Lecture 17 Platelet Pharmacology Flashcards
What is the specific effect of inhibiting COX1 on platelet function
By preventing the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H aspirin blocks the pathway that leads to platelet thromboxane A2 release. Thromboxane A2 activates platelets via binding to the TPα surface receptor
Which COX isoform is important for aspirins action as an antiplatelet drug
COX1 is expressed in platelets and is involved in aggregation
Why is clopidogrel in ineffective prodrug
Approximately 85% of absorbed clopidogrel is hydrolysed by hepatic carboxylesterase (CES1) to an inactive metabolite
What is the other name for gp IIb/IIIa
Integrin αiibβ3
What evidence is there for the long-term use of ticagrelor in preventing thrombotic events
Ticagrelor at two different doses on a background of aspirin reduced thrombotic events (CV death/MI/stroke) when given for several years. This was significantly better than placebo for all endpoints
What evidence from mice models supports the efficacy of ticagrelor in prevents platelet aggregation
Ticagrelor effectively inhibits platelet aggregation in wild type mice to the levels seen in P2Y12 knockout mice models whose platelets can’t aggregate
The PLATO trial compared aspirin and clopidogrel to aspirin and ticagrelor. What did the results of this trial show on the risk of bleeding associated to surgery
Bleeding related to bypass surgery was decreased with ticagrelor compared to clopidogrel reflecting the rapid offset of action
Why is clopidogrel less often used now in the clinic
The complexity of factors influencing the response to clopidogrel makes the response of each patient impossible to predict accurately
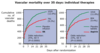
What does the data below show about the response of patients to prasugrel compared to clopidogrel

Patients treated with 60mg of prasugrel had a much more consistent inhibition of platelet aggregation than patients treated with clopidogrel
Aspirin is an effective and strong antiplatelet drug T of F
F – it is a weak APT
What is different about ticagrelor compared to other P2Y12 antagonists
Ticagrelor is the first oral reversibly binding platelet P2Y12 antagonist. It is from a different class of drug to clopidogrel and prasugrel and not a prodrug so doesn’t require conversion to an active metabolite. Ticagrelor reversibly binds to a different site on the P2Y12 receptor than the thienopyridines
Why is aspirin only a weak antiplatelet drug
Overall aspirin has excellent efficacy in inhibiting platelet thromboxane A2 release but this process plays a limited role in platelet reactivity
What is meant by aspirin resistance
The continued secretion of thromboxane A2 by platelets in response to appropriate agonist stimulation (such as arachidonic acid and collagen) despite therapy with aspirin at a standard dose
High platelet reactivity despite aspirin therapy signifies aspirin resistance T or F
F
The PLATO trial compared aspirin and clopidogrel to aspirin and ticagrelor. What did the results of this trial show on the incidence of CV death/MI/stroke
Aspirin + ticagrelor group has decreased incidence of CV death/MI/stroke
Ticagrelor is cost effective compared to clopidogrel T or F
T – NICE verified its cost-effectiveness
Give an example of a drug interaction that increases the responsiveness of a patient to clopidogrel
Rifampicin is a drug used for treating tuberculosis that ramps up the response of the liver to clopidogrel. Pretreatment of patients with rifampicin increases clopidogrel active metabolite production (4-fold increase). This leads to a much more effective blockade of P2Y12 receptors which leads to a greater inhibition of platelet aggregation
True aspirin resistance is rate T or F
T
Give an example of a drug interaction that changes the response of a patient to clopidogrel
CYP2C19 metabolises many other drugs such as proton-pump inhibitors. Omeprazole is often given with aspirin and clopidogrel to counteract the increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding that is likely with these drugs. However omeprazole has a negative impact on the effect of clopidogrel by impairing its conversion to its active metabolite which in turn decreases the inhibitory effect of clopidogrel on platelet activation
The CURE study investigated the effects of clopidogrel plus aspirin compared to aspirin alone in patients with ACS. What were the results of this study
Clopidogrel plus aspirin was effective in reducing the incidence of CV death/MI/stroke
What is the molecular mechanism of action of aspirin
The acetyl group from aspirin forms a covalent bond with a serine residue in the COX enzyme. This prevents the arachidonic acid that was made at the plasma membrane from entering the COX channel and reaching the cyclooxygenase site
Other than ADP what factors can activate platelets
Thromboxane A2 binding to the TPα receptor collagen binding to CPVI and 5HT binding to 5HT2A
What are the downsides of gp IIb/IIIa antagonists
They have a narrow therapeutic window as they aren’t effective at low doses and high doses cause to greater risk of bleeding. The increased risk of major bleeding actually offsets their benefit in reducing ischaemic events
What does the data below show about the key issue with clopidogrel

This data shows that there is massive variation between individuals in their response to clopidogrel. Some patients had a complete inhibition of platelet aggregation whilst in others it had almost no effect