within the bone into the sinuses.
What’s up with the middle meningeal layer?
The Arachnoid mater
- Avasular membrane with trabeculae into the subarachnoid space (that contains a nd v)
- Does not enter the grooves or fissures EXCEPT the longitudinal fissure.
- Arachnoid granulations for CSF reabsorption

What u got on the inner meningeal layer?
The Pia mater
Follows the brain and invests in the surface of the brain.
What are the types of intracranial haemorrhage?
Extradural (B)
- Between the periosteal layer of the dura and the inside of the bony structure. Lemon shaped from damage to the menangial arteries and veins.
Subdural (A)
- Is between the layers of the dura mater (periosteal and menangeal) from damage to the cerebral veins - often in older people from even small bangs
Subarachnoid (C)
- From damage to cerebral arteries normally

Label bony structures of the orbital cavity?

Roof = Frontal
Floor = maxilla
Lateral = zygomatic
Medial = ethmoid, palatine, lacrimal

Layers of the eyelid?


Label? Function? nerve supply?

Supplied by the facial nerve like all facial expression muscles, the palpebral part is what enables blinking

What’s going on with that orbital septum thing?
It is a continuation of the periosteal layer and forms a seal. Has connections with the tendon of levator palpebrae superioris, tarsus and superior tarsus muscle.
What’s good with the tarsus?
It is protection of the eyeball. Secretes oily substance from the tarsus gland that stops the eye drying out. Styes/chalazions form from swelling of these glands.
The superior tarsal muscle is smooth and under sympathetic control but the LPS is inervated by CNx 3. Damage to these leads to partial or full ptosis respectively.
Horner’s syndrome?
Ptosis, miosis and anhidrosis from damage to the sympathetic trunk
Eyelids: blood supply? innervation?
Opthalmic artery, facial artery and superficial temporal artery
Sensory: CN V(1 upper lid and 2 lower lid)
Motor: CN III, VII, sympathetic fibres
Contents of the orbital cavity?
- eye ball
- extrinsic muscles (rectus and oblique muscles)
- periorbita (periosteal layer)
Superior, inferior, medial and lateral rectus all orginiate from inside the fascial ring at the back of the cavity as well as occulomotor, abducens, V1, optic nerve and opthalmic nerve running inside the ring.
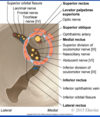
Lacrimal apparatus?
Consists of the lacrimal gland, canaliculi, sac and duct
To do with producing tears



