Lecture 1: Skull Flashcards
(12 cards)

…



Pathalogical condition?

Combined with absence of clavicle, falure of the bregma to form (closure of frontal fontanelle) it is called Cleidocranial dysplasia

Pathological condition?

Craniosynostosis - when posterior fontanelle closes quickly in first month of life and so when head grows it grows from anterior point. very common.

What is the pterion?
Clinically important as it is the weakest part of the skull due to many bones coming together. The anterior part of the middle meningeal artery runs right behond this part. (main artery supplying the meninges)

intracranial foramina?
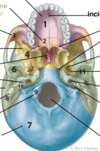
21 - foramen magnum
11 - foramen ovale
26 - jugular foramen
foramen rotundum not seen on this image

Anterior intracranial fossae

Anterior
- parts of the frontal (anterior and lateral directions), eithmoid (midline) and sphenoid bone (body and lesser wings)
- Is above the nasal cavity and is filled by the frontal lobes
- frontal crest forms attachment of falx cerebri
- the ethmoid bone, specifically the cristae galli is another attachment for the falx
- the cribriform plate is a sieve-like structure allowing small olfactory nerves to pass through
Middle intracranial fossa

Middle
- seperated from anterior by the anterior edge of the chiasmatic sulcus against the body of the sphenoid. Laterally by the greater wings and the lesser wings of the spheniod bone (SOF forms gap between).
- The floor is formed from the elevated sphenoid bone. Laterally there are large depressions formed from the greater wings of the sphenoid bone and the squamous part of the temporal bone.
- Depressions contain the temporal lobes and the hypophyseal fossa contains the pituitary gland
- The greater wigs contains the foramen rotundum (V2), ovale (V3), spinosum (middle men. a and v), SOF as well as Foramen lacerum (fibrous closing) and the opening of the carotid canal.

posterior intracranial fossa

Consists mostly of the temporal and occipital bones with small contributions from the sphenoid and parietal bones
Largest and deepest fossa containing the brainstem and the cerebellum
contains the foramen magnum, hypoglossal canal, jugular foramen and internal acoustic meatus are contained within
Boundaries:
- anteriorally the join of the clivus (sloped bone anterior to foramen magnum formed from the body of sphenoid and basilar part of occipital bone) and the dorsum sallae
- Laterally the superior part of the petrous bone (petromastral part of temoral bone).

Aire filled spaces in the skull?
Sinuses
Has nothing to do with making the skull lighter (little kids don’t have fully formed sinuses esp. fontal sinus and they seem to do fine)
Label : 20, 19, 18, 16, 14, 13, 12


Surface anatomy of the pterior?
Where the MMA and the Sylvian point are (where lateral fissure splits into ascending and posterior rami)
Point for potetial epidural haemorrhage
1cm diameter around pterior found 2.6cm behind and 1.3cm above the posterolateral margin of the frontozygomatic suture overlapping anterior branch of MMA in 68%.
70% aMMA is in a bony canal of parietal bone vs a groove that is seen more often in males


