Lect 8 Tissue Architecture Flashcards
Cytoskeletal Filaments
What are the 3 types of filaments?
Intermediate Filaments
Microtubules
Microfilaments
Intermediate Filaments
What enables cells to withstand mechanical stress?
Where are they located in cells?
Where are they anchored?
What underlies and strengthens the nuclear envelope?
- Tensile strength (rope like properties)
- Cytoplasm of most animal cells
- Plasma membrane at cell-cell junctions
- Mesh-like structure called nuclear lamina

Microtubules
What are they? Why are they important?
What functions does it have in the cell?
Components?
Long and stiff hollow tubes important for organization in all euk cells
Transportation of vesicles, organelles; Form mitotic spindle for chromosome segregation; Part of cilia and flagella
a- & B-tubulins with a plus (+ extend away from centrosome) end and minus (- attach to centrosome) end

Microfilaments
What are they composed of?
What are they essential for?
- Actin filaments (F-actin) with structural polarity (+ & - ends)
- Cell movement (Locomotion, phagocytosis, cell division, contraction)

Extracellular Matrix and Basal Lamina
ECM Proteins?
- Proteoglycans (cell-cell interactions), Collagens, Laminin & Fibronectin (Basement membrane)

Collagen
Main structural protein in ECM/CT and basal laminae is what?
Two main types?
What is the structural formation of collagen?
- Collagen
- Sheet forming (Type IV - Basement membrane) & Fibrillar Collagens (Type I, II, III)
- Trimeric Collagenous Helix
Scurvy
Loss of what cofactors?
What enzymes become inhibited?
What are the clinical sx? Why does this occur?
Fe and ascorbate
Prolyl Hydroxylase/Lysyl Hydroxylase
Wounds re-open due to loss of collagen synthesis
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Caused by what?
Which Collagens are affected?
Mutation in collagen (AD) or collagen synthesis (AR)
Collagen I, III, V (skin, bones, blood vessels, organs)
Cell Connections and Junctions
What are cell junctions?
What are focal contacts?
What do these have roles in?
What are the four types? (CAOS)
Link cells to neighboring cells
Link cells to ECM or Basil Lamina
Migration, Immune system function, Wound healing, Tissue architrecture, Intracellular signaling pathways
Anchoring Junctions; Occluding Junctions; Channel-Forming Junctions; Signal Relaying Junctions

Adherin
Adhesion type?
Principal CAMs or Adhesion Receptors?
Attachments?
Role?
Cell-Cell
Cadherins
Catenin binds to Actin
Role in metastasis
Desmosomes
Adhesion type?
Attachments?
Role?
Cell-Cell
Bond to intermediate filaments
Role in strength
Gap Junctions
Adhesion type?
Principal CAMs or Adhesion Receptors?
Cell-Cell
Connexins
Hemidesmosomes
Adhesion type?
Principal CAMs or Adhesion Receptors?
Attachments?
Cell to ECM
Integrin
Attaches to intermediate filaments
Focal Adhesion
Adhesion type?
Principal CAMs or Adhesion Receptors?
Attachments?
Role?
Cell to ECM
Integrins
Attaches to Actin filaments
Resisting shear stress
Tight Junctions
Adhesion type?
Principal CAMs or Adhesion Receptors?
Attachments?
Role?
Cell-Cell
Occludin & Claudins
Attaches to Actin filaments
Maintains concentration gradient
Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMs)
What are the three major domains and functions?
What are the 4 major families?
- Extracellular
- Binding to adjacent cell/matrix proteins
- Transmembrane
- Links CAM to membrane
- Cytoplasmic
- Bind to cytoskeleton via linker proteins
- Cadherins; Ig Superfamily; Integrins; Selectins
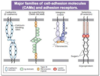
Cadherin Superfamily
_ dependent adhesion molecule
Important in formation of what?
Types of Cadherins?
Ca2+ dependent adhesion molecule
Junctions between cells (desmosomes and adherens junctions)
E-cadherin (epithelial), N-cadherin (neural), VE-cadherin (vascular-endothelial), LI-cadherin (liver-intestine)
EMT & Cadherin Switching
Cadherins serve as biomarkers for what?
What is EMT? What is it used for?
- Invasive, metastatic tumors
- Epithelia to Mesenchymal Transition
- Decreased E-cadherin and increased N-cadherin –> increased invasiveness of tumor cells and metastatic potential
Ig Superfamily CAMs
What are they?
What types of interactions?
Calcium-independent transmembrane glycoproteins
Immune cell interactions
Selectins
What are they and what do they bind to?
Important roles in what?
Increased presentation during what?
WBC surface marks include what?
Low-affinity of selectins to ligands allows for what?
Calcium dependent glycoproteins that bind to extracellular carbohydrates
Host defense mechanism
Local inflammatory response
CHO which act as ligands for selectins
Leukocyte “rolling” durin leukocyte adhesion cascade
Integrins
Couple the _ to the _. Examples?
What can they activate?
- Couple the ECM to cell cytoskeleton
- Fibronectin, Collage, Laminin, Vitronectin
- Signaling Pathways


